Effect of oxygen on-active Al concentration in ZnO Al-thin films made by PLD

Applied Surface Science 320(2014)756–763
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
Applied Surface
Science
j o u r n a l h o m e p a g e :w w w.e l s e v i e r.c o m /l o c a t e /a p s u s
c
Effect of oxygen on active Al concentration in ZnO:Al thin ?lms made by PLD
M.Kodu ?,T.Arroval,T.Avarmaa,R.Jaaniso,I.Kink,S.Leinberg,K.Savi,M.Timusk
Institute of Physics,University of Tartu,Ravila 14c,50411Tartu,Estonia
a r t i c l e
i n f o
Article history:
Received 5March 2014
Received in revised form 20July 2014Accepted 25August 2014
Available online 16September 2014
Keywords:
Pulsed laser deposition ZnO AZO ZnO:Al
Thin oxide ?lms Resistivity
a b s t r a c t
Al doped ZnO is used as a material for transparent conductive electrodes in solar energy and display screen applications,as well as semiconducting material in electronic and photonic devices.For effective use it is essential to control the electrical and optical properties of ZnO:Al thin ?lms.In order to investigate the in?uence of oxygen environment on effective Al solubility and intrinsic defects introduced at high doping levels during the ?lm growth,ZnO:Al thin ?lms were deposited in vacuum and oxygen background by pulsed laser deposition method.Films were doped with varying Al concentrations by using targets with Al doping levels of 1–10at%.In vacuum,substantially increased free electron concentrations were observed for all Al doping levels,which indicates that the formation of acceptor-type defects,acting as electron killer centers,was largely suppressed during the growth in oxygen-poor conditions.The dependence of carrier mobility from Al concentration was also greatly in?uenced by oxygen conditions during the ?lm growth,suggesting that ionized impurity concentrations in the ?lms deposited in vacuum and oxygen background were signi?cantly different.The results were interpreted in the context of intrinsic acceptor-type defects V Zn (zinc vacancy),which concentration is strongly modi?ed by the presence of oxygen during the ?lm deposition.These vacancies are assumed to in?uence free electron concentration and electron mobility by acting as deep electron acceptors and charged electron scattering centers (V Zn 2?).
?2014Elsevier B.V.All rights reserved.
1.Introduction
Transparent conductive oxides (TCOs)are important class of materials among transparent conductors.These are essential materials in energy applications and optoelectronic devices.For example,TCOs are used as transparent electrodes in light emitting diodes and organic light emitting diodes,?at panel displays,solar cells and other opto-electronic devices [1,2].In addition,TCOs are used as antistatic coatings,transparent heating elements,and heat re?ecting ?lters on architectural and automotive glazing [1,2].The most well-known and widely used TCO is indium tin oxide (ITO)but other doped oxides,such as In 2O 3:X,SnO 2:X,ZnO:X,TiO 2:X,are actively investigated and developed as well [1].As indium reserves are limited in the world and not all indium used in different devices is being recycled,there is need for other,more abundant and cheaper material to replace the In-based TCOs.For electrode applications,promising materials with properties comparable to those of ITO are ZnO based doped oxides.Among these,ZnO doped
?Corresponding author.Tel.:+3727374711;fax:+3727383033.E-mail address:Margus.Kodu@ut.ee (M.Kodu).
with Ga or Al has shown high conductivity together with high opti-cal transparency in the visible spectral range [3].
So far,ZnO:Al (AZO)thin ?lms have been grown by several meth-ods whereas molecular beam epitaxy,sputtering and pulsed laser deposition (PLD)methods have provided the ?lms with the highest quality [3].
Previously,some studies on optimization of process parame-ters for PLD of AZO thin ?lms have been carried out.For instance,the in?uence of growth temperature [4–8]and oxygen pressure [4–6,9,10]on structural,electrical,and optical properties of AZO ?lms has been studied.Typically,optimal substrate temperature and oxygen pressure for obtaining AZO ?lms with low electrical resistance and high optical transmittance have been found to be ~300?C and 5×10?4–5×10?3mbar,respectively.
There are reports about optimization of Al doping level of laser deposited AZO ?lms [11–13].Regarding the electrical resistivity,optimal Al doping level was found to be 1.3at%by Kim et al.[11]and 2at%by Shukla et al.[13].In these two reports,the investi-gated AZO ?lms were deposited in oxygen ambient using ceramic ZnO:Al target.Liu and Lian [12]deposited AZO ?lms from metallic Zn-Al targets at relatively high oxygen pressure (1.1×10?1mbar)and found the minimal resistivity at the Al doping level of 3.16at%.
https://www.sodocs.net/doc/5c17565469.html,/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.138
0169-4332/?2014Elsevier B.V.All rights reserved.
M.Kodu et al./Applied Surface Science320(2014)756–763757
Therefore,there are quite a few experimental works about the in?uence of oxygen ambient during deposition on electrical proper-ties of AZO?lms with speci?c Al doping concentrations[4–6,9,10]. In those papers,the variation of electron concentration in the?lms is usually explained by modi?cation of the concentration of oxy-gen vacancies.However,it is highly questionable whether oxygen vacancies can play such a role in ZnO as these are deep rather than shallow donor defects[14–16].In addition,experiments on optimization of Al doping concentration are typically conducted under?xed oxygen conditions[11–13,17]and do not account for the possible effect of oxygen partial pressure on effective Al solubil-ity in ZnO.It is plausible that instead of intrinsic donor-type defects intrinsic acceptor-type defects,like zinc-vacancies[15,18,19],are more relevant in determining the electrical properties of synthe-sized AZO?lms.
This work investigates the in?uence of oxygen ambient on active Al doping concentration and on electrical and optical properties of the?lms grown by PLD.For that purpose,AZO thin?lms were deposited onto amorphous SiO2substrates using PLD targets with different Al doping concentrations(1–10at%).In addition to electri-cal properties and optical properties in the visible spectral region, the transmittance and re?ectance in the near-IR spectral region were measured.Structural characterization methods were used in order to identify possible in?uence of deposition atmosphere on the?lm structure.
2.Experimental details
AZO?lms with~100nm thickness were deposited by PLD method on10×10×1mm fused quartz substrates.Prior to depo-sition the substrates were cleaned by(a)removing the organic impurities in a H2O:H2SO4:H2O2solution,(b)processing the sub-strates in ultrasonic bath in acetone,and?nally(c)rinsing the substrates in methanol.For preparation of1–10at%Al AZO targets, appropriate quantities of ZnO(Alfa Aesar,Puratronic,99.9995% purity)and Al2O3(Aldrich,99.997%purity)powders were thor-oughly mixed,pressed into pellets,and sintered in ambient air for8h at1000?C and then for15h at1200?C.A KrF excimer laser(COMPexPro205,Coherent;wavelength248nm,pulse width 25ns)was used for ablation.The AZO?lms were deposited using a laser pulse energy density of1.5J/cm2on the target,repetition rate of10Hz,substrate temperature of300?C,and the distance between the substrate and the target of7.5cm.Two different environments were used for deposition:vacuum(pressure under10?6mbar)and oxygen gas with a pressure of10?3mbar.Other details of the depo-sition process are described elsewhere[20].
Film thickness was measured with spectroscopic ellipsometer Woollam M-2000x,structural characterization of the?lms was performed with X-ray diffractometer Rigaku SmartLab,and chem-ical composition of the deposited?lms was analyzed with X-ray ?uorescence(XRF)device Rigaku ZSX400.A four-point probe con-nected to the Keithley2400SourceMeter was used to measure the sheet resistance of the?lms.Charge carrier concentration and mobility were obtained with Hall effect device.Optical transmit-tance and re?ectance of the?lms were measured with UV–Vis-NIR spectrophotometer Jasco V-570.
3.Results and discussion
3.1.Structural properties
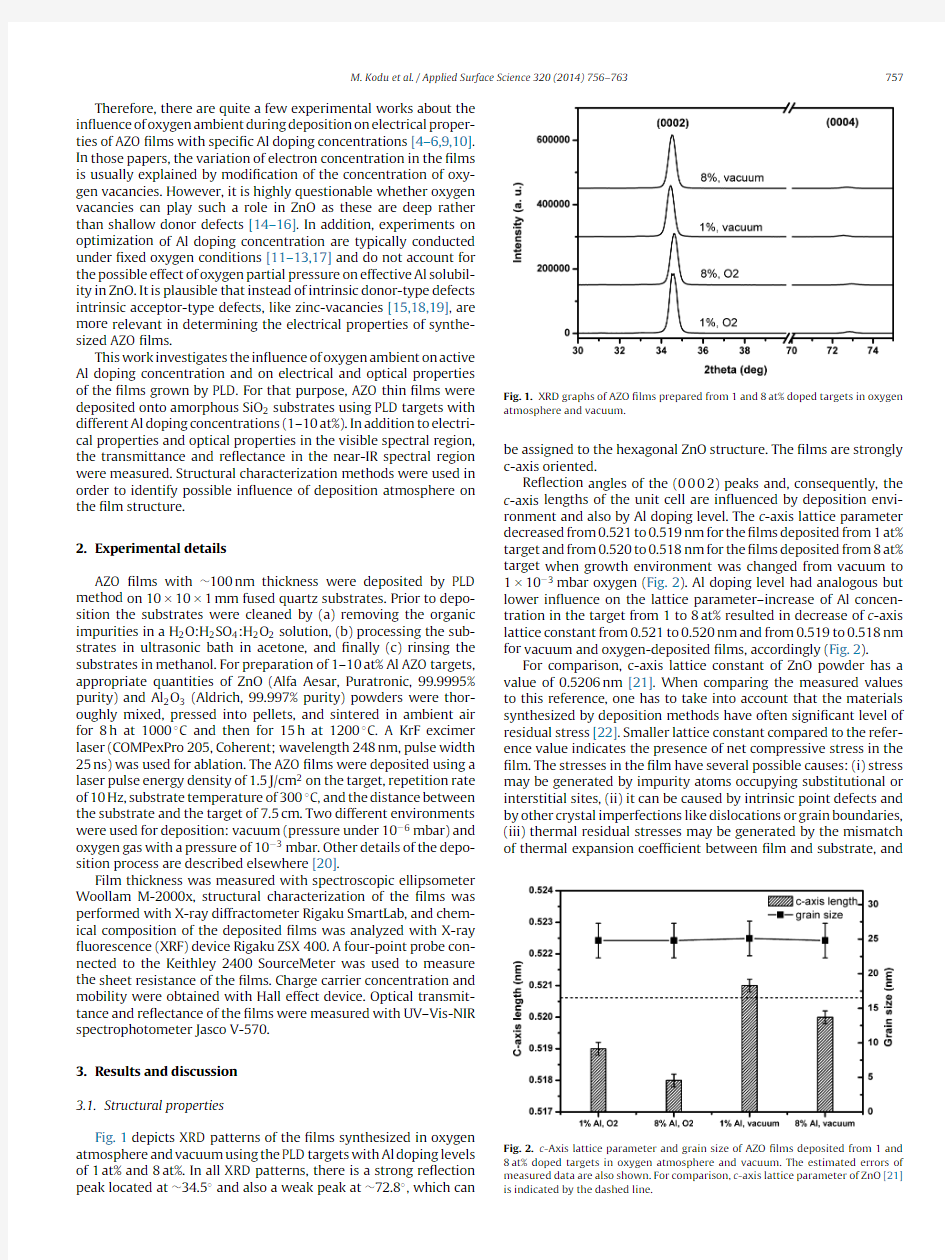
Fig.1depicts XRD patterns of the?lms synthesized in oxygen atmosphere and vacuum using the PLD targets with Al doping levels of1at%and8at%.In all XRD patterns,there is a strong re?ection peak located at~34.5?and also a weak peak at~72.8?,which
can Fig.1.XRD graphs of AZO?lms prepared from1and8at%doped targets in oxygen atmosphere and vacuum.
be assigned to the hexagonal ZnO structure.The?lms are strongly c-axis oriented.
Re?ection angles of the(0002)peaks and,consequently,the c-axis lengths of the unit cell are in?uenced by deposition envi-ronment and also by Al doping level.The c-axis lattice parameter decreased from0.521to0.519nm for the?lms deposited from1at% target and from0.520to0.518nm for the?lms deposited from8at% target when growth environment was changed from vacuum to 1×10?3mbar oxygen(Fig.2).Al doping level had analogous but lower in?uence on the lattice parameter–increase of Al concen-tration in the target from1to8at%resulted in decrease of c-axis lattice constant from0.521to0.520nm and from0.519to0.518nm for vacuum and oxygen-deposited?lms,accordingly(Fig.2).
For comparison,c-axis lattice constant of ZnO powder has a value of0.5206nm[21].When comparing the measured values to this reference,one has to take into account that the materials synthesized by deposition methods have often signi?cant level of residual stress[22].Smaller lattice constant compared to the refer-ence value indicates the presence of net compressive stress in the ?lm.The stresses in the?lm have several possible causes:(i)stress may be generated by impurity atoms occupying substitutional or interstitial sites,(ii)it can be caused by intrinsic point defects and by other crystal imperfections like dislocations or grain boundaries, (iii)thermal residual stresses may be generated by the mismatch of thermal expansion coef?cient between?lm and substrate,
and
Fig.2.c-Axis lattice parameter and grain size of AZO?lms deposited from1and 8at%doped targets in oxygen atmosphere and vacuum.The estimated errors of measured data are also shown.For comparison,c-axis lattice parameter of ZnO[21] is indicated by the dashed line.
758M.Kodu et al./Applied Surface Science320(2014)756–763
(iv)the compressive stresses may be caused by atomistic peening effect[17,22].In Fig.2one can notice two trends regarding c-axis parameter:(1)parameter decreases when Al concentration in the target rises from1to8at%regardless of the growth atmosphere, and(2)parameter is smaller for the?lms deposited in O2as com-pared to the?lms deposited in vacuum.Typically,the reduction of c-axis lattice parameter with increasing Al doping is attributed to the replacement of Zn2+ion in the lattice by Al3+ion,which has a smaller radius(53.5pm)than Zn2+(74pm)[9,17,23,24].Therefore, the?rst trend can be attributed to the rising concentration of Al Zn centers in the?lms when Al concentration in the target is raised from1to8at%.The second trend,the shortening of lattice constant in O2,can possibly be caused by intrinsic defect,which formation energy,and hence also its concentration in growing?lm depends on oxygen environment.According to previous studies[15,18,19,25], the most likely candidate for this defect is zinc vacancy(V Zn)as its formation energy depends strongly on oxygen activity and is low at oxygen-rich conditions.Thus,high concentration of V Zn can be the cause for c-parameter shortening in case of?lms deposited in oxygen environment.
It has been found that Al doping level affects also the crys-talline quality of the?lms[11–13].The intensity of XRD peaks decreased and the full-width at half-maxima(FWHM)increased monotonically when Al doping level was raised.Thus,the grain size,calculated using XRD peak widths from Debye-Scherrer equa-tion,decreased consistently with rising Al percentage in the?lm [11–13].However,XRD peak intensities and FWHMs of our?lms deposited in vacuum and oxygen environment using1and8at% targets did not show considerable dependence on Al doping level or oxygen environment.The grain sizes,calculated using Debye-Scherrer equation were~25nm in all cases.
Most of the XRD peak broadening is caused by the sample and arises from two main sources:crystallite size and strain.Debye-Scherrer equation accounts only for the effect of crystallite size on the XRD peak broadening.To be more speci?c,only the inhomo-geneous strain in the crystal contributes to the peak broadening. Homogeneous strain means that all the crystallites in the sample are strained by the same amount,which results in XRD peak shif-ting.In Fig.2it can be seen that XRD peak shifting of our AZO?lms is mainly in?uenced by O2deposition pressure and,in lesser amount, by Al concentration in the?lms.This means that the compressive stresses in our samples are governed mainly by oxygen conditions. Lu et al.[17]linked the homogeneous compressive stress,observed in the sputtered AZO?lms,with the crystallite size of their samples –they observed that XRD peak shifting was inversely proportional to the crystallite size obtained using the Debye-Scherrer equation. In our case,as can be seen in Fig.2,such one-to-one relation is not observable.Crystallite size of PLD?lms is largely in?uenced by substrate temperature[7,26].In addition,there is a strong depend-ence of grain size on?lm thickness[7,27].AZO?lm thicknesses in references[11,13,17],where the authors observed the reduction of crystallite size with increasing Al doping concentration,are in range of250–400nm,which are considerably thicker than?lms investi-gated in this work(~100nm).It is feasible that the crystallite sizes of our?lms are mostly determined by the combination of substrate temperature and?lm thickness,especially when considering that the thicknesses of our?lms are much smaller and closer to the size of the crystallites.
3.2.Film composition
As can be seen in Fig.3,the Al concentration was somewhat lower in the?lms than nominal doping percentage in correspond-ing targets.In addition,in the case of?lms deposited from the same target,there was less Al in the?lms grown in oxygen environment as compared to the?lms grown in vacuum.The average ratios
of Fig.3.XRF analysis results of AZO?lms deposited from targets with Al doping levels of1–10at%.
the Al concentrations in the?lm and in the target were~0.6for oxygen-deposited?lms and~0.7for vacuum-deposited?lms.
The primary advantage of the PLD method is its ability to trans-fer the material stoichiometrically from a target to a?lm.However, as discussed in the comprehensive paper of Schou[28],there are several physical aspects that in?uence the material transfer pro-cesses during PLD growth and can considerably alter the chemical composition of growing?lm.Non-stoichiometric transfer of tar-get’s composition to the?lm can be typically attributed to four causes[26,28]:
(1)Non-uniformities in the source angular distribution.
(2)Re-sputtering effects or re-evaporation effects.
(3)Species dependent background gas scattering effects.
(4)Selective backscattering of plasma species to the target.
If different components of the PLD plasma plume have differ-ent angular distributions(1),then the growing?lm has different elemental composition than the target.Different angular distribu-tions of component plume species can be attributed to differences in charge or mass of the species[26,28].Effect(1)depends mainly on laser energy density used for ablation but may depend also on other parameters.Also,on-axis enrichment of light or heavy species has been found[26].For example,Urbassek and Sibold[29]demon-strated in their theoretical work that at low laser?uence there is a strong increase in concentration of the heavy element along the normal of the target.According to Leuchtner[30],the abla-tion threshold of ZnO is at the laser?uence~0.7J/cm2and there is a rapid increase in the concentration of Zn ions in addition to Zn neutrals above the threshold?uence.In addition,the kinetic energy distribution of Zn ions was different from the energy distri-bution of neutral Zn atoms.Energy density used in the present work (1.5J/cm2)is well above the threshold for ablation and therefore it is possible that non-congruent transfer is induced by different dis-tribution of neutrals and charged species of Zn and Al in the plasma. Re-sputtering(2)of atoms from the surface of growing?lm by arriv-ing particles has been identi?ed as a concern,especially at higher ?uences(>4J/cm2)and when deposition is carried out in vacuum [28,31].For multi-elemental targets it has been found that sputter-ing mainly occurred for the component with the lowest mass and with the highest volatility.Zn has2.5times higher mass than Al and in that regard Al should be more prone to re-sputtering from the ?lm surface.However,Zn is known as one of the high-volatile ele-ments[32]and Al probably has much lower volatility.In addition,
M.Kodu et al./Applied Surface Science320(2014)756–763
759
Fig.4.Dependence of resistivity on Al concentration in PLD?lms:(a)AZO?lms deposited in1×10?3mbar oxygen,(b)AZO?lms deposited in vacuum.
the actual?uence1.5J/cm2is well below4J/cm2and therefore it cannot be concluded that re-sputtering of atoms has any signi?cant role in the reduction of Al concentration.
Scattering in background gas(3)can be also eliminated as the main mechanism behind the reduced Al concentration in the?lms because,as it can be seen in Fig.3,there is a large deviation from nominal Al concentration already in the?lms deposited in vacuum. Note that collisional broadening effect is shown to be signi?cant at background gas pressures at least two orders of magnitude larger [26]than the O2pressure(10?3mbar)used in the present work.
Finally,the selective backscattering of PLD plasma species(4) may induce non-congruent Al/Zn transfer from target to substrate. This process occurs during the initial stage of plasma plume for-mation and before its expansion[26].For instance,authors of reference[33]found that enrichment of Ge in their?lms made from germanium-silicon alloy was the result of enhanced backscattering of Si atoms in the plasma plume.Also,Claeyssens et al.[34]stud-ied the plasma plume of ZnO target ablated using193nm pulsed excimer laser and concluded that the enrichment of target surface by Zn is caused by material backscattering within the initial dense plasma.
3.3.Electrical properties
As can be seen in Fig.4,AZO?lms deposited in vacuum have distinctively lower resistivities than the?lms deposited in oxygen atmosphere.Also the variation of resistivity with doping concen-tration is higher for the?lms deposited in vacuum–the resistivities of the?lms deposited in oxygen steadily increase from9.7×10?4 to2.3×10?3 cm with doping concentration growing from0.6to 5.2at%,while the resistivities of the?lms grown in vacuum show minimum value of2.0×10?4 cm at around3–4at%doping con-centration.
For the?lms deposited in oxygen environment,similar depend-ence on doping concentration has been reported in earlier studies [11,13]–the minimum resistivities were obtained using PLD tar-gets with1–2at%Al concentration and resistivities of the?lms increased quickly with increasing Al doping level.
There are some reports on investigation of AZO thin?lms with?xed Al percentage deposited under vacuum.In refer-ences[7,27,35],vacuum-deposited ZnO?lms that were made using targets with2.0,3.2and3.4at%of Al,respectively,were investigated.The minimal resistivities(~2×10?4 cm)of
our Fig.5.Dependence of carrier concentration(n e)and Hall mobility( )on Al con-centration in PLD?lms:O2–AZO?lms deposited in1×10?3mbar oxygen,vac–AZO ?lms deposited in vacuum.
vacuum-deposited AZO?lms approximately coincide with the results reported in these references[7,27,35].
The results obtained from Hall effect measurements(Fig.5)also show signi?cant in?uence of deposition environment on electri-cal properties of thin?lms.For the?lms deposited in oxygen,the carrier concentration is relatively insensitive to Al doping concen-tration and varies from1.7×1021to2.9×1021cm?3.At the same time,the Hall mobility decreases from37.1to13.7cm2×V?1×s?1 with the increase of Al concentration from0.6to5.2%in the?lms, whereas there is quite drastic decrease of Hall mobility between Al concentrations from0.6to2.3at%.For the?lms grown in vac-uum,these dependences are substantially different.As one can see in Fig.5,the carrier concentration in these?lms increases steadily from3.4×1020to1.1×1021cm?3with Al concentration increasing from0.9to4.3%,and falls again with the increase of Al concentration to7.2%.Hall mobility has now the highest value (33.7cm2×V?1×s?1)at Al concentration of2.8at%.
The carrier concentration is generally limited by the solid sol-ubility of the dopant[3,36].When attempting to achieve doping levels exceeding this limit,the concentration of free carriers may even decrease due to formation of secondary phases(like Al2O3or ZnAl2O4)or other defects that act as a carrier traps[11–13].
The carrier concentration maximum is at Al concentration of 3–4at%for vacuum-deposited?lms.These values are higher than the solubility limit of1–2at%obtained for Al doped ZnO ceramic samples annealed at high temperatures[37,38].However,for thin ?lms deposited at lower temperatures at nonequilibrium condi-tions,Ellmer[36]has proposed dopant solubility limit of about 4at%Al for AZO thin?lms,though the impurity concentration may be even signi?cantly higher[39].
The observed dependences of electrical properties on Al doping level of oxygen-deposited?lms are in agreement with previ-ous results for AZO?lms laser deposited in oxygen environment [11–13].In these earlier studies,the Hall mobility was found to decrease steadily with increasing Al content.The carrier concen-tration increased abruptly when Al impurities were added to pure ZnO,achieved maximum value at around2at%of Al in the target, and decreased slowly when Al doping level was further increased [11–13].
In references[11–13],the decreasing carrier mobility at higher doping levels is attributed to the deterioration of crystal quality of the?lms that is caused by increasing Al impurity concentration in ZnO crystal lattice.However,XRD analysis of our AZO?lms did not show any signi?cant deterioration of crystal quality with the increase in Al doping level(Fig.1).
760M.Kodu et al./Applied Surface Science320(2014)756–763
Among different scattering mechanisms in?uencing the charge carrier mobility in doped semiconductor TCOs,the most rele-vant are the ionized impurity scattering and the grain boundary scattering[40,41].Typically,at carrier concentrations above 1–3×1020cm?3the mobility is dominated by ionized impu-rity scattering mechanism and below that value,grain boundary scattering dominates.However,at extremely high dopant concen-trations the assumption of statistically homogeneous distribution of dopants is no longer valid and the effect of dopant clustering has to be taken into account.Clusters of impurities act as scattering centers with higher charge as compared to Al Zn1+and this results in higher scattering ef?ciency because of ii~Z?2dependence of the mobility on the charge of the scattering center[40,42].The mobility maximum at an Al concentration of2.8at%or at a carrier concentra-tion of8.9×1020cm?3in the case of our vacuum-deposited?lms can,therefore,be assigned to the switching of prevailing scatter-ing mechanism.In the region where the mobility increases with the carrier concentration(at n e values up to~9×1020cm?3),scattering at grain boundaries is dominant and,in the region where the mobil-ity decreases with increasing carrier concentration,scattering at ionized impurities contributes more signi?cantly to the mobility (Fig.5).Segregation effects due to formation of impurity phases like Al2O3and ZnAlO4are also possible at high doping concentra-tions[43].These effects probably in?uence electrical properties of vacuum-deposited?lms with Al over4.2at%where n e decreases with increasing Al concentration(Fig.5).In addition,the role of compensating native defects has to be acknowledged.Walukiewich [44]explained strong reduction of mobility in heavily doped n-type GaAs by formation of compensating native defects V Ga acting as electron scattering centers.Also,the decreased concentration of electrically active donors in n-type GaAs has been attributed to the formation of compensating native defects.Walukiewich[45]found that in GaAs,V Ga compensates intentionally introduced donors and the concentration of free electrons is much lower than dopant con-centration.This effect was attributed to the strong dependence of V Ga defect formation energy on the Fermi level position and,hence, the concentration of compensating acceptor defects increases sig-ni?cantly at high donor doping levels.The possible in?uence of intrinsic defects on electron mobility and concentration of AZO ?lms deposited in this work is discussed in the following section.
3.4.Discussion of electrical properties
ZnO may contain several intrinsic defects,either of donor type, i.e.O vacancy(V O),Zn interstitial(Zn i)and Zn antisite(Zn O),or of acceptor type,i.e.Zn vacancy(V Zn)and O interstitial(O i).According to the model calculations,the acceptor type centers V Zn and O i have relatively high formation energies in zinc-rich conditions and low formation energies in oxygen-rich conditions[25].In oxygen-rich conditions,the formation of zinc vacancies(V Zn)is more favored than of oxygen interstitials among acceptor type defects,whereas V Zn is regarded as the dominant compensating center and electron acceptor in n-type ZnO[15,25,46,47].As a result,n-type conductiv-ity is theoretically predicted to be favored in Zn-rich(oxygen-poor) conditions due to low concentration of electron-killer centers[27].
Ryoken et al.[46]have found that the electron concentration decreases considerably in AZO(0.5at%Al)?lms when oxygen radi-cals(O*)instead of O2gas are used during the deposition.This effect has been attributed to the shift in the defect equilibrium by the oxygen chemical potential.In the presence of more active oxy-gen species(or at higher oxygen pressure)the defect equilibrium is shifted towards the higher level of defects(such as V Zn–zinc vacancy)compensating Al Zn donors and as a result the electron concentration is limited in spite of high Al-doping level.On the contrary,under conditions where the oxygen chemical potential is lower(or in vacuum)the defect equilibrium is closer to the state where the formation of V Zn acceptor centers is inhibited.These results and arguments are in agreement with the data shown in Fig.5,where it can be seen that for all doping levels the elec-tron concentration is higher for the?lms deposited in oxygen-poor conditions(in vacuum).
The most relevant defect reactions taking place during AZO?lm growth and in?uencing free electron concentration can be formu-lated in Kr?ger-Vink notations as follows[46]:
Al2O3→2Al Zn++2O O+2e +1/2O2(1) Al2O3→2Al Zn++3O O+V Zn (2) 2Al Zn++2O O+2e +1/2O2→Al2O3(3) Equation(1)describes the increase of free electron concentra-tion in Al doped ZnO and equation(2)accounts for the formation of compensating defects to inhibit the electron concentration.Equa-tion(3)represents the situation where Al concentration is over solubility limit.The defect equilibrium is likely to be in some intermediate state.According to the theoretical predictions,zinc vacancy V Zn has the lowest formation energy from the native point defects and its value depends strongly on oxygen activity [15,25].Therefore,under oxygen-poor conditions the processes(1) is dominating and in oxygen-rich conditions the process(2)is more effective.High concentrations of zinc vacancies can have consider-able effect on AZO electrical properties as they may in?uence the(a) mobility–acting as a charged scattering center,and(b)free elec-tron concentration–acting as an electron killer center.Thus,the substantial differences in electron concentrations and in behavior of n e vs.Al concentration dependence for vacuum-and oxygen-deposited?lms observed in this work(Fig.5)can be explained as follows:
(1)The?lms deposited in O2:at high concentration of V Zn these
defects passivate additional Al donors and hinder n e from ris-ing with increasing Al concentration in the?lms.In addition, the decreasing mobility with increasing Al concentration is explainable by increasing concentration of charged V Zn vacan-cies acting as effective scattering centers(Eq.(2)).
(2)The?lms deposited in vacuum:n e increases with rising Al
doping level until the solubility limit is reached at around4at% of Al(thereafter Eq.(1)→Eq.(3)).Mobility increases with Al concentration until~3at%according to the grain barrier limited scattering mechanism and after that level,ionized impurity scattering mechanism prevails,including the enhanced scat-tering due to effect of cluster formation at higher Al doping levels.
The outcome of this work endorse the fact that,during AZO PLD process,O2deposition pressure strongly in?uences defect equilib-ria and this,in turn,controls the electrical conductivity of AZO?lms. However,according to recent theoretical works[14–16],the dom-inating active defects are probably not O vacancies,which role is almost always emphasized in the experimental investigations of AZO thin?lms[4–6,9,10],but the Zn vacancy acceptor centers, which concentration is readily in?uenced by oxygen activity during deposition process.Our study demonstrates that the effective solu-bility of Al dopants is greatly in?uenced by O2deposition pressure. The interpretation of our results is compatible with the concept of zinc vacancies being most relevant intrinsic acceptor-type defects that affect the electrical properties of Al doped ZnO.
3.5.Optical properties
Transmittance and re?ectance spectra of AZO?lms deposited in oxygen and vacuum are shown in Fig.6.There is a distinctive
M.Kodu et al./Applied Surface Science320(2014)756–763
761
Fig.6.Transmittance and re?ectance spectra of AZO thin?lms deposited from targets with different Al concentrations in oxygen atmosphere(a)and in vacuum(b).
difference in the in?uence of the Al doping level on the optical properties of the?lms grown in two different atmospheres.Trans-mittance spectra of the?lms deposited in oxygen are all similar and depend little on Al concentration in the target.The same is valid for the re?ectance spectra.All?lms deposited in oxygen have good transmittance(>80%)over the visible and near-IR range.Also the oscillation of the transmittance and re?ectance,coming from thin ?lm interference,is clearly seen.All these?lms have re?ectance in near-IR spectral region below10%.
The spectra of AZO?lms deposited in vacuum show stronger dependence on the Al doping level.The transmittances of all the ?lms in this set are over80%in the visible spectral region.How-ever,transmittance values in the near-IR spectral region depend strongly on Al concentration and are clearly lower for higher doping concentrations.For instance,at a wavelength of2500nm,the?lm with0.9at%of Al has the highest transmittance value of81%and the ?lm with4.3at%of Al has the lowest transmittance value of28%.The Al concentration has also a marked effect on the re?ectance spectra of vacuum-deposited?lms.The?lms with higher doping concen-tration have relatively higher re?ectance in the near-IR region. Comparing the spectra in the near-IR region of vacuum-deposited ?lms it can be concluded that the re?ectances and transmittances are closely related,i.e.low transmittance in the IR region means that there is high re?ectance in that region.
Strong absorption in the UV region is due to excitations across the fundamental band gap[2].Absorption coef?cients of the AZO ?lms were calculated from transmittance and re?ectance data using the relation T=(1?R)2exp(??t),where T is transmittance,R is re?ectance,t is?lm thickness,and?is absorption coef?cient. Optical band gaps(E g)were obtained by plotting?2vs.photon energy and extrapolating linear part of the graph to the energy axis.Determined E g values for vacuum-and oxygen-deposited?lms are shown in Fig.7.As can be seen in?gure,the band gaps of Al doped ZnO?lms are higher than3.3eV,the value determined for undoped ZnO[47].Also,the values of E g are much larger for vacuum-deposited?lms than for oxygen-deposited?lms.The shift of optical band gap toward shorter wavelengths is probably caused by different occupation of states by free electrons at the bottom of conduction band of ZnO.This feature is usually described as a Burstein–Moss effect[2].The E g vs.Al%dependencies for the?lms deposited in O2and vacuum are,therefore,different because of different free electron concentrations in these?lms.However,it is also known that the residual lattice strains can in?uence the band gap value of semiconductor material.For instance,Ghosh et al.
[48]found that strain along c-axis modi?ed band gap values of ZnO thin?lms deposited on different substrates by sol-gel process. In Ref.[48],tensile lattice strain decreased optical band gap and compressive lattice strains increased band gap value.As was described earlier in Section3.1,high level of Al doping decreases the c-axis lattice parameter,which is an indication of compressive stresses in our AZO?lms.The effect of lattice strain on E g value described by Ghosh[48]may be an additional factor behind the monotonically rising E g with Al doping concentration as seen in Fig.7.
Screening of the ions by free electron plasma causes high re?ectance at the wavelengths beyond1000nm(Fig.6).The onset of this effect is characterized by the plasma frequencyωp?n1/2
e
or the plasma wavelength p?n1/2
e
,which are proportional or inversely proportional,respectively,to the square root of free elec-tron density n e[2,4].The rise of re?ectance in the IR-region starts at1100nm and is steeper for the?lms with higher carrier con-centrations.It can be seen from Figs.5and6that there is a direct correlation between the carrier concentration and the re?ectivity (transmittance)of the?lms in the near-IR region for the AZO?lms deposited in vacuum.Because of lower carrier concentrations,the re?ectance caused by free electron gas is negligible for oxygen-deposited?lms up to2500nm(Fig.6)and these?lms show high transmittances up to the end of the measured spectral range.
Figures of merit(FOM)were estimated for the best AZO?lms deposited in this work in order to compare their performance with AZO?lms deposited before using PLD and RF sputtering meth-ods.FOM characterizes TCO?lm electrical and optical performance. Typically FOM is de?ned as FOM=T10/R sheet[49],where T is
optical
Fig.7.Variation of optical band gap as a function of Al concentration in AZO?lms.
762M.Kodu et al./Applied Surface Science320(2014)756–763 Table1
Figures of merit(FOM)of AZO?lms.
Material Method T10R sheet
( /square)FOM
(×10?3)
Reference
AZO PLD0.28 3.190.3[8]
AZO PLD0.25 4.852.1[4]
AZO PLD0.08324 3.5[12]
AZO PLD0.3512.328.7[10]
AZO Sputtering0.431043.0[50]
AZO(oxygen)PLD0.4381.1 5.3This work AZO(vacuum)PLD0.5415.834.2This work
transmittance of the?lm and R sheet is its sheet resistance,and this de?nition of FOM is also used in this work.The comparison of our ?lms with the results obtained in the literature is summarized in Table1.
It can be seen from Table1that the performances reached in different papers can vary signi?cantly.The best?lms obtained in this work are at a comparable level with high quality AZO?lms deposited before.When comparing best AZO?lms made in this work,it can be seen that vacuum-deposited?lms clearly outper-form oxygen-deposited?lms since the optical transmittance in the visible range and the resistivity are both better for vacuum-grown ?lms.
4.Conclusions
In this work,ZnO:Al thin?lms were laser-deposited from ceramic ZnO targets that were doped with1–10at%Al.Deposi-tion was carried out in oxygen atmosphere(1×10?3mbar)and in vacuum conditions onto amorphous SiO2substrates at300?C.As a result,c-axis oriented polycrystalline AZO thin?lms were obtained. According to XRD analysis,the c-axis parameter of hexagonal crys-tal lattice was slightly in?uenced by the deposition atmosphere and Al doping level.However,the grain size of the AZO?lms did not show considerable dependence on the deposition conditions or Al concentration.
According to the XRF elemental analysis,the transfer of material from AZO targets to?lms was non-stoichiometric.On average,for AZO?lms deposited in vacuum the Al concentration(Al/(Al+Zn)) in the?lms was~70%of nominal Al concentration in the targets. The effective Al transfer from target to?lm was even lower(~60%) for the?lms deposited in oxygen.
Compared to the oxygen-deposited?lms,the resistivities of the vacuum-deposited?lms were lower for all Al concentrations and this difference increased with rising doping concentration.The low-est resistivity(2.0×10?4 cm)was obtained at around4at%Al doping level in the?lm.Oxygen environment during the deposi-tion in?uenced considerably the carrier concentrations(n e)and mobilities( )of AZO?lms.For the?lms deposited in oxygen,n e vs. Al%and vs.Al%showed similar dependencies as reported before. However,vacuum-deposited?lms were characterized by signi?-cantly higher carrier concentrations and also by higher mobilities at high Al doping levels.
Due to low carrier concentrations(~2×1020cm?3),oxygen-deposited?lms had high transmittances in visible and near-IR spectral region.Films grown in vacuum showed increased re?ectance in the near-IR spectral region as the result of increased carrier concentrations(up to1.1×1021cm?3).
The large difference between the carrier concentrations in oxygen-deposited and vacuum-deposited?lms can be attributed to higher effective solubility of Al in the?lms deposited in vac-uum.The detailed interpretation of this difference is in agreement with the results showing that under oxygen-rich conditions,the formation of the dominant compensating defect V Zn,that acts as a deep acceptor in ZnO,is promoted.High concentration of charged compensating defects(V Zn+2e1?→V Zn2?)in oxygen-deposited ?lms leads also to the reduction of carrier mobility with increasing Al concentration as a result of enhanced ionized impurity scatter-ing.
In previous works,the effect of oxygen atmosphere to the elec-trical properties of AZO?lms is usually explained by its in?uence on the concentrations of intrinsic donor defects(V O,Zn i,Zn O) [4–6,9,10].However,the experimental results of this work indicate that the O2atmosphere in?uences the active Al dopant concentra-tion in AZO?lms.The mechanism is probably related to the charge compensating intrinsic acceptor-type defects like V Zn,which con-centration is in?uenced by oxygen pressure during the deposition process.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the European Union through the European Regional Development Fund(projects3.2.1101.12-0014 and3.2.1101.12-0027).Authors wish to gratefully acknowledge Prof.Jaan Aarik for valuable remarks and Dr.Hugo M?ndar for help with the X-ray diffraction analysis.
References
[1]B.Szyszka,W.Dewald,S.K.Gurram,A.P?ug,C.Schulz,M.Siemers,V.Sittinger,
S.Ulrich,Recent developments in the?eld of transparent conductive oxide ?lms for spectral selective coatings,electronics and photovoltaics,Curr.Appl.
Phys.12(2012)S2–S11.
[2]C.G.Granqvist,Transparent conductors as solar energy materials:A panoramic
review,Sol.Energy Mater.Sol.Cells152(2007)9–159,8.
[3]H.Liu,V.Avrutin,N.Izyumskaya,ü.?zgür,H.Morkoc?,Transparent conduct-
ing oxides for electrode applications in light emitting and absorbing devices, Superlattices Microstruct.48(2010)458–484.
[4]B.Dong,H.Hu,Gu.Fang,X.-Z.Zhao,D.-Y.Zheng,Y.-P.Sun,Comprehensive
investigation of structural,electrical,and optical properties for ZnO:Al?lms deposited at different substrate temperature and oxygen ambient,J.Appl.Phys.
103(2008)073711.
[5]S.-M.Park,T.Ikegami,K.Ebihara,P.-K.Shin,Structure and properties of trans-
parent conductive doped ZnO?lms by pulsed laser deposition,Appl.Surf.Sci.
253(2006)1522–1527.
[6]A.V.Singh,R.M.Mehra,N.Buthrath,A.Wakahara,A.Yoshida,Highly conductive
and transparent aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin?lms prepared by pulsed laser deposition in oxygen ambient,J.Appl.Phys.90(2001)5661–5665. [7]H.Tanaka,K.Ihara,T.Miyata,H.Sato,T.Minami,Low resistivity polycrystalline
ZnO:Al thin?lms prepared by pulsed laser deposition,J.Vac.Sci.Technol.22 (2004)1757–1762.
[8]H.Agura,A.Suzuki,T.Matsushita,T.Aoki,M.Okuda,Low resistivity transparent
conducting Al-doped ZnO?lms prepared by pulsed laser deposition,Thin Solid Films445(2003)263–267.
[9]T.Ohshima,Y.Murakami,H.Kawasaki,Y.Suda,Y.Yagyu,Effect of oxygen gas
pressure on electrical,optical,and structural properties of Al-doped ZnO thin ?lms fabricated by pulsed laser deposition for use as transparent electrodes in all-solid-state electrochromic devices,Japan,J.Appl.Phys.50(2011)08JD09.
[10]P.Gondoni,M.Ghidelli,F.Di Fonzo,M.Carminati,V.Russo,A.Li Bassi,C.S.Casari,
Structure-dependent optical and electrical transport properties of nanostruc-tured Al-doped ZnO,Nanotechnology23(2012)365706.
[11]H.Kim,A.Pique,J.S.Horwitz,H.Murata,Z.H.Kafa?,C.M.Gilmore,D.B.Chrisey,
Effect of aluminum doping on zinc oxide thin?lms grown by pulsed laser deposition for organic light-emitting devices,Thin Solid Films377–378(2000) 798–802.
[12]Y.Liu,J.Lian,Optical and electrical properties of aluminum-doped ZnO thin
?lms grown by pulsed laser deposition,Appl.Surf.Sci.253(2007)3727–3730.
[13]R.K.Shukla,Anchal Srivastava,Atul Srivastava,K.C.Dubey,Growth of trans-
parent conducting nanocrystalline Al doped ZnO thin?lms by pulsed laser deposition,J.Cryst.Growth294(2006)427–431.
[14]A.Janotti,C.G.Van de Walle,Hydrogen multicentre bonds,Nat.Mat.6(2007)
44–47.
[15]A.Janotti,C.G.Van de Walle,Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor,
Rep.Prog.Phys.72(2009)126501.
[16]F.Oba,M.Choi,A.Toga,I.Tanaka,Point defects in ZnO:an approach from?rst
principles,Sci.Technol.Adv.Mater.12(2011)034302.
[17]J.G.Lu,Z.Z.Ye,Y.J.Zeng,L.P.Zhu,L.Wang,J.Yuan,B.H.Zhao,Structural,optical,
and electrical properties of(Zn,Al)O?lms over a wide range of compositions,J.
Appl.Phys.100(2006)073714.
[18]F.Tuomisto,V.Ranki,K.Saarinen,D.C.Look,Evidence of the Zn vacancy acting
as the dominant acceptor in n-type ZnO,Phys.Rev.Lett.91(2003)205502. [19]A.F.Kohan,G.Ceder,D.Morgan,C.G.Van de Walle,First-principles study of
native point defects in ZnO,Phys.Rev.B61(2000)15019–15027.
M.Kodu et al./Applied Surface Science320(2014)756–763763
[20]M.Kodu,Aints,T.Avarmaa,V.Denks,E.Feldbach,R.Jaaniso,M.Kirm,A.Maa-
roos,J.Raud,Hydrogen doping of MgO thin?lms prepared by pulsed laser deposition,Appl.Surf.Sci.257(2011)5328–5331.
[21]R.R.Reeber,Lattice parameters of ZnO from4.2?to296?K,J.Appl.Phys.41
(1970)5063–5066.
[22]A.J.Detor,A.M.Hodge,E.Chason,Y.Wang,H.Xu,M.Conyers,A.Nikroo,
A.Hamza,Stress and microstructure evolution in thick sputtered?lms,Acta
Mater.57(2009)2055–2065.
[23]S.Yun,S.Lim,Effect of Al-doping on the structure and optical properties of
electrospun zinc oxide nano?ber?lms,J.Colloid Interf.Sci.360(2011)430–439.
[24]B.K.Sharma,N.Khare,Stress-dependent band gap shift and quenching of
defects in Al-doped ZnO?lms,J.Phys.D:Appl.Phys.43(2010)465402. [25]J.C.Fan,K.M.Sreekanth,Z.Xie,S.L.Chang,K.V.Rao,P-Type ZnO materials:
Theory,growth,properties and devices,Prog.Mater.Sci.58(2013)874–985.
[26]D.B.Chriesy,G.K.Hubler,Pulsed Laser Deposition of Thin Films,John Wiley&
Sons,Inc,New York,1994.
[27]A.Suzuki,M.Nakamura,R.Michihata,T.Aoki,T.Matsushita,M.Okuda,Ultra-
thin Al-doped transparent conducting zinc oxide?lms fabricated by pulsed laser deposition,Thin Solid Films517(2008)1478–1481.
[28]J.Schou,Physical aspects of the pulsed laser deposition technique:The stoi-
chiometric transfer of material from target to?lm,Appl.Surf.Sci.255(2009) 5191–5198.
[29]H.M.Urbassek,D.Sibold,Gas-phase segregation effects in pulsed laser desorp-
tion from binary targets,Phys.Rev.Lett.70(1993)1886–1890.
[30]R.Leuchtner,Mass spectrometry and photoionization studies of the ablation of
ZnO:ions,neutrals,and Rydbergs,Appl.Surf.Sci.127(1998)626–632. [31]E.van de Riet,J.C.S.Kools,J.Dieleman,Incongruent transfer in laser deposition
of FeSiGaRu thin?lms,J.Appl.Phys.73(1993)2890–2896.
[32]R.Eason,Pulsed Laser Deposition of Thin Films,John Wiley&Sons,Inc,Hobo-
ken,New Jersey,2007.
[33]C.B.Arnol,M.J.Aziz,Stoichiometry issues in pulsed-laser deposition of alloys
grown from multicomponent targets,Appl.Phys.A69(Suppl.)(1999)S23–S27.
[34]F.Claeyssens,A.Cheesman,S.J.Henley,M.N.R.Ashfold,Studies of the plume
accompanying pulsed ultraviolet laser ablation of zinc oxide,J.Appl.Phys.92 (2002)6886–6894.
[35]B.-Z.Dong,G.-J.Fang,J.-F.Wang,W.-J.Guan,X.-Z.Zhao,Effect of thickness on
structural,electrical,and optical properties of ZnO:Al?lms deposited by pulsed laser deposition,J.Appl.Phys.101(2007)033713.[36]K.Ellmer,Resistivity of polycrystalline zinc oxide?lms:current status and
physical limit,J.Phys.D:Appl.Phys.34(2001)3097–3108.
[37]M.H.Yoon,S.H.Lee,H.L.Park,H.K.Kim,M.S.Jang,Solid solubility limits of Ga
and Al in ZnO,J.Mater.Sci.Lett.21(2002)1703–1704.
[38]Y.Zhang,W.Wang,R.Tan,Y.Yang,X.Zhang,P.Cui,W.Song,The solubil-
ity and temperature dependence of resistivity for aluminum-doped zinc oxide ceramic,Int.J.Appl.Ceram.Technol.9(2012)374–381.
[39]R.B.H.Tahar,N.B.H.Tahar,Mechanism of carrier transport in aluminum-doped
zinc oxide,J.Appl.Phys.92(2002)4498.
[40]K.Ellmer,R.Mientus,Carrier transport in polycrystalline transparent conduc-
tive oxides:A comparative study of zinc oxide and indium oxide,Thin Solid Films516(2008)4620–4627.
[41]K.Ellmer,R.Mientus,Carrier transport in polycrystalline ITO and ZnO:Al II:
The in?uence of grain barriers and boundaries,Thin Solid Films516(2008) 5829–5835.
[42]Ph.Ebert,T.Zhang,F.Kluge,M.Simon,Z.Zhang,K.Urban,Importance of many-
body effects in the clustering of charged Zn dopant atoms in GaAs,Phys.Rev.
Lett.83(1999)757–760.
[43]M.Vinnichenko,R.Gago,S.Cornelius,N.Shevchenko,A.Rogozin,A.Kolitsch,F.
Munnik,W.M?ller,Establishing the mechanism of thermally induced degra-dation of ZnO:Al electrical properties using synchrotron radiation,Appl.Phys.
Lett.96(2010)141907.
[44]W.Walukiewicz,Carrier scattering by native defects in heavily doped semi-
conductors,Phys.Rev.B41(1990)10218–10220.
[45]W.Walukiewicz,Amphoteric native defects in semiconductors,Appl.Phys.Lett.
54(1989)2094–2096.
[46]H.Ryoken,I.Sakaguchi,N.Ohashi,T.Sekiguchi,S.Hishita,H.Haneda,Non-
equilibrium defects in aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin?lms grown with a pulsed laser deposition method,J.Mater.Res.20(2005)2866–2872.
[47]F.K.Shan,Y.S.Yu,Band gap energy of pure and Al-doped ZnO thin?lms,J.Eur.
Ceram.Soc.24(2004)1869–1872.
[48]R.Ghosh,D.Basak,S.Fujihara,Effect of substrate-induced strain on the struc-
tural,electrical,and optical properties of polycrystalline ZnO thin?lms,J.Appl.
Phys.96(2004)2689–2692.
[49]G.Haacke,New?gure of merit for transparent conductors,J.Appl.Phys47
(1976)4086–4089.
[50]T.Minami,S.Suzuki,T.Miyata,Transparent conducting impurity-co-doped
ZnO:Al thin?lms prepared by magnetron sputtering,Thin Solid Films398–399 (2001)53–58.
2017山香教育理论基础整理笔记(教育学、心理学、教育心理学)
第一章教育与教育学 1、《学记》——“教也者,长善而救其失者也” 2、战国时荀子——“以善人者谓之教” 3、许慎在《说文解字》中认为“教,上所施,下所效也。”“育,养子使作善也。” 4、最早将“教育”一词连用的则是战国时期的孟子:“得天下英才而教育之,三乐也。” 5、分析教育哲学的代表人物谢弗勒在《教育的语言》中把教育定义区分为三种: 规定性定义:作者自己认为的定义,即不管他人使用的“教育”的定义是什么,我认为“教育”就是这个意思。运用规定性定义虽然有一定的自由度,但是,要求作业在后面的论述和讨论中,前后一贯地遵守自己的规定。 描述性定义:回答“教育实际上是什么”的定义。尽量不夹杂自己的主观看法,适当地对术语或者使用该术语的方法进行界定。 纲领性定义:回答“教育应该是什么”的定义。即通过明确或隐含的方式告诉人们教育应该是什么或者教育应该怎么样。 6、教育是一种活动。“教育”是以一种“事”的状态存在,而不是以一种“物”的状态出现。因而。我们就把“活动”作为界定教育的起点。 7、教育活动是人类社会独有的活动。 8、“生物起源论”代表人物: 利托尔诺在《各人种的教育演变》中指出教育是超出人类社会以外的,在动物界中就存在的。 沛西·能在《教育原理》中也认为教育是一个生物学过程,扎根于本能的不可避免的行为。 9、“终身教育”概念的提出,指明人在生理成熟后仍继续接受教育。 10、社会性是人的教育活动与动物所谓“教育”活动的本质区别。 11、教育的本质:教育活动是培养人的社会实践活动。 12、教育是人类通过有意识地影响人的身心发展从而影响自身发展的社会实践活动。 13、学校教育是一种专门的培养人的社会实践活动。 14、学校教育自出现以来就一直处于教育活动的核心。 15、学校教育是由专业人员承担的,在专门机构——学校中进行的目的明确、组织严密、系统完善、计划性强的以影响学生身心发展为直接目标的社会实践活动。 16、学校教育的特征:①可控性②专门性③稳定性 17、教育概念的扩展——大教育观的形成 18、1965年,法国教育家保罗·朗格朗在《终身教育引论》中指出,教科文组织应赞同“终身教育”的原则。 19、1972年,埃德加·富尔在《学会生存》中对“终身教育”加以确定,并提出未来社会是“学习化社会”。 20、“终身教育”概念以“生活、终身、教育”三个基本术语为基础。 从时间上看,终身教育要求保证每个人“从摇篮到坟墓”的一生连续性的教育过程; 从空间上看,终身教育要求利用学校、家庭、社会机构等一切可用于教育和学习的场所; 从方式上看,终身教育要求灵活运用集体教育、个别教育、面授或远距离教育; 从教育性质上看,终身教育即要求有正规的教育与训练,也要求有非正规的学习和提高,既要求人人当先生,也要求人人当学生。 21、教育的形态,是指教育的存在特征或组织形式。 22、在教育发展史上,教育的形态经历了从非形式化到形式化,再到制度化教育的演变。
教育学教育心理学理论及代表人物
教育学有关理论、代表人物 1、神话起源说—— 2、生物起源说——利托尔诺(法国) 3、心理起源说——孟禄(美国) 4、劳动起源说——马克思(前苏联) 5、中国史上第一部教育文献——《学记》——乐正克 6、西方较早讨论教育问题的着作——《论演说家的培养》(《雄辩术原理》)——昆体良(古罗马) 7、非制度化教育思潮——库姆斯、伊里奇 8、雄辩与问答法——苏格拉底(古希腊) 9、《理想国》——柏拉图(古希腊) 10、《政治学》——亚里士多德(古希腊) 11、教育学作为一门独立学科的萌芽——《大教学论》——夸美纽斯(捷克) 班级授课制,泛智教育。 12、首次提出把教育学作为一门独立的学科——培根(英国) 13、自然主义教育——《爱弥儿》——卢梭(法国) 14、教育学进入大学讲坛——康德(德国)、《林哈德与葛笃德》——裴斯泰洛齐(瑞士)
15、科学教育思潮的兴起,课程体系——《教育论》——斯宾塞(英国) 16、实验教育学——梅伊曼、拉伊(德国) 17、发展性教学理论——《教育与发展》——赞科夫(前苏联) 高难度进行教学的原则、高速度进行教学的原则、理论知识主导作用原则(重理性原则)、理解学习过程原则、对差等生要下功夫的原则 18、范例教学——瓦.根舍因(德国) 19、和谐教育思想——苏霍姆林斯基(前苏联) 20、《教育漫话》——洛克(英国) “白板说”、绅士教育、国民教育思想与民主教育思想。 22、规范教育学的建立——《普通教育学》——赫尔巴特(德国) 传统教育学代表、教师中心,教材中心,课堂中心、四段教学法、统觉观念。 23、实用主义教育学——《民本主义与教育》——杜威(美国) 现代教育学代表、教育即生长,教育即生活,教育即经验的改造或重组、在做中学、儿童中心主义。 24、第一部马克思主义的教育学着作——《教育学》——凯洛夫(前苏联) 25、我国第一部马克思主义的教育学着作——《新教育大纲》——杨贤江 26、设计教学法——克伯屈(美国)
教育心理学理论
教育心理学理论 一、学习分类理论 1、加涅 (1)学习八水平分类 按学习水平简繁程度分为:①信号学习;②刺激—反应学习;③连锁反应;④言语联想学习;⑤辨别学习;⑥概念学习;⑦规则学习;⑧解决问题学习 (2)学习六水平分类 ①连锁学习;②辨别学习;③具体概念学习;④定义概念学习;⑤规则学习;⑥解决问题学校 (3)学习结果分类 ①言语信息的学习;②智慧技能的学习;③认知策略的学习;④态度的学习;⑤运动技能的学习 2、奥苏贝尔学习性质分类(两个维度互不依赖、相互独立) (1)根据学习的方式:接受学习、发现学习 (2)根据学习材料与学习者原有知识结构的关系:有意义学习、机械学习 3、我国学习结果的分类 ①知识学习;②技能学习;③道德品质或行为习惯的学习 二、学习理论 1、联结理论 (1)经典条件反应论 ①巴甫洛夫:学习就是形成刺激与反应之间的联系 一级条件反射、二级条件反射 动力定型:大脑皮层对刺激的定型系统所形成的反应定型系统 外抑制、超限抑制、消退、泛化、分化 正诱导:一个部位发生抑制引起周围发生兴奋地过程。 负诱导:一个部位发生兴奋引起周围发生抑制的过程。 同时诱导、继时诱导 第一信号系统:能够引起条件反应的物理性的条件刺激。 第二信号系统:能够引起条件反应的以语言符号为中介的条件刺激。 ②华生:通过建立条件作用,形成刺激与反应间的联结的过程。遵循频因律、 近因律。(学习的实质在于形成习惯) (2)操作性条件说 ①桑代克(联结试误说):在一定的情景和一定的反应之间建立联结,这种联结 通过尝试错误的过程而自动形成。三条学习规律:效果率、练习律、准备率②斯金纳 正强化、负强化、消退 惩罚:惩罚Ⅰ呈现厌恶刺激;惩罚Ⅱ消除愉快刺激 普雷马克原理:用学生喜爱的活动去强化学生参与不喜爱的活动。 强化程式:连续强化程式(灯一开就亮); 间接强化程式:a 定时强化(按时发工资) b 定比强化(计件工作) c 变时强化(随堂测验)d 变比强化(买彩票) (3)社会学习理论(班杜拉) 学习分为参与性学习和替代性学习(通过观察别人而进行的学习。) 观察学习:注意——保持——复制——动机
教育心理学的各种理论
1.桑代克的尝试——错误说 刺激——反应联结 基本规律:效果律练习律准备律 2.巴普洛夫——经典性条件作用论俄国 没有食物,只有铃声产生的唾液是条件刺激 看到食物就产生唾液是无条件反应 基本规律:获得与消退刺激泛化(对事物相似性的反应)与分化(对事物差异性的反应) 3.斯金纳——操作性条件作用论 基本规律:强化(+-)逃避条件作用和回避条件作用(负强化)消退惩罚 4.加涅——信息加工学习理论 模式——信息流控制结构(期望执行控制) 5.1-4属于联结学习理论 6.7-10属于认知学习理论 7.苛勒——完形、顿悟说 德国基本内容:学习是通过顿悟过程实现的学习的实质是在主体内部构成完形 8.布鲁纳——认知、结构学习理论 美国学习的目的在于以发现学习的方式,使学科的基本结构转变为学生头脑中的认知结构。 学习观——实质是主动地形成认知结构过程包括获得转化评价教学观——目的在于理解学科的基本结构 教学原则——动机原则结构原则程序原则强化原则 9.奥苏泊尔——有意义的接受学习美国 学习方式分类:接受学习发现学习 学习材料与原有知识结构分类:机械学习意义学习 先行组织者:是先于学习任务本身呈现的一种引导性材料,他的抽象,概括和综合水平高于学习任务,并且与认知结构中原有的观念和新的学习任务相关联。 10.建构主义学习理论
学习动机 1.学习动机的两个基本成分:学习需要学习期待 2.奥苏泊尔学校情境中的成就动机: 认知内驱力(要求理解掌握事物内部动机) 自我提高内驱力(个人学业的成就“三好学生”) 附属内驱力(获得教师、家长的赞扬) 在儿童早期,附属内驱力最为突出 在青年期,认知内驱力和自我提高内驱力成为学习的主要动机 学习期待就其作用来说就是学习诱因 3.学习动机的种类: 社会意义:低级动机(个人、利己主义) 高尚动机(利他主义) 与学习活动的关系:近景的直接性动机(兴趣、爱好、求知欲) 远景的间接性动机(个人前途,父母期望)动力来源:内部动机(个体需要引起) 外部动机(由外部诱因引起) 4.学习动机理论 强化理论:外部强化自我强化 需要层次理论:美国马斯洛五需要(从低级到高级排列) 生理的需要安全的需要归属和爱的需要 尊重的需要自我实现的需要自我实现的需要包括:认知审美创造的需要(最高级的需要)成就动机理论:代表人:阿特金森 力求成功的动机避免失败的动机 成败归因理论:美国维纳三维度六因素 6因素:能力高低努力程度任务难度运气好坏身心状态外界环境3维度:稳定性可控性内在性 自我效能感理论:美国班杜拉 人的行为受行为的结构因素与先行因素的影响。 行为的结果因素就是通常所说的强化: A.直接强化:外部因素(惩罚奖励) B.替代性强化:通过一定的榜样 C.自我强化:自我评价自我监督 5.学习动机的激发:
3中学教育心理学考试测试题第三章 学习的基本理论
中学教育心理学考试测试题第三章学习的基本理论 一、单项选择题(下列各题所给选项中只有一个符合题意的正确答案,答错、不答或多答均不得分) 1.根据学习的定义,下列属于学习的现象是( D )。 A.吃了酸的食物流唾液 B.望梅止渴 C.蜘蛛织网 D.儿童模仿电影中人物的行为 2.对黑猩猩做“顿悟实验”的是( A )。 A.苛勒 B.托尔曼 C.桑代克 D.巴甫洛夫 3.加涅提出了( A )模式。 A.积累学习 B.发现学习 C.观察学习 D.接受学习 4.操作性条件反射学说的代表人物是( A )。 A.斯金纳 B.巴甫洛夫 C.桑代克 D.班杜拉 5.美国心理学家布鲁纳认为学习的实质在于( B )。 A.构造一种完形 B.主动地形成认知结构 C.形成刺激与反应间的联结 D.对环境条件的认知 6.( B )强调学习的主动性和认知结构的重要性,主张教学的最终目标是促进学生对学科结构的一般理解。A.斯金纳 B.布鲁纳 C.苛勒 D.加涅 D A D 10.下列不属于意义学习的条件的一项是( D ) A.材料本身必须具有逻辑意义 B.学习者认知结构必须具有能够同化新知识的适当的认知结构 C.学习者必须具有积极主动地将新知识与认知结构中的适当知识加以联系的倾向性,并使两者相互作用D.学习材料要高于学习者的能力范围 11.( A )学习理论认为学习是学生建构自己的知识的过程,学生是信息意义的主动建构者。 A.建构主义 B.认知一结构 C.信息加工 D.尝试一错误 12.“一朝被蛇咬,十年怕井绳”,这种现象指( C )。 A.消退 B.刺激比较 C.刺激泛化 D.刺激分化 13.根据经典条件反射作用理论,食物可以诱发狗的唾液分泌反应,则唾液是( C )。 A.中性刺激 B.无条件刺激 C.条件反应 D.无条件反应 14.看见路上的垃圾后绕道走开,这种行为是( C )。 A.强化 B.惩罚 C.逃避条件作用 D.消退 15.先行组织者教学技术的提出者是美国著名心理学家( C )。 A.斯金纳 B.布鲁纳 C.奥苏伯尔 D.桑代克 二、多项选择题(下列各题所给选项中有两个或两个以上符合题意的正确答案,不答、少答或多答均不得分) 1.学习的定义说明( ABD )。 A.学习是行为或行为潜能的变化 B.学习引起的变化是持久的 C.学习引起的变化是短暂的 D.学习是由反复经验引起的
教育心理学家的基本理论
教育心理学家的基本理论 1、行为学派(刺激——反应联结学习理论) 2、认知学派(认知结构学习理论) 3、掌握学习和指导学习理论 4、人本主义的学习理论 5、精神分析学派 一、行为学派(刺激——反应联结学习理论 1、桑代克 A:学习理论(三条基本学习规律)(P136) ①准备律 ②练习律——应用律、失用律 ③效果律 B:迁移 ①迁移一词的提出(P209) ②共同要素论(P215) C:1903年著《教育心理学》是教育学心理学成为独立学科的开始 D:1913年,将《教育心理学》扩展《教学心理学大纲》,共分为人的本性、学习心理、个别差异及原因。(P8) 2、巴甫洛夫——经典条件反射学习理论 A:消退(P140) B:恢复 C:类化(P140)——一朝被蛇咬,十年怕井绳 D:分化(P140) E:高级条件反射——刺激强化(P141) 3、斯金纳——操作条件反射学习理论 A:有机体行为分类(P142) ①应答性行为——经典条件反射 ②操作性行为——操作条件反射 B:操作条件反射主要规律(P142) ①假如一个操作发生后,接着给予强化刺激,那么这一类反应今后发生的概率就会增加。 ②由于行为效果的强化是使行为频率增加的根本原因,所以通过对有机体的有选择的强化,就可以使行为朝着所需要的方向发展。 C:程序教学(P157) ①小步子逻辑序列 ②要求学生作出积极反应 ③及时反馈 ④学生自定步调 ⑤低的错误率 4、班杜拉——社会学习理论(P143) A:观察式学习(模仿)(P143) “上行下效”、“耳濡目染”(P144)B:替代性强化(P143、149) “杀鸡儆猴”(P149)C:自我强化(P149)D:符号强化(P144) 二、认知学派(认知结构学习理论) 1、布鲁纳——发现学习理论(P158)1)、主动认知——认为学习是一个主动认知的过程。 2)、语言学习——语言学习是儿童心理发展的关键。 3)、学习过程——重视学习的过程。4)、学习结构——强调形成学习结构。5)、直觉思维——强调直觉思维的重要性。6)、内部激励——强调内部动机的重要性。7)、早期教育——强调基础学科的早期学习。 8)、信息提取——强调信息提取(记忆问题不是贮存,而是提取) 9)、发现学习——提倡发现学习。 ——以早期教育为起点,以开发智力为核心,以学科知识结构为基础,以发现学习为手段,以直觉思维为必备要素,以内部激励为动力的旨在培养科学精英的教学思想。
教育心理学章节习题 学习的基本理论
一、选择题:在每小题给出的四个选项中,只有一项是符合题目要求的,把所选选项前的字母填在题后的括号内。 1.首先打出行为主义心理学旗帜的是()。 A.巴甫洛夫 B.斯金纳 C.桑代克 D.华生 2.以下心理学家不属于认知心理学派的是()。 A.苛勒 B.斯金纳 C.布鲁纳 D.奥苏伯尔 3.布鲁纳认为,学生掌握学科的基本结构的最好方法是()。 A.建构法 B.发现法 C.顿悟法 D.接受法 4.程序性教学实际上是()理论在实践中的运用。 A.学习的操作性条件作用 B.观察学习
C.认知学习 D.认知同化 5.加涅的信息加工系统中的第二级是()。 A.感受器 B.感受登记 C.短时记忆 D.长时记忆 6.苛勒在研究黑猩猩的学习时采用的实验是()。 A.迷箱实验 B.迷津实验 C.叠箱实验 D.“三座山”实验 7.建构主义的理论流派中,在皮亚杰的思想之上发展起来的是()。A.社会建构主义 B.激进建构主义 C.信息加工建构主义 D.社会主义建构主义 8.建构主义强调,知识的特点具有()。 A.主观性 B.客观性 C.普遍适应性
D.永恒性 9.将符号所代表的新知识与学习者认知结构中已有的适当观念建立起非人为的和实质性的联系属于()。 A.机械学习 B.意义学习 C.接受学习 D.发现学习 10.在发现教学中,教师的角色是学生学习的()。 A.促进者和引导者 B.领导者和参谋 C.管理者 D.示范者 11.孩子哭闹着要买玩具,母亲对其不予理睬,这是()。 A.正强化 B.负强化 C.惩罚 D.消退 12.以下心理学家及其理论匹配不正确的一项是()。 A.奥苏伯尔——认知发现说 B.苛勒——完形一顿悟说 C.托尔曼——认知目的说 D.加涅——信息加工理论
山香2016年教育心理学第三章 学习的基本理论
第三章学习的基本理论 第一节学习概述 一、学习的含义 (一)广义的学习 1、广义学习的含义:人和动物在生活过程中,凭借经验而产生的行为/行为潜能的相对持久的变化。 2、产生广义学习的三个特征: (1)学习必须使个体产生行为或行为潜能的变化。 (2)这种变化是相对持久的。有些主体的变化,如疲劳,创伤等引起的变化是暂时的,经过一段时间或一旦条件改变就会自行消失,这种变化不能称作学习。 (3)这种变化是由反复经验而引起的。 (二)狭义的学习 1、狭义学习的含义:指人类的学习,指个体在社会生活实践中,以语言为中介,自觉地、积极主动地掌握社会、个体的经验的过程。 2、人类学习与动物学习的本质区别: (1)人的学习是掌握人类社会历史经验、科学文化知识,获得个体行为经验的过程。 (2)人的学习是在社会生活实践中,与他人的交往时,以语言的中介进行的。 (3 3 (1)学生学习的含义:在教师的指导下,有目的、有计划、有组织、有系统地进行的,是在较短的时间内接受前人所积累和科学文化知识,并以此来充实自己的过程。 (2)学生学习内容:①知识、技能和学习策略的掌握,②问题解决能力、创造性的发展,③道德品质和健康心理的培养。 (3)学生学习的特点:①以系统地掌握人类的间接经验为主;②在教师的指导下进行,有较强的计划性、目的性、组织性;③具有一定程度的被动性;④要促进学生全面发展:学生不但要学习知识技能,还要发展智能,培养行为习惯、道德品质和健康的心理。 二、学习的分类 (一)从学习的主体来说,学习可以分为:动物学习、人类学习和机器学习。 (二)按学习的意识水平,[美]心理学家阿瑟.雷伯将学习分为:内隐学习和外显学习。 (三)加涅的学习结果分类:认为学习结果就是各种习得的才能、本领。获得以下五种才能:言语信息、智慧技能、认知策略、态度、动作技能。 1、言语信息的学习:帮助学生解决“是什么”的问题。掌握以言语信息传递的内容,学习结果是以言语信息表现出来的。 2、智慧技能的学习:解决“怎么做”的问题,用以对外界的符号、信息进行处理加工。辨别技能是最基本的智慧技能,按不同的学习水平及其所包含的心理运算的复杂程度,依次为:辨别、概念、规则、高级规则 3、认知策略的学习:学习者用以支配自己的注意、学习、记忆和思维的有内在组织的才能,这种才能使得学习过程的执行控制成为可能。智慧技能指向外部环境,而认知策略指向学习者内部。 4、态度的学习:态度是通过学习获得的内部状态,这种状态影响着个人对某种事物、人物及事件所采取的行动。加涅提出三类态度:(1)儿童对家庭和其他社会关系的认识;(2)对某种活动所伴随的积极的喜爱情感;(3)有关个人品德的某些方面,如热爱国家等。 5、运动技能的学习:运动技能又称为动作技能,也是能力的一个组成部分。
教育心理学专题练习第三章学习的基本理论
第三章学习的基本理论 一、单选题 1.被誉为现代教育心理学奠基人的是()。 A桑代克 B.巴甫洛夫 C.斯金纳 D.布鲁纳 2.下列不属于学习引起的变化的是()。 A. 幼儿会喊爸爸、妈妈 B.青春期嗓音变化 C.骑车 D.会使用电脑 3学习对某种信号作出一般性和弥散性的反应是()学习。 A.刺激——反应 B.连锁 C.辨别 D.信号 4.属于巴甫洛夫的经典性条件反射的学习类型是( )学习。 A.刺激——反应 B.信号 C.概念 D.连锁 5.属于操作性条件反射的学习类型是( )学习。 A.信号 B.规则 C.解决问题 D.刺激——反应 6联合两个或两个以上的刺激——反应动作,以形成一系列动作联结的学习类型是()学习。 A. 连锁 B.概念 C.辨别 D. 刺激——反应 7.各类动作技能的形成都离不开()学习。 A.信号 B.规则 C.连锁 D.刺激——反应 8.对一系列类似的刺激分别作出适当的反应的学习是()学习。 A.连锁 B.概念 C.辨别 D.规则 9.()学习是指认识一类事物的共同属性,并对其抽象特征作出反应。 A.解决问题 B.概念 C.辨别 D.规则 10.把鲸鱼、象、狗等概括为“哺乳动物”,这属于()学习。 A.解决问题 B.概念 C.辨别 D.规则 11.理解“功=力×距离”这一公式,这是()学习。 A.信号 B.概念 C.辨别 D.原理 12.掌握教育学基本原理后,用之于解决教育中的实际问题,这是()学习。 A.解决问题 B.规则 C.概念 D.刺激——反应 13.()是调节和控制自己的注意、学习、记忆、思维和问题解决过程的内部组织起来的能力。 A.智慧技能 B.认知策略 C.动作技能 D.态度 14.()是使用符合与环境相互作用的能力。 A.智慧技能 B.认知策略 C.言语信息 D.态度 15.()表现为学会陈述观点的能力。 A.智慧技能 B.认知策略 C.言语信息 D.态度 16.()是对外的平稳而精确的操作能力。 A.智慧技能 B.认知策略 C.言语信息 D.动作技能 17.()表现为个体对人、对物或某些事件的意向。 A.智慧技能 B.认知策略 C.言语信息 D.态度 18.在试误学习的过程中,学习者对环境刺激作出反应后能获得满意的结果时,其联结就会增强,这是()。 A.效果律 B.练习律 C.准备律 D.强化律 19.在试误学习的过程中,刺激与反应的联结,如果练习运用,联结的力量逐渐增大,如果不运用,则逐渐减小,这是( ).。
教育心理学-第三章 学习的基本理论 - 副本
《教育心理学》学习的基本理论 一、不定项选择题 1.下列属于学习的现象是()。 A.吃了酸的食物流唾液B.了解低碳生活并付诸行动C.蜘蛛织网D.儿童模仿电影中人物的行为2.一名学生能够运用三角形的面积公式解决一个他从来没有见到过的三角形的面积,这表明他已经具备了()。 A.言语信息B.动作技能C.智慧技能D.认知策略E.态度 3.某位学生近一段及时完成作业,老师告诉他放学后不必再留在教室里完成作业了,此后该生继续按时完成作业,这时该生受到了()。 A.正强化B.负强化c.正惩罚D.负惩罚 4.奥苏贝尔提倡的一种学习类型是()。 A.有意义-发现学习B.有意义-接受学习C.机械-接收学习D.机械-发现学习 5.引导学生分辨勇敢和鲁莽、谦让和退缩属于刺激()。 A.获得B.消退C.分化D.泛化 6.“孟母三迁”终使孟子成才,能够有效解释该现象的理论是()。 A.认知学习理论B.社会学习理论C.人本主义理论D.建构主义理论 7.学生学习“功=力×距离”,这种学习属于()。 A.辨别学习B.符号学习C.概念学习D.规则或原理学习 8.()指教材被分成若干小步子,学生可自定学习步调,让学生对所学内容进行积极反应,并给予及时强化和反馈使错误率最低。 A.程序教学B.组织教学C.个别化教学D.指导教学 9.()强调学习的主动性和认知结构的重要性,主张教学的最终目标是促进学生对学科结构的一般理解。 A.布鲁纳B.班杜拉C.桑代克D.巴甫洛夫 10.布鲁纳认为任何知识结构都可以用适合形式呈现,以下不属于他提出的呈现方式的一项是()。A.动作表象B.图像表象C.符号表象D.情感表象 11.最初主张S-R联结存在意识中介的心理学家或心理学流派是()。 A.格式塔学派B.布鲁纳C.斯金纳D.托尔曼 12.人和动物一旦学会对某一特定的条件刺激作出条件反应以后,其他与该条件刺激相类似的刺激也能诱发其条件反应,称为()。 A.刺激分化B.消退C.刺激泛化D.获得 13.操作性条件作用论的提出者是()。 A.桑代克B.苛勒C.斯金纳D.巴甫洛夫 14.布鲁纳的学习论是()。 A.完形顿悟说B.有意义接受学习论C.认知结构学习论D.建构主义 15.观察者看到榜样受到强化而如同自己也受到强化一样,这称为()。 A.外部强化B.自我强化C.直接强化D.替代强化 16.“一朝被蛇咬,十年怕井绳”,这种现象是指()。
教育心理学考试重点第三章学习的基本理论+实战演练
教育心理学考试重点提示:第三章学习的基本理论 重点提示 统观近几年全国各省的教师资格认证教育心理学考试,本章的考查重点是: (1)学习的定义。 (2)学习的主要理论: 尝试一错误学习的基本规律。 经典性条件反射的基本规律。 布鲁纳的认识一结构学习论。 当今建构主义学习理论的基本观点。 考纲链接 1.学习的实质与特征: (1)学习的概念。广义的学习指人和动物在生活过程中,凭借经验而产生的行为或行为潜能的变化。狭义的学习指人类的学习,是在社会生活实践中,以语言为中介,自觉地、积极主动地掌握社会的和个体的经验的过程。 (2)人类学习与动物学习的区别。首先,人的学习除了要获得个体的行为经验外,还要掌握人类世世代代积累起来的社会历史经验和科学文化知识;其次,人的学习是在改造客观世界的生活实践中,在与其他人的交往过程中,通过语言的中介作用而进行的;此外,人的学习是一种有目的的、自觉的、积极主动的过程。 2.学生的学习:是在教师的指导下,有目的、有计划、有组织、有系统地进行,在较短时间内接受前人所积累的科学文化知识,并以此来充实自己的过程。 3.学习内容:一是知识、技能和学习策略的掌握;二是问题解决能力和创造性的发展;三是道德品质和健康心理的培养。 4.加涅关于学习层次和学习结果的分类: (1)加涅关于学习层次分类:信号学习、刺激-反应学习、连锁学习、语言联结学习、辨别学习、概念学习、规则或原理学习、解决问题学习。 8.认知学习理论: (1)完形-顿悟说:由苛勒提出,主要观点:学习是通过顿悟实现的;学习的实质在于构造完形。 (2)认知-结构学习论:由布鲁纳提出。他主张学习的目的在于以发现学习的方式,使学科的基本结构转变为学生头脑中的认知结构。 10.建构主义学习理论。基本观点: (1)知识观。知识并不是问题的最终答案;知识并不能精确地概括世界的法则;知识不可能以实体的形式存在于具
《教育心理学》分章强化题三:第三章学习的基本理论
《教育心理学》分章强化题三:第三章学习的基本理论 一、选择题 1.下列现象可以归入到学习中的现象有()。 A.事故后体会到交通法规的重要性 B.疲劳时记忆力下降 C.乳儿抓住碰到的东西 D.青春期少年的嗓音变化 2.新生渐渐知道铃声代表上课,这属于()。 A.信号学习 B.辨别学习 C.概念学习 D.言语联结学习 3.各种动作技能的学习,都离不开()。 A.连锁学习 B.言语联结学习 C.解决问题的学习 D.信号学习 4.使用符号与环境相互作用的能力属于()。 A.认知策略 B.言语信息 C.动作技能 D.智慧技能 5.在试误学习过程中,当刺激与反应之间的联结不准备实现时,实现则感到烦恼,这符合()。
A.练习律 B.准备律 C.效果律 D.联结律 6.家长对考试成绩好的孩子给予物质奖励是()。 A.正强化 B.负强化 C.消退 D.惩罚 7.一个学生上课讲话,老师要他写“我上课讲话,真丑”1000遍,这属于()。 A.正强化 B.负强化 C.惩罚 D.替代强化 8.认为学习是个体利用本身的智慧与理解力对情境及情境与自身关系的顿悟的学说为()。 A.认知-结构学习论 B.有意义接受学习论 C.完形-顿悟说 D.建构主义学习论 9.有意义接受学习论的提出者是()。 A.苛勒 B.布鲁纳 C.斯金纳 D.奥苏伯尔 10.将符号所代表的新知识与学习者认知结构中已有的适当观念建立起非人为和实质性的联系的学习是()。 A.接受学习 B.发现学习 C.机械学习 D.意义学习 11.认为知识并不是对现实的准确表征,它只是一种解释、一种假设的理论为(或认为学生的学习不仅是对新知识的理解,而且是对新知识的分析、检验和批判的力量是)()。
教育心理学第三章 学习的基本理论
第三章学习的基本理论 1)什么是学习?人类学习和动物学习有什么本质的区别? 广义的学习指人和动物在生活过程中,凭借经验而产生的行为或行为潜能的相对持久的变化。 定义说明:1、学习表现为行为或行为潜能的变化。2、学习所引起的行为或行为潜能的变化是相对持久的。3、学习是由反复经验而引起的。 狭义的学习指人类的学习,指个体在社会生活实践中,以语言为中介,自觉地、积极主动地掌握社会的和个体的经验的过程。 人类学习vs. 动物学习有本质的区别: 1. 人的学习除了要获得个体的行为经验外,还要掌握人类世世代代积累起来的社会历史经验和科学文化知识。 2. 人的学习是在改造客观世界的生活实践中,在与其他人的交往过程中,通过语言的中介作用而进行的。 3. 人类的学习是一种有目的、自觉的、积极主动的过程。 2)学生的学习的内容和特点什么?(人类学习和学生学习有什么区别) 含义:学生的学习是人类学习中的一种特殊形式,它是在老师的指导下,有目的、有计划、有组织、有系统的进行的,是在较短的时间内接受前人所积累的文化科学知识,并以此来充实自己的过程。 学习内容:一是知识、技能和学习策略的掌握;二是问题解决能力和创造性的发展;三是道德品质和健康心理的培养。 人类学习和学生学习之间是一般与特殊的关系,学生的学习既与人类的学习有共同之处,但又有其特点:①以间接经验的掌握为主线;②具有较强的计划性、目的性和组织性;③具有一定程度的被动性。 3)加涅按照学习结果的不同把学习分成那些类型? 1、言语信息, 2、智慧技能, 3、认知策略, 4、态度, 5、运动技能。 4)简述奥苏贝尔对学习的分类 根据两个维度对认知领域的学习分类:一个是学习进行的方式,分为接受学习和发现学习;另一个维度是学习材料与学习者原有知识的关系,可分为机械学习和有意义学习。这两个维度互不依赖,彼此独立。并且每一个维度都存在许多过渡形式。 5)我国心理学家对学习是怎样分类的? 分为知识的学习、技能的学习和行为规范的学习三类。 6)联结学习理论的基本观点有哪些?(行为主义) 联结学习理论认为:一切学习都是通过条件作用,在刺激(S)和反应(R)之间建立直接联结的过程。强化在刺激—反应之间的建立过程中起着重要作用。在刺激—反应联结之中,个体学到的是习惯,而习惯是反复练习和强化的结果。习惯一旦形成,只要原来的或类似的刺激情境出现,习得的习惯性反应就会自动出现。 7 桑代克是美国著名心理学家,他采用实证主义的取向,使教育心理学研究走向了科学化的道路,是科学教育心理学的开创者,是第一个系统论述教育心理学的心理学家,被称为“现代教育心理学之父”。是最早用动物实验来研究学习规律的心理学家。 (一)经典实验:猫开笼取食的实验。 (二)学习的联结说(又叫试误说):通过这类实验,桑代克提出学习不是建立观念之间的联结,而是建立刺激—反应(S—R)联结,即在一定的刺激情境与某种正确反应之间形成联结,其中不需要观念或思维的参与。这种刺激—反应联结主要是通过尝试错误、
教育学心理学主要理论及代表人物
昆体良古罗 马 1.《雄辩术原理》世上第一部研究系统的教学方法论著,被公认为是西方教育史上的伟大 教育家,是第一位教学理论家和教学法专家。 2. 最早提出分班教学的思想 杜威美国1.提出实用主义教育学,杜威出版《民主主义与教育》《经验与教育》,克伯屈出版《设计教学法》,提倡活动课。 思想:强调儿童的主体地位:①教育即生活,教育即生长②教育社会化③做中学④教育即经验的不断改造。以儿童为中心,反对教师中心论 2.现代教育代言人现代教育的主要特点是民主 3.教育无目的论“教育是一个社会过程。” 4.问题的解决杜威的五步模式①困惑②诊断③假设④推断⑤验证 5.问题解决步骤的五步模式⑴疑难⑵分析⑶假设⑷检验和评价⑸结论 桑代克 美 国 1.1903年出版西方第一本《教育心理学》,是教育心理学体系的创始,标志着教育心理学 称为一门独立的学科。 2.学习理论之联结派的学习理论——联结学习:尝试-错误说(小猫“迷箱”试验) 试误成功条件:练习律、准备律、效果律 3.教育心理学体系(现代教育心理学)和联结主义学习心理学创始人,被誉为教育心理学 之父 4. 学习迁移理论之联结主义的相同要素说(代表人物:桑代克、伍德沃斯) 桑代克:相同要素说,即学习上的迁移是相同联结的转移。 伍德沃斯:共同成分说,即两种学习活动含有共同成分,则发生迁移,学习也就更容易。 以刺激——反应联结理论为基础。只有当学习情景和迁移情景存在共同成分时,才能产生迁移。即材料相似性是决定迁移的条件 5.现代教育测验之父 6.智力水平越高,迁移越大。 7.问题解决理论之试误说,又称联结说——(猫“迷箱”实验) 问题的解决过程是刺激情境与适当反应之间的联结完成的,联结的建立是通过尝试错误完成的。 贾德美国1.学习迁移理论之机能心理学的经验泛化说—“水下击靶”实验 他认为一个人对他的经验进行了概括,就可以完成从一个情境到另一个情境的迁移。概括就等于迁移,原理、法则等概括化的理论知识对迁移作用很大。 沃尔夫德国 1.学习迁移理论之官能心理学的形式训练说 他把迁移的实质理解为新的官能经训练而发展,认为促进迁移的条件与学习内容无大关系而偏重于形式。 魏特海默 苛勒德国 1.学习理论之认知派学习理论——格式塔的顿悟学习理论(黑猩猩取香蕉实验):学习是 一个顿悟的过程,是突然察觉到解决问题的办法。主要代表人物:魏特海墨、科夫卡和克勒 2.学习迁移理论之格式塔学派的关系转换说(代表人物:苛勒)—“小鸡啄米实验” 强调“顿悟”是迁移的一个决定因素。强调个体的作用,愈能加以概括化,愈易产生迁移。 3.问题解决理论之顿悟说(苛勒)——黑猩猩取香蕉实验 4.格式塔心理学(完形心理学)创始人魏特海墨、科夫卡和克勒研究内容是意识体验, 论点“整体大于部分之和” 解决问题时从整体把握全部问题情境和认知结构的豁然改组,而不是一次次经验的积累。 反对元素分析认为每一个心理现象都是一个整体是一个格式塔是一个完形 学习的实质在于构造完型,刺激与反应之间的联系而需要意识作为中介 布鲁美国1.结构化教材和发现学习模式(明确结构,掌握课题,提供资料→建立假说,推测答案→验证→做出结论) 2.领导美国20C60y的结构主义课程改革,主张突出学科基本结构,让学生通过发现法学习,重视智力发展(动机原则、结构原则、程序原则、反馈原则) 3.学习理论之现代认知学习理论——认知发现理论 强调认知学习和认知发展,提倡发现学习。学习的核心内容是各门学科的基本知识结构。3教学方法:发现学习,新课标中也叫“探究学习”。即教师提出课题和一定的材料,引导学生自己进行分析、综合、抽象、概括等一系列活动,最后得到学习结果。 4.提出假设考验说,研究人工概念的形成(人需要利用已有的知识主动提出一些可能的假设,即猜想这个概念是什么)——人工概念是认为的、在程序上模拟的概念,这种方法最早是赫尔于1920年首创的。 5.强调非特殊成分的迁移,也叫普遍迁移。即学习了基本的普遍的概念或原理,可作为学
教育心理学主要理论知识
第一章做合格教师 第一部分主要理论知识 1.合格教师心理素质 教师心理素质是教师在专业发展过程中,在心理过程和个性心理特征两方面所表现出来的本质特征。 教师的心理素质包括如下方面,即教师的智力素质、教师的情感素质、教师意志素质、教师的教育教学素质、教师的人格素质、教师的信念。 2、教师的智力素质 教师的智力是从事教育工作应具备的基本心理素质,是教师从事教育教学工作的心理基础。教师的智力素质表现在以下方面: (1)敏锐的观察力(2)良好的记忆力(3)丰富的想象力⑷多方位的立体思维能力 ⑸注意分配的能力 3、教师的情感素质特点 教育过程是师生情感交流的过程,教育工作最大的特点就是以情感人。 (1)成熟而稳定的情感(2)爱的情感:对教育事业的热爱、对学生的热爱、对所教学科的热爱 4、教师的意志特点 (1)实现教育目的的自觉性(2)克服困难的坚韧性(3)选择教育决策的果断性(4)解决矛盾的沉着自制性 4.教师的教育能力素质 因材施教的教育能力、获取信息的能力、独创能力、教育科研能力、心理教育能力、教育机智 5.教师的教学素质:包括教师的知识结构与教学能力。 6.教师的知识结构 教师的知识水平是其从事教学工作的前提条件。根据有关专家的研究,教师的知识结构可由三方面组成,分别为本体性知识、实践性知识和条件性知识。 7.本体性知识。 教师职业的本体性知识是教师所具有的特定的学科知识,如语文知识、数学
知识等,也即人们所熟知的科目知识。 林崇德等人的研究表明,教师的本体性知识与学生成绩之间几乎不存在统计上的关系。 由于学科不同,本体性知识的具体内容是不同的。仅仅从一般意义上说,教师的本体性知识应包括四个方面:教师应对学科的基础知识有广泛而准确的理解,熟练掌握相关的技能、技巧;教师要基本了解与所教学科相关的知识点、相关性质以及逻辑关系;教师需要了解该学科的发展历史和趋势,对于社会、人类发展的价值以及在人类生活实践中的多种表现形态;教师需要掌握每一门学科所提供的独特的认识世界的视角、域界、层次及思维的工具与方法等。 8.实践性知识 教师的实践性知识是教师在开展有目的的教育教学活动过程中解决具体问题的知识,是教师教育教学经验的积累和提炼,它主要来源于课堂教育教学情景之中和课堂内外的师生互动行为,带有明显的情景性、个体性,体现出教师个人的教育智慧和教学风格。研究表明,教龄对教师的实践性知识存在着显著影响,教师的实践性知识水平随着教龄的增加而逐步上升。 9.条件性知识 教师的条件性知识是指教师所具有的教育学与心理学知识。条件性知识是:个教师成功教学的重要保障,而这种知识是目前广大的一般教师所普遍缺乏的。教师的条件性知识分为三个方面,即学生身心发展的知识、教与学的知识和学生成绩评价的知识。 正如杜威指出的那样,科学家的学科知识与教师的学科知识是不一样的,教师必须把学科知识“心理学化”,以便学生能理解。 10.教师的教学能力 教师的教学能力是教师从事教学活动,完成教学任务的能力,是教师专业能力的重要方面。 ⑴教学认知能力⑵教学设计的能力 ⑶教学操作能力:①表达能力②课堂组织管理能力③运用现代教育技术的能力
相关文档
- 教师考试必备-课件-教育心理学第2章-学习的基本理论
- 教育学教育心理学理论及代表人物
- 《教育心理学》 第二章 学习的基本理论
- 教育心理学的基本理论
- 教育心理学的基本理论
- 教育心理学基本理论知识
- 教育心理学章节习题 学习的基本理论
- 教育心理学-第三章 学习的基本理论 - 副本
- 教育心理学主要理论知识
- 教育心理学学习的基本理论
- 《教育心理学》 学习的基本理论
- 教育心理学的基本理论共62页
- 教育心理学第三章 学习的基本理论
- 教育心理学的各种理论
- 教育心理学家的基本理论
- 教育心理学专题练习-第三章-学习的基本理论
- 教育学心理学主要理论及代表人物
- 教育心理学第三章学习的基本理论 ppt课件
- 教育心理学第三章学习的基本理论
- 教育心理学专题练习第三章学习的基本理论
