Neurofuzzy Velocity Tracking Control with Reinforcement Learning

Neurofuzzy Velocity Tracking Control with Reinforcement Learning XUE Jinlin1, ZHANG Weigong2, GONG Zongyang2
College of Engineering, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing 210031, China
Email: xuejinlin@https://www.sodocs.net/doc/2e6960749.html,
Department of Instrument Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
Abstract– A control method of neurofuzzy controller with reinforcement learning is proposed to implement velocity tracking control of a vehicle manipulated by a robot driver. In neurofuzzy velocity tracking control, a neural network adjusts a fuzzy controller by fine-tuning the membership. The learning algorithm of the neural network is reinforcement learning, which is based on evaluating the system performance and giving credit for successful actions. After the designed controller is trained fully, the preliminary experiment is implemented to track the desired velocity. Experimental results show that the errors of velocity tracking meet the national standard. The maximum error usually appears at switch points of driving stages where displacement variety of acceleration pedal or brake pedal operated by the robot driver is larger. The error will reduce when displacement variety of the pedals becomes small except the near region of switch points. The robot driver embodies driving behavior of a skilled driver as operating the pedals, especially in the alternative switch process of the two pedals. Keywords– neurofuzzy control, neinforcement learning, velocity tracking; robot driver, driving behavior
I. INTROD UCTION
A robot driver for vehicle testing should be adopted to ensure accurate and efficient testing according to vehicle emission test norms, and velocity tracking control is one of the key technologies in vehicle emission testing manipulated by the robot driver[1,2]. However, it is a difficult task for the robot driver to control a tested vehicle by operating acceleration pedal as well as brake pedal to track velocities of a driving cycle given, because the vehicle is an extremely complex system with non-linear characteristics. The best control strategy is able to ensure control accuracy of velocity tracking and has a “human-like” driving behavior, that is, it should be able to think, judge and act like a skilled human driver[3].
In view of that, a new method based on a neurofuzzy control with reinforcement learning is presented to implement velocity tracking control. The Neurofuzzy system, combining both the linguistic, human-like reasoning of fuzzy system with the powerful computing ability of neural network, is that the network’s learning method is utilized to automatically design and adjust the parameters of fuzzy system according to input and output samples, as a consequence to achieve self-learning and adaptive function of fuzzy system. And reinforcement learning, as a learning algorithm for a neural network, is based on evaluating the system performance and giving credit for successful actions[4]. The fuzzy control, reinforcement learning and neural network are combined to imitate cognitive learning process of human in order to realize the intelligent control of velocity tracking control based on the robot driver.
II. NEUROFUZZY CONTROL WITH
REINFORCEMENT LEARNING
The structure of the neurofuzzy controller with reinforcement learning, based on the well-known GARIC architecture[5], is shown in Fig. 1. It is mainly composed of a fuzzy controller (the Action Selection Network, ASN) as an actor and a neural network (the Action Evaluation Network, AEN) that criticizes the actions made by the ASN. The outputs of the two networks feed into the Stochastic Action Modifier (SAM) which explores the effective actions by giving a stochastic deviation to the actions made by the ASN. Q learning[6], as one of methods of reinforcement learning, is used to reward or punish the actions in this work.
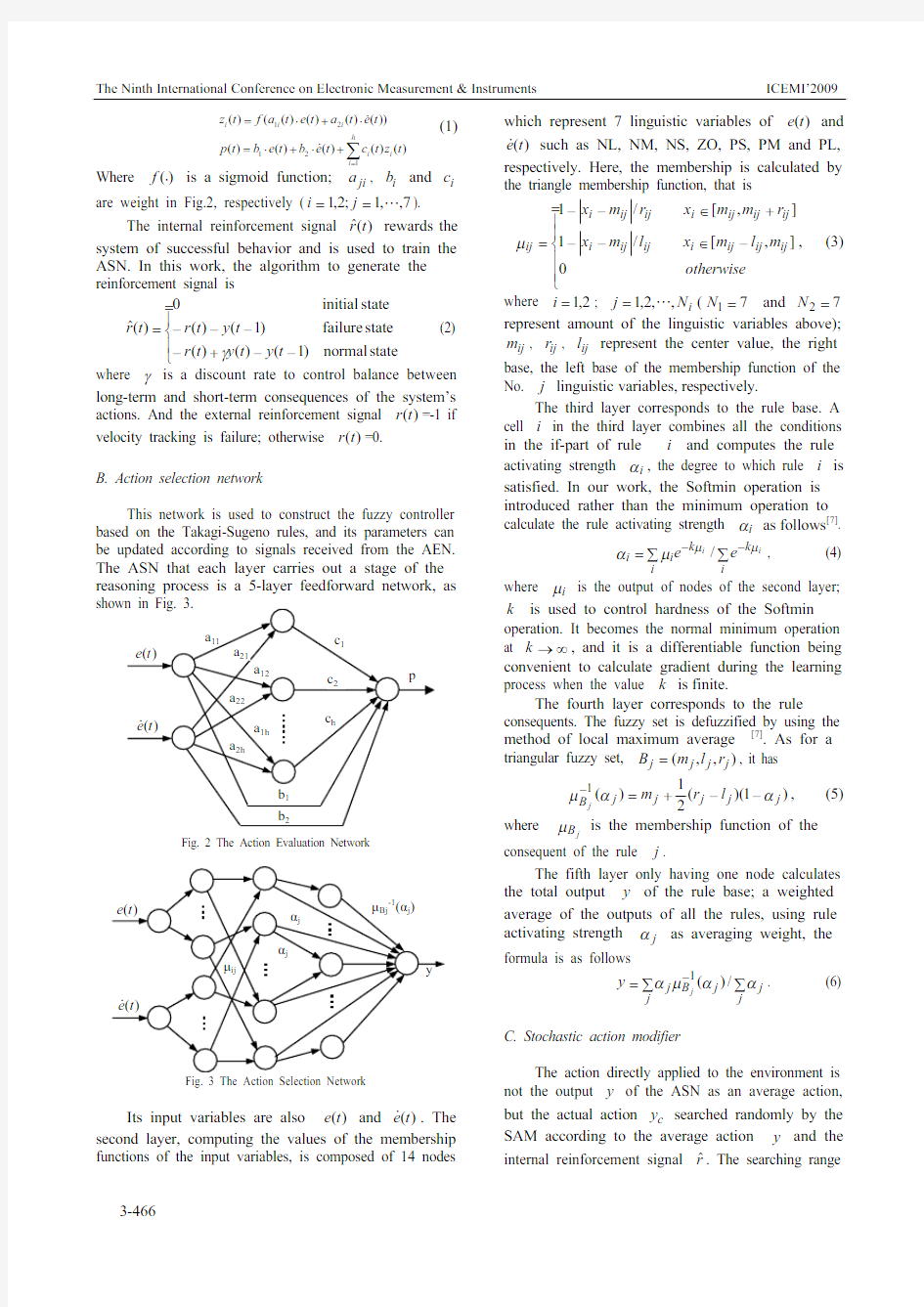
Fig. 1 Neuro-fuzzy control system with reinforcement learning A. Action evaluation network
This is a neural predictor and indicates the current state “goodness”, mapping the input state vector )(t
X to the reward signal )(t r from the environment. Here, the designed AEN is shown in Fig.
2. The state variables are )(t e and )(t e , measurements of velocity error (the desired tracking velocity minus the actual tracking velocity) and error variety, respectively. The hidden-layer activation function is a sigmoid function. In our work the size of the hidden layer of h=7 was found suitable, because increasing the size requires a longer learning time. The network output p is a measure of the goodness of the state of the network, that is, a prediction of external reinforcement signal )(t r. Output of each node is calculated by the following equation.
_____________________________ 978-1-4244-3864-8/09/$25.00 ?2009 IEEE
12121()(()()()())()()()()()i i i h
i i i z t f a t e t a t e t p t b e t b e
t c t z t | (1)
Where )( f is a sigmoid function; ji a , i b and i c are weight in Fig.2, respectively (7,,1;2,1" j i ).
The internal reinforcement signal )(?t r
rewards the system of successful behavior and is used to train the ASN. In this work, the algorithm to generate the reinforcement signal is
state normal )1()()( state failure )1()( state initial 0)(?°ˉ
°
?- t y t y t r t y t r t r
J (2) where J is a discount rate to control balance between long-term and short-term consequences of the system’s actions. And the external reinforcement signal )(t r =-1 if velocity tracking is failure; otherwise )(t r =0. B. Action selection network
This network is used to construct the fuzzy controller based on the Takagi-Sugeno rules, and its parameters can be updated according to signals received from the AEN. The ASN that each layer carries out a stage of the reasoning process is a 5-layer feedforward network, as
Fig. 2 The Action Evaluation Network
Fig. 3 The Action Selection Network
Its input variables are also )(t e and )(t e
. The second layer, computing the values of the membership functions of the input variables, is composed of 14 nodes
which represent 7 linguistic variables of )(t e and )(t e
such as NL, NM, NS, ZO, PS, PM and PL, respectively. Here, the membership is calculated by the triangle membership function, that is
°°
ˉ
°
°?- otherwise m l m x l m x r m m x r m x
ij ij ij i ij ij i ij ij ij i ij ij i ij 0],[ /1],[ /1P , (3)
where 2,1 i ; i N j ,,2,1" ( 71 N and 72 N represent amount of the linguistic variables above); ij m , ij r , ij l represent the center value, the right
base, the left base of the membership function of the
No. j linguistic
variables, respectively. The third layer corresponds to the rule base. A cell i in the third layer combines all the conditions in the if-part of rule i and computes the rule activating strength i D , the degree to which rule i is satisfied. In our work, the Softmin operation is introduced rather than the minimum operation to calculate the rule activating strength i D as follows [7].
|| i
i
k k i i i i e e P P P D /, (4)
where i P is the output of nodes of the second layer; k is used to control hardness of the Softmin operation. It becomes the normal minimum operation at f o k , and it is a differentiable function being convenient to calculate gradient during the learning
process when the value k is
finite. The fourth layer corresponds to the rule consequents. The fuzzy set is defuzzified by using the method of local maximum average [7]. As for a triangular fuzzy set, ),,(j j j j r l m B , it has
)1)((2
1
)(1
j j j j j B l r m j D D P , (5)
where j B P is the membership function of the consequent of the rule j .
The fifth layer only having one node calculates the total output y of the rule base; a weighted average of the outputs of all the rules, using rule activating strength j D as averaging weight, the
formula is as follows
|| j
j j j B j j
y D D P D /)(1
. (6) C. Stochastic action modifier
The action directly applied to the environment is not the output y of the ASN as an average action, but the actual action c y searched randomly by the SAM according to the average action y and the
internal reinforcement signal r
?. The searching range
is equivalent to the variance of the probability density function of c y , and the formulas for them are
)]1(?exp[]
2/)exp[(21
)(22 t r
y y y prob c c V V S
V (7) The result of the SAM is directly affected by the internal reinforcement signal. The search range ? is small
if the next signal )1(? t r
is normal, and the probability that the actual action c y approaching the average action y is large. Otherwise, the search range is large, and the probability that the actual action c y deviating from the average action y becomes large. Therefore, it is necessary to train the ASN fully to predict the action better.
III. Experiment and results
According to the testing specification illustrated in literature [8], the tolerance error between the desired velocity and the actual velocity is within ±2 km/h when a long-period emission testing is carried out on the chassis dynamometer. Therefore, the control goal is realized by controlling velocity to enable the actual velocity to follow the desired velocity. The control scheme of the designed neurofuzzy controller with reinforcement learning is shown in Fig. 4. The controller based on the velocity error
e , the error variety e
and the external reinforcement signal r generated by the velocity error, can output the control signal D representing acceleration pedal displacement and brake pedal displacement. If 0!D , the acceleration pedal of the tested vehicle is controlled by the robot driver to take action; if 0 D , the brake pedal takes action. Thereby, the actual velocity V of the tested vehicle is controlled and adjusted to follow the desired velocity V d .
Fig. 4 Velocity tracking control based on the neurofuzzy system
The external reinforcement signal r is defined in accordance with the control requirements of velocity tracking control as follows:
°ˉ°?
-! d 2km/h
, 12km/h
, 0d d V V V V r ?7? where the value 0 represent that the velocity tracking is
successful, and the value ?1 unsuccessful ?
A. Training of the neurofuzzy networks
First of all, the ASN is trained by MATLAB on the basis of the training data extracted from the experimental data of the literature [2]. And the internal reinforcement signal is calculated to use for training the ASN.
Then, the neurofuzzy system is trained: the initial state is set X = 0 at t=0; the output y of the ASN is calculated, then the practical action c y is obtained in accordance with the internal reinforcement signal. And the correlative membership is modified; it is judged whether the control becomes failure. If the control fails, the training should transfer to the step , otherwise to the next step; if the training expires, it ends, otherwise to the step . B. Experimental results
After the training, the M-files about the networks is converted into the VC ++ language, because the control program is compiled in a industrial computer. Then, a FIAT Siena 1.5L car is tested and manipulated by the DNC-III robot driver on the BOCO NJ 150/80 chassis dynamometer according to the test norms proposed by the literature [8]. The partly experimental results are shown in Fig. 5, where the actual outputs of velocity tracking are illustrated in the Fig. a), the tracking errors in the Fig. b) and the percentage values corresponding to the acceleration pedal displacement and the brake pedal displacement in the Fig. c), where the brake pedal displacement is restored to the positive values in view of the practical operation and is shown by the dotted line.
D uring the acceleration stage of the first 15s as shown in Fig. 5, displacement of the accelerator pedal increases from zero to 25.8% gradually within the first 5s so as to ensure the tested vehicle to be accelerated in accordance with the desired velocity. Of course, the actual velocity is lower than the desired velocity due to the slower response of the tested vehicle in the first 5s. Hereafter when the actual speed exceeds the desired speed, displacement of the accelerator pedal can reduce moderately, and on the contrary, displacement of the accelerator pedal can increase properly, for example within 205 - 215s. At 215s, the vehicle turns into the stage of constant velocity, and the displacement must quickly become smaller to adapt to this change. However, there exists a little overshoot. In the stage of constant velocity, the displacement variety is much smaller between 19.0% - 20.4% in about 216 - 224s and 12.2% - 11.0% in about 229 - 232s, and the velocity error is also smaller. During the deceleration stage in 225 - 228s and 233 - 240s, the acceleration pedal is released by the robot driver and the brake pedal is manipulated to control the velocity. Of course, in the switch point of the stages such as in 225s and 233s, the action of
releasing the accelerator pedal and stepping on the brake pedal is quick, which aims to meet the requirement of velocity tracking and is in line with the driving commonsense. Also, the brake pedal movement is relatively gentle during the deceleration process.
Fig.5 Partly experimental results
It is shown from the test results that, the velocity fluctuation is small compared to the test norms and the maximum error values do not exceed 1.8 km/h, and also keep in the range of the limit standard ±2.0 km/h during the whole test. The maximum error usually appears at switch points of driving stage of the tested vehicle where displacement variety of acceleration pedal and brake pedal operated by the robot driver becomes larger. The error will reduce when displacement variety of acceleration pedal and brake pedal becomes small during the same driving stage except the near region of switch points. Therefore, it means that the robot driver embodies driving behavior of a skilled human driver during the process of operating the pedals, especially in the alternative switch process of the two pedals.
IV . CONCLUSIONS
A new application of neurofuzzy control with reinforcement learning in velocity tracking controlled by a robot driver is proposed. The membership of fuzzy controller using driving knowledge is fine-tuned by using the neural network, which learning algorithm is reinforcement awarding for successful control actions and punishing for poor control actions. The controller designed can gain a good performance of tracking the desired velocities. And the operation of the robot driver on the pedals reflects the driving behavior of a skilled human driver. In the further work, it is necessary to test the control performance of the presented controller and to verity its adaptability for the different vehicles.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank the Automobile Technical Center of Yuejin Automobile Group Company for providing experimental support and its technicians who provided technical support.
REFERENCE
[1]
Zhang Weigong and Cheng Xiaobing, “Key technologies of vehicle robot driver,” Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 20-23, 2005.
[2] Chen Xiaobing, Zhang Weigong and Zhang Bingjun, “Study
on Speed Tracking Control Strategy for Robot D river on Chassis Dynamometer”, China Mechanical Engineering , vol. 16, no. 18, pp: 1669-1673, 2005.
[3] Xue Jinlin, Zhang Weigong and Gong Zongyang, “Robotic
driver for indoor test of vehicles,” Automobile Engineering , vol. 29, no. 10, pp. 893-895, 2007.
[4] C. T. Lin and C. S. G . Lee, “Reinforcement
structure/parameter learning for neural-network-based fuzzy logic control systems,” IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems , vol. 2, no. 1, pp:46-63, 1994.
[5] H. Berenji and P. Khedkar. “Learning and tuning fuzzy logic
controllers through reinforcements ?” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks , vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 724-740, 1992.
[6] A. J. Smith, “Applications of the Self-Organizing Map to
Reinforcement Learning,” Neural Networks , vol. 15, no, 8, pp: 1107-1124, 2002.
[7] Li Renhou, “Intelligent Control Theory and Method ?” Xidian
University Press , pp. 236-241, 1999.
[8] Ministry of Environmental Protection of P.R.C. and General
Administration of Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine of P.R.C., “GB 18352.3 2005: Limits and measurement methods for emissions from light-duty vehicles(?,?),” Standards Press of China , 2005. v e l o c i t y / k m ?h -1
e r r o r / k m ?h -1
d i s p l a c
e m e n t /%
b)
brake
acceleration
c)
time /s
time /s
自动化英语单词
后验估计 a posteriori estimate 先验估计 a priori estimate 交流电子传动AC (alternating current) electric drive 验收测试acceptance testing 可及性accessibility 累积误差accumulated error 交-直-交变频器AC-DC-AC frequency converter 主动姿态稳定active attitude stabilization 驱动器,执行机构actuator 线性适应元adaline 适应层adaptation layer 适应遥测系统adaptive telemeter system 伴随算子adjoint operator 容许误差admissible error 集结矩阵aggregation matrix 层次分析法AHP (analytic hierarchy process) 放大环节amplifying element 模数转换analog-digital conversion 信号器annunciator 天线指向控制antenna pointing control 抗积分饱卷anti-integral windup 姿态轨道控制系统AOCS (attritude and orbit control system) 非周期分解aperiodic decomposition 近似推理approximate reasoning 关节型机器人articulated robot 配置问题,分配问题assignment problem 联想记忆模型associative memory model 联想机associatron 渐进稳定性asymptotic stability 实际位姿漂移attained pose drift 姿态捕获attitude acquisition 姿态角速度attitude angular velocity 姿态扰动attitude disturbance 姿态机动attitude maneuver 吸引子attractor 可扩充性augment ability 增广系统augmented system 自动-手动操作器automatic manual station 自动机automaton 自治系统autonomous system 间隙特性backlash characteristics 基座坐标系base coordinate system 贝叶斯分类器Bayes classifier 方位对准bearing alignment 波纹管压力表bellows pressure gauge 收益成本分析benefit-cost analysis 双线性系统bilinear system 生物控制论biocybernetics 生物反馈系统biological feedback system 黑箱测试法black box testing approach 盲目搜索blind search 块对角化block diagonalization 玻耳兹曼机Boltzman machine 自下而上开发bottom-up development 边界值分析boundary value analysis 头脑风暴法brainstorming method 广度优先搜索breadth-first search 蝶阀butterfly valve 计算机辅助工程CAE (computer aided engineering) 清晰性calrity 计算机辅助制造CAM (computer aided manufacturing) 偏心旋转阀Camflex valve 规范化状态变量canonical state variable 电容式位移传感器capacitive displacement transducer 膜盒压力表capsule pressure gauge 计算机辅助研究开发CARD 直角坐标型机器人Cartesian robot 串联补偿cascade compensation 突变论catastrophe theory 集中性centrality 链式集结chained aggregation 混沌chaos 特征轨迹characteristic locus 化学推进chemical propulsion 经典信息模式classical information pattern 分类器classifier 临床控制系统clinical control system 闭环极点closed loop pole 闭环传递函数closed loop transfer function 聚类分析cluster analysis 粗-精控制coarse-fine control 蛛网模型cobweb model 系数矩阵coefficient matrix 认知科学cognitive science 认知机cognitron 单调关联系统coherent system 组合决策combination decision 组合爆炸combinatorial explosion 压力真空表combined pressure and vacuum gauge 指令位姿command pose 相伴矩阵companion matrix 房室模型compartmental model 相容性,兼容性compatibility 补偿网络compensating network 补偿,矫正compensation
Ant常用语法及选项
1.
velocity入门使用教程
V elocity入门使用教程 一、使用velocity的好处: 1.不用像jsp那样编译成servlet(.Class)文件,直接装载后就可以运行了,装载的过程在web.xml里面配置。【后缀名为.vhtml是我们自己的命名方式。也只有在这里配置了哪种类型的文件,那么这种类型的文件才能解析velocity语法】 2.web页面上可以很方便的调用java后台的方法,不管方法是静态的还是非静态的。只需要在toolbox.xml里面把类配置进去就可以咯。【调用的方法$class.method()】即可。 3.可以使用模版生成静态文档html【特殊情况下才用】 二、使用 1、下载velocity-1.7.zip 、velocity-tools-2.0.zip 2、解压后引用3个jar文件velocity-1.7.jar、velocity-tools-2.0.jar、velocity-tools-view-2.0.jar 还有几个commons-…..jar 开头的jar包 三、配置文件: Web.xml
科技英语语法_同位语从句_名词性从句_定语从句
2015/12/2 Wednesday
西安电子科技大学
西安电子科技大学
§5. 2 同位语从句
1、一般情况 (1)公式
§5. 2 同位语从句 The latter(后一)form has the advantage that it can be extended(扩展) to complex quantities .
+ 某些抽象名词 +
the this a/an O no
形容词 物主代词
that从句[“that”在
从句中无词义、无 成分]
③ “动宾译法”:这时该“抽象名词” 来自于可带有宾语从句的及物动词。
西安电子科技大学
西安电子科技大学
§5. 2 同位语从句
(2)译法 ① “~ 这一 ……” 的
§5. 2 同位语从句 During the past several years, there has been an increasing [a growing] recognition [realization; awareness] within business(商务)and academic(学术的) circles(界)that certain nations have evolved(发展)into information societies .
The assumption that β = constant is often made to simplify analysis. R = r is the condition that power delivered(提供)by a given source is a maximum .
西安电子科技大学
西安电子科技大学
§5. 2 同位语从句 Here we have used the definition (定义)that acceleration(加速度)is the rate(速率)of change of velocity .
② 这一 ……:~ 以下的
§5. 2 同位语从句 The main theoretical development in this decade(十年)has been in the recognition that material properties should be included in analytical models . This is equivalent to a statement that everything is attracted by the earth.
This account for(解释)the observation(观察到的情况)that the resistivity of a metal increases with temperature .
1
VRay中文使用手册
VRay中文使用手册 9030 目录 1. license 协议 2. VRay的特征 3. VRay软件的安装 4. VRay的渲染参数 5. VRay 灯光 6. VRay 材质 7. VRay 贴图 8. VRay 阴影 9. VRay的分布式渲染 10. Terminology术语 11. Frequently Asked Questions常见问题 VRay的特征 VRay光影追踪渲染器有Basic Package 和 Advanced Package两种包装形式。Basic Package具有适当的功能和较低的价格,适合学生和业余艺术家使用。Advanced Package 包含有几种特殊功能,适用于专业人员使用。 Basic Package的软件包提供的功能特点
·真正的光影追踪反射和折射。(See: VRayMap) ·平滑的反射和折射。(See: VRayMap) ·半透明材质用于创建石蜡、大理石、磨砂玻璃。(See: VRayMap) ·面阴影(柔和阴影)。包括方体和球体发射器。(See: VRayShadow) ·间接照明系统(全局照明系统)。可采取直接光照 (brute force), 和光照贴图方式(HDRi)。(See: Indirect illumination) ·运动模糊。包括类似Monte Carlo 采样方法。(See: Motion blur) ·摄像机景深效果。(See: DOF) ·抗锯齿功能。包括 fixed, simple 2-level 和 adaptive approaches等采样方法。(See: Image sampler) ·散焦功能。(See: Caustics ) ·G-缓冲(RGBA, material/object ID, Z-buffer, velocity etc.) (See: G-Buffer ) Advanced Package软件包提供的功能特点 除包含所有基本功能外,还包括下列功能: ·基于G-缓冲的抗锯齿功能。(See: Image sampler) ·可重复使用光照贴图 (save and load support)。对于fly-through 动画可增加采样。(See: Indirect illumination) ·可重复使用光子贴图 (save and load support)。(See: Caustics) ·带有分析采样的运动模糊。(See: Motion blur ) ·真正支持 HDRI贴图。包含 *.hdr, *.rad 图片装载器,可处理立方体贴图和角贴图贴图坐标。可直接贴图而不会产生变形或切片。
jetTemplate模板学习和使用
一、如何配置jetTemplate ? ? ? ? ?
拓展方法:可以非常好的进行格式化处理和一些小的模板处理。
?? ??? ???? ?
?o o
二、model and view 我们发现在这一块基本上没有什么区别,把数据对象放在map中,在后面的页面就可以帮我们完成整个的处理。 返回值表示对应的html文件。 这一块没有什么问题。这一块非常方便。 三、页面的布局
| ID | 姓名 | 邮箱 | 书籍 |
| ${user.id} | ${https://www.sodocs.net/doc/2e6960749.html,} | ${user.email} | 书籍列表 |
整个的思路也非常简单,就是使用#include和#tag layout_block("mainContent")两个标志就可以搞定了。 四、页面渲染 这一块也很简单,看上面的例子和官网上的说明就OK了。
log4j学习
log4j 如同Hadoop一样,把需要的jar包(hadoop.jar )和配置文件,放到CLASSPATH中, 配置Log4j也要如此,把log4j-1.2.8.jar,log4j.properties放到classpath中。配置 文件配置的是Log输出到哪里,如何输出,何时输出,哪些类的log要输出(等级)(Where, How,When,Who) 代码中用到的 private final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); 得到类的全名,Log4j框架就会去找相应的package是否有设置输出log,以及它的等级。 如果等级为DEBUG那么log.isDebugEnabled()为true。如下所示,如果等级为INFO, 那么log.isInfoEnabled()、log.isWarnEnabled()、log.isErrorEnabled()这三个为true, 其他的为false?(有待确认) 等级可分为OFF、FATAL、ERROR、WARN、INFO、DEBUG、ALL,如果配置OFF则 不打出任何信息,如果配置为INFO这样只显示INFO, WARN, ERROR的log信息,而 DEBUG信息不会被显示,具体讲解可参照第三部分定义配置文件中的logger。 if (log.isDebugEnabled()){ log.debug("111"); } if (log.isInfoEnabled()){ https://www.sodocs.net/doc/2e6960749.html,("222"); } 完整的文章如下: 在强调可重用组件开发的今天,除了自己从头到尾开发一个可重用的日志操作类外,Apache为我们提供了一个强有力的日志操作包-Log4j。 Log4j是Apache的一个开放源代码项目,通过使用Log4j,我们可以控制日志信息输送的目的地是控制台、文件、GUI组件、甚至是套接口服务器、NT的事件记录器、UNIX Syslog守护进程等;我们也可以控制每一条日志的输出格式;通过定义每一条日志信息的级别,我们能够更加细致地控制日志的生成过程。最令人 感兴趣的就是,这些可以通过一个配置文件来灵活地进行配置,而不需要修改应用的代码。 此外,通过Log4j其他语言接口,您可以在C、C++、.Net、PL/SQL程序中使用Log4j,其语法和用法与在Java程序中一样,使得多语言分布式系统得到一个统一一致的日志组件模块。而且,通过使用各种第三方扩展,您可以很方便地将Log4j集成到J2EE、JINI甚至是SNMP应用中。 说明:下面分为三部分, 第一部分讲解如何配置log4j; 第二部分为对log4j.properties配置文件中的各个属性的讲解; 第三部分为对log4j的详细讲解。 如果只想配置上log4j,那么只需要看前两个部分就可以,如果想对log4j深入了解,则还需看第三部分。 一、Log4j配置
fluent 使用基本步骤
fluent 使用基本步骤 步骤一:网格 读入网格(*.msh) File →Read →Case 读入网格后,在窗口显示进程 检查网格 Grid →Check Fluent对网格进行多种检查,并显示结果。注意最小容积,确保最小容积值为正。 显示网格 Display →Grid 以默认格式显示网格 能够用鼠标右键检查边界区域、数量、名称、类型将在窗口显示,本操作关于同样类型的多个区域情形专门有用,以便快速区不它们。 网格显示操作 Display →Views 在Mirror Planes面板下,axis 点击Apply,将显示整个网格 点击Auto scale, 自动调整比例,并放在视窗中间 点击Camera,调整目标物体位置 用鼠标左键拖动指标钟,使目标位置为正 点击Apply,并关闭Camera Parameters 和Views窗口 步骤二:模型 1. 定义瞬时、轴对称模型 Define →models→Solver 保留默认的,Segregated解法设置,该项设置,在多相运算时使用。
在Space面板下,选择Axisymmetric 在Time面板下,选择Unsteady 2. 采纳欧拉多相模型 Define→Models→Multiphase (a) 选择Eulerian作为模型 (b)如果两相速度差较大,则需解滑移速度方程 (c)如果Body force比粘性力和对流力大得多,则需选择implicit b ody force 通过考虑压力梯度和体力,加快收敛 (d)保留设置不变 3. 采纳K-ε湍流模型(采纳标准壁面函数) Define →Models →Viscous (a) 选择K-ε( 2 eqn 模型) (b) 保留Near wall Treatment面板下的Standard Wall Function设置 在K-εMultiphase Model面板下,采纳Dispersed模型,dispersed湍流模型在一相为连续相,而材料密度较大情形下采纳,而且Stocks数远小于1,颗粒动能意义不大。 4.设置重力加速度 Define →Operating Conditions 选择Gravity 在Gravitational Acceleration下x或y方向填上-9.81m/s2 步骤三:材料 Define →Materials 复制液相数据作为差不多相 在Material面板。点击Database, 在Fluid Materials 清单中,选Water -Liquid (h2o(1))
词缀在英语词汇中的运用
词缀在英语词汇中的运用—— 浅淡构词法中的后缀 The Application of Affixes in English Vocabulary Memorization— A Brief Study on suffix of English Word Formation 摘要:词汇是英语学习者的主要障碍之一。它在运用语言进行交际过程中至关重要,它直接影响听、说、读、写各项能力的发挥,好么对于语言学习者来说,首先就要克服这个障碍。英语构词法可以帮助我们正确辩认单词的词形,词性和理解词意,并迅速扩大词汇量,有助于提高英语的阅读速度和理解能力,是学习英语和提高学习质量的有效的方法,被誉为“学习英语的最短最佳的途径”。而构词法中的后缀是构词能力最强的一种,也是英语扩充词汇的最主要的方法之一。后缀是加在词根或单词后面的部分,通常把它们的词性改变为名词、形容词、动词和副词[4]。一旦掌握这些规律,对词汇的获得就不再是那么困难了,而且还会大大激发学习兴趣,也就解决了学习者对词汇的习得的困难了,从而就能更有效地学习和掌握英语了。 关键词:英语词汇;英语构词法;后缀。 Abstract:Vocabulary is one of the main obstacles to the English learners.It is extremely crucial in the process of communication by using language,it directly influences the development of the ability of listening,speaking,reading,writing ect.therefore we must overcome the obstacle first as language learners. English Word Formation can help us distinguish the form and nature of word and apprehend the maening of word correctly,and enlarge our vocabulary quickly .It can help us enhance the velocity of reading English and the ability of apprehension.It is an efficient way and powerful weapon for English study ,and it is claimed to be one of the shortest and best way of English study.Affixation is one of the efficient ways of learning
LAMMPS手册中文讲解
LAMMPS手册-中文解析 一、简介 本部分大至介绍了LAMMPS的一些功能和缺陷。 1.什么是LAMMPS? LAMMPS是一个经典的分子动力学代码,他可以模拟液体中的粒子,固体和汽体的系综。他可以采用不同的力场和边界条件来模拟全原子,聚合物,生物,金属,粒状和粗料化体系。LAMMPS可以计算的体系小至几个粒子,大到上百万甚至是上亿个粒子。 LAMMPS可以在单个处理器的台式机和笔记本本上运行且有较高的计算效率,但是它是专门为并行计算机设计的。他可以在任何一个按装了C++编译器和MPI的平台上运算,这其中当然包括分布式和共享式并行机和Beowulf型的集群机。 LAMMPS是一可以修改和扩展的计算程序,比如,可以加上一些新的力场,原子模型,边界条件和诊断功能等。 通常意义上来讲,LAMMPS是根据不同的边界条件和初始条件对通过短程和长程力相互作用的分子,原子和宏观粒子集合对它们的牛顿运动方程进行积分。高效率计算的LAMMPS通过采用相邻清单来跟踪他们邻近的粒子。这些清单是根据粒子间的短程互拆力的大小进行优化过的,目的是防止局部粒子密度过高。在并行机上,LAMMPS采用的是空间分解技术来分配模拟的区域,把整个模拟空间分成较小的三维小空间,其中每一个小空间可以分配在一个处理器上。各个处理器之间相互通信并且存储每一个小空间边界上的”ghost”原子的信息。LAMMPS(并行情况)在模拟3维矩行盒子并且具有近均一密度的体系时效率最高。 2.LAMMPS的功能 总体功能:
可以串行和并行计算 分布式MPI策略 模拟空间的分解并行机制 开源 高移植性C++语言编写 MPI和单处理器串行FFT的可选性(自定义) 可以方便的为之扩展上新特征和功能 只需一个输入脚本就可运行 有定义和使用变量和方程完备语法规则 在运行过程中循环的控制都有严格的规则 只要一个输入脚本试就可以同时实现一个或多个模拟任务粒子和模拟的类型: (atom style命令) 原子 粗粒化粒子 全原子聚合物,有机分子,蛋白质,DNA 联合原子聚合物或有机分子 金属 粒子材料 粗粒化介观模型 延伸球形与椭圆形粒子 点偶极粒子
LAMMPS的语法中文解释
lammps做分子动力学模拟时,需要一个输入文 件(input script),也就是in文件,以及关于体系的 原子坐标之类的信息的文件(data file)。lammps在 执行计算的时候,从这个in文件中读入命令,所以对LAMMPS的使用最主要的就是对in 文件的编写和使 用。下面介绍一些关于in文件的事项 λ每一非空行都被认为是一条命令(大小写敏 感,但极少有命令或参数大写的)。 λ in文件中各命令的顺序可能会对计算产生影 响,但大部分情况下不会有影响。 每行后的“λ&” 表示续行(类似fortran)。 λ“#”表示注释(类似bash)。 λ每行命令中的不同字段由空格或者制表符分 隔开来,每个字段可以由字母、数字、下划线、或 标点符号构成。 λ每行命令中第一个字段表示命令名,之后的 字段都是相关的参数。 λ很多命令都是在需要修改默认值的情况下才 特别设置的。 in文件整体来看分为4个部分 1. Initialization 这一部分包含了关于计算体系最基本的信息, 例如: units: 单位系统(units style),lammps现在提供包 括lj、real、metal、si和cgs几种单位系统。 dimension: 定义了两维或者三维模拟(默认是三 维)。 boundary: 定义了分子动力学体系使用的边界条 件,例如周期性边界条件或者自由边界条件等。 atom_style: 定义模拟体系中的原子属性,这一 命令与力场设置的参数中的原子类型(atom type)不 同。 pair_style: 相互作用力场类型,例如范德化势或者硬球势等。 bond_style: 键合相互作用势类型。 angle_style: 键角作用势类型。 dihedral_style: 二面角作用势类型。 improper_style: 混合作用势类型。 其他还有一些参数设置,例如newton, processors, boundary, atom_modify等。 2. Atom definition lammps提供3种定义原子方式: 通过read_data或read_restart命令从data或restart文 件读入,这些文件可以包含分子拓扑结构信息,这 一方法在续算上也很有用。
Velocity教程
Velocity教程 关键字: velocity教程 Velocity是一个基于java的模板引擎(template engine)。它允许任何人仅仅简单的使用模板语言(template language)来引用由java代码定义的对象。当Velocity应用于web开发时,界面设计人员可以和java程序开发人员同步开发一个遵循MVC架构的web站点,也就是说,页面设计人员可以只关注页面的显示效果,而由java程序开发人员关注业务逻辑编码。Velocity将java代码从web页面中分离出来,这样为web站点的长期维护提供了便利,同时也为我们在JSP和PHP之外又提供了一种可选的方案。 官方网站:https://www.sodocs.net/doc/2e6960749.html,/velocity/ Velocity脚本摘要 1、声明:#set ($var=XXX) 左边可以是以下的内容 Variable reference String literal Property reference Method reference Number literal #set ($i=1) ArrayList #set ($arr=["yt1","t2"]) 技持算术运算符 2、注释: 单行## XXX 多行#* xxx xxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx*# References 引用的类型 3、变量Variables 以"$" 开头,第一个字符必须为字母。character followed by a VTL Identifier. (a .. z or A .. Z). 变量可以包含的字符有以下内容: alphabetic (a .. z, A .. Z) numeric (0 .. 9) hyphen ("-") underscore ("_") 4、Properties $Identifier.Identifier $https://www.sodocs.net/doc/2e6960749.html,
从句语法知识及真题解析
从句语法知识及真题解析 ●复合句——形容词性(定语)从句 1.尤其要注意whose的用法 whose在从句中做定语,修饰名词。所以,如果关系代词后面紧接的是名词,且关系代词又不在从句中做主语或宾语,那么,这个关系代词就应该是whose。如: 2.介词+ which的用法 如果从句中主宾成分齐全,考生便可考虑关系代词是否在从句中做状语,而状语通常用介词短语充当,于是可以得知,关系代词前面应有介词,再分析所给的选项,根据与名词的搭配作出正确选择。如: We are not conscious of the extent to which work provides the psychological satisfaction that can make the difference between a full and an empty life. 3.as 与which用作关系代词的区别 (1)as与the same, such, so, as等关联使用。如:As the forest goes, so goes its animal life. (2)as和which都可以引导非限定性定语从句,但as在句中的位置比较灵活,可出现在句首、句中、句末,而which只能出现在句末,尤其是当先行词是整个句子时。如: As is true in all institutions, juries are capable of making mistakes. As is generally accepted, economic growth is determined by the smooth development of production. 常见的这类结构有:as has been said before, as has been mentioned above, as can be imagined, as is known to all, as has been announced, as can be seen from these figures, as might/could be expected, as is often the case, as has been pointed out, as often happens, as will be shown等。 4.关系代词that与which用于引导定语从句的区别 (1)如果关系代词在从句中做宾语,用that, which都可以,而且可以省略; (2)先行词是不定代词anything, nothing, little, all, everything时,关系代词用that; (3)先行词由形容词最高级或序数词修饰或由next,last, only, very修饰时,用that; (4)非限定性定语从句只能用which引导; (5)关系代词前面如果有介词,只能用which。 5.but做关系代词,用于否定句,相当于who…not, that…n ot 这个结构的特点是主句中常有否定词或含有否定意义的词。如: There are few teachers but know how to use a computer. There is no complicated problem but can be solved by a computer. ●二、复合句——名词性从句 一个句子起名词的作用,在句中做主语、宾语/介词宾语、表语、同位语,那么这个句子就是名词性从句。 1.what/whatever的用法 考生应把握:what是关系代词,它起着引导从句并在从句中担当一个成分这两个作用。如: They lost their way in the forest, and what made matters worse was that night began to fall. (what既引导主语从句又在从句中做主语) Water will continue to be what it is today—next in importance to oxygen. (what既引导表语从句又在从句中做表语) 2.whoever和whomever的区别 whoever和whomever相当于anyone who,用主格与宾格取决于其在从句中做主语还是做宾语。如: They always give the vacant seats to whoever comes first. (whoever在从句中做主语) 3.有关同位语从句的问题 (1)引导词通常为that, 但有时因名词内容的需要,也可由whether及连接副词why, when, where, how引导。that不表示任何意义,其他词表示时间、地点、原因等。如: The problem, where I will have my college education, at home or abroad, remains untouched.
GOCAD中文手册
GOCAD综合地质与储层建模软件 简易操作手册 美国PST油藏技术公司 PetroSolution Tech,Inc.
目录 第一节 GOCAD综合地质与储层建模软件简介┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉1 一、GOCAD特点┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉1 二、GOCAD主要模块┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉1 第二节 GOCAD安装、启动操作┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉2 一、GOCAD的安装┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉2 二、GOCAD的启动┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉3 第三节 GOCAD数据加载┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉5 一、井数据加载┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉5 二、层数据加载┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉11 三、断层数据加载┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉11 四、层面、断层面加载┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉12 五、地震数据加载┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉12 第四节 GOCAD构造建模┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉13 一、准备工作┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉13 二、构造建模操作流程┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉14 三、构造建模流程总结┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉40 第五节建立GOCAD三维地质模型网格┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉41 一、新建三维地质模型网格流程┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉41 二、三维地质模型网格流程┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉41 三、三维地质模型网格流程总结┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉47 第六节 GOCAD储层属性建模┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉48 一、建立属性建模新流程┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉48 二、属性建模操作流程┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉48 三、属性建模后期处理┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉66 四、网格粗化┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉74 第七节 GOCAD地质解释和分析┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉┉78
AVL-FIRE中文入门教程+AVL-FIRE软件的使用方法
A VL-FIRE中文入门教程+A VL-FIRE软件的使用方法 流场分析的基本流程(FIRE软件) ID:qxlqixinliang 一、网格自动生成 (2) 二、网格划分工具的使用 (5) 1、Mesh tools (5) 2、surface tools (7) 3、edge tools (7) 三、网格和几何信息工具 (8) 1、网格check (8) 2、Geo info (9) 四、流场求解求解器的设置 (9) AVL Fire 软件的使用方法 .................................................................错误!未定义书签。
一、网格自动生成 根据电池包内部流场的特点,我们一般使用fame的网格自动生成和手动划分网格,两者相结合基本上能完成网格划分。对于电池数量较少的模型(如下图)完全可以用网格自动生成功能来实现网格划分。 下面介绍网格自动生成的流程: 1)准备面surface mesh和线edge mesh:要求:面必须是封闭曲面,一般FIRE中可以应用的是.stl的文件,在PRO/E,CATIA 等三维的造型软件中都可以生成;与面的处理相似的还要准备边界的线数据 2)Hybrid assistant,选择start new meshing,分别定义表面网格define surface mesh和线网格define edge mesh 3)然后进入高级选项fame advanced hybrid,在这里定义最大网格尺寸和最小网格尺寸,最大网格尺寸是最小网格尺寸的2^n倍 4)选择connecting edge,一般在计算域的进出口表面建立face selection,这样可保证edge 处的网格贴体,否则网格在几何的边角会被圆滑掉,另外还可以保证进出口面的网格方向与气流方向正交,有利于计算的精确性和收敛性。通过add添加上进出口的selection 即可。
vr中文手册
VR中文手册 目录 1. VRay的特征 2. VRay的渲染参数 3. VRay 灯光 4. VRay 材质 5. VRay 贴图 6. VRay 阴影 一、VRay的特征 VRay光影追踪渲染器有Basic Package 和Advanced Package两种包装形式。Basic Package具有适当的功能和较低的价格,适合学生和业余艺 术家使用。Advanced Package 包含有几种特殊功能,适用于专业人员使用。 Basic Package的软件包提供的功能特点 ·真正的光影追踪反射和折射。(See: VRayMap) ·平滑的反射和折射。(See: VRayMap) ·半透明材质用于创建石蜡、大理石、磨砂玻璃。(See: VRayMap) ·面阴影(柔和阴影)。包括方体和球体发射器。(See: VRayShadow) ·间接照明系统(全局照明系统)。可采取直接光照(brute force), 和光照贴图方式(HDRi)。(See: Indirect illumination) ·运动模糊。包括类似Monte Carlo 采样方法。(See: Motion blur) ·摄像机景深效果。(See: DOF) ·抗锯齿功能。包括fixed, simple 2-level 和adaptive approaches等采样方法。(See: Image sampler) ·散焦功能。(See: Caustics ) · G-缓冲(RGBA, material/object ID, Z-buffer, velocity etc.) (See: G-Buffer ) Advanced Package软件包提供的功能特点 除包含所有基本功能外,还包括下列功能: ·基于G-缓冲的抗锯齿功能。(See: Image sampler) ·可重复使用光照贴图(save and load support)。对于fly-through 动画可增加采样。(See: Indirect illumination) ·可重复使用光子贴图(save and load support)。(See: Caustics) ·带有分析采样的运动模糊。(See: Motion blur ) ·真正支持HDRI贴图。包含*.hdr, *.rad 图片装载器,可处理立方体贴图和角贴图贴图坐标。可直接贴图而不会产生变形或切片。 ·可产生正确物理照明的自然面光源。(See: VRayLight) ·能够更准确并更快计算的自然材质。(See: VRay material) ·基于TCP/IP协议的分布式渲染。(See: Distributed rendering) ·不同的摄像机镜头:fish-eye, spherical, cylindrical and cubic cameras (See: Camera)
