Matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD)

Review
Matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD)☆
Steven A.Barker ?
School of Veterinary Medicine,Department of Comparative Biomedical Science,Louisiana State University,Baton Rouge,Louisiana 70803,United States
Received 5May 2006;accepted 30June 2006
Abstract
A review of the many uses of matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD)in the extraction and analysis of a variety of compounds from a range of samples is provided.Matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD)has found particular application as a somewhat generic analytical process for the preparation,extraction and fractionation of solid,semi-solid and/or highly viscous biological samples.Its simplicity and flexibility contribute to it being chosen over more classical methods for these purposes.MSPD is based on several simple principles of chemistry and physics,involving forces applied to the sample by mechanical blending to produce complete sample disruption and the interactions of the sample matrix with a solid support bonded-phase (SPE)or the surface chemistry of other solid support materials.These principles are discussed as are the factors to be considered in conducting a MSPD extraction.?2006Elsevier B.V .All rights reserved.
Keywords:Matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD);Solid phase extraction (SPE);Drug analysis;Tissue analysis;Food analysis
Contents
1.Introduction..............................................................151
2.
MSPD extraction ...........................................................1542.1.Factors to consider in performing a MSPD extraction ....................................1543.MSPD and SPE............................................................1554.Conclusions..............................................................155References .......................
......
(156)
1.Introduction
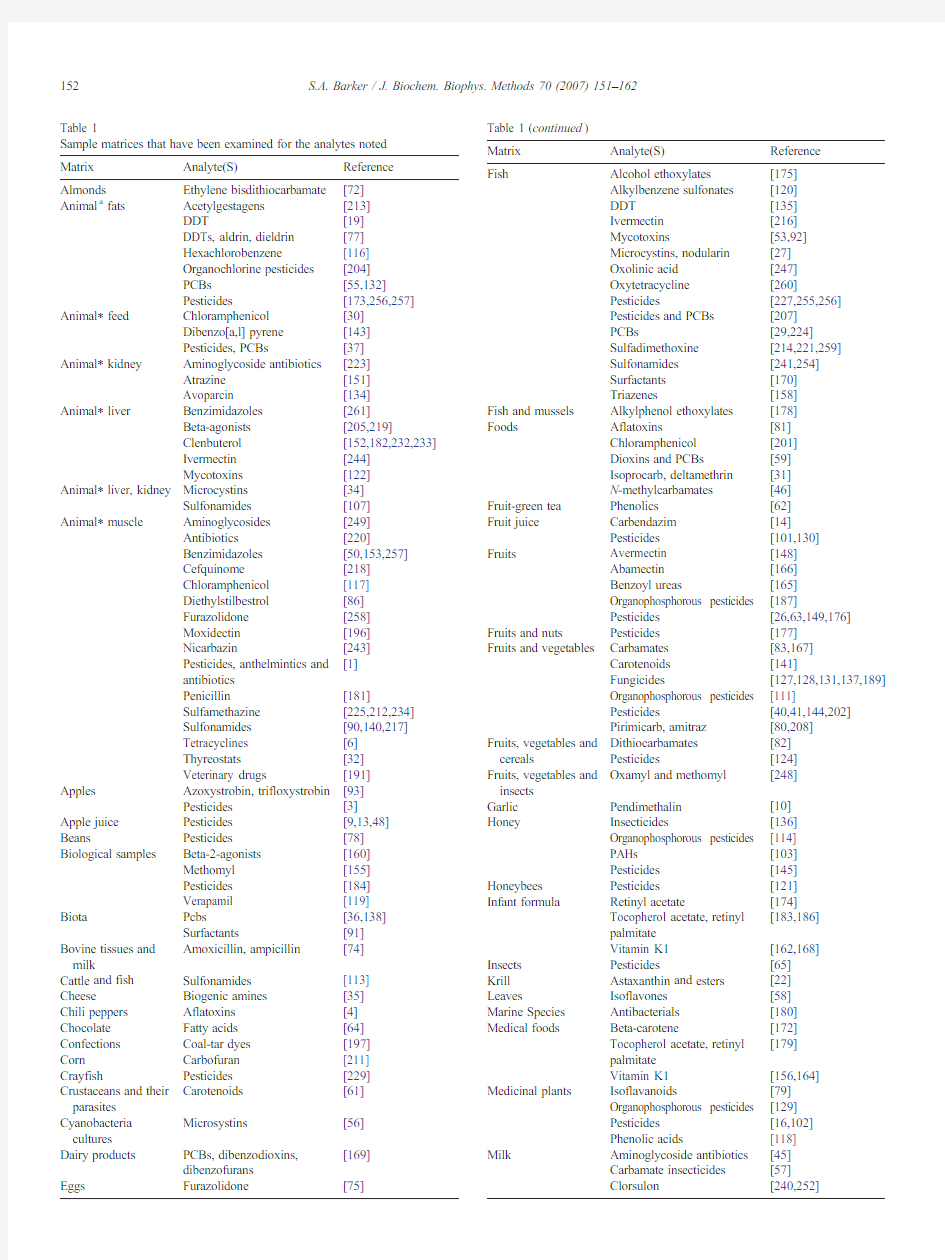
Since its introduction in 1989[1],matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD)has been cited as the extraction method employed in over 250publications [1–262].It has proven to be an efficient and somewhat generic technique for the isolation of a wide range of drugs,pesticides,naturally
occurring constituents,and other compounds from a wide variety of complex plant and animal samples (Table 1).MSPD was patented in 1993[226]and its many uses have been extensively reviewed [52,76,110,133,139,157,159,161,163,190,192,199,200,215,222,228,230,231,236,237,245,246,251].Matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD)has found particular application as an analytical process for the preparation,extraction and fractionation of solid,semi-solid and/or highly viscous biological samples.Its simplicity and flexibility have been cited as contributing to it being chosen over more classical methods for these purposes.Indeed,MSPD is based on several simple principles of chemistry and physics,involving forces applied to the sample by mechanical blending to
produce
J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods 70(2007)151–
162
https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,/locate/jbbm
☆
Submitted as a review to the Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods at the invitation of Dr.Eric Heftmann for the “Special Issue on Sample Preparation ”.
?Tel.:+122550783602;fax:+12255783086.E-mail address:sbarker@https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html, .0165-022X/$-see front matter ?2006Elsevier B.V .All rights reserved.doi:10.1016/j.jbbm.2006.06.005
Table1
Sample matrices that have been examined for the analytes noted
Matrix Analyte(S)Reference Almonds Ethylene bisdithiocarbamate[72]
Animal a fats Acetylgestagens[213]
DDT[19]
DDTs,aldrin,dieldrin[77]
Hexachlorobenzene[116]
Organochlorine pesticides[204]
PCBs[55,132]
Pesticides[173,256,257] Animal?feed Chloramphenicol[30]
Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene[143]
Pesticides,PCBs[37]
Animal?kidney Aminoglycoside antibiotics[223]
Atrazine[151]
Avoparcin[134]
Animal?liver Benzimidazoles[261]
Beta-agonists[205,219]
Clenbuterol[152,182,232,233]
Ivermectin[244]
Mycotoxins[122]
Animal?liver,kidney Microcystins[34]
Sulfonamides[107]
Animal?muscle Aminoglycosides[249]
Antibiotics[220]
Benzimidazoles[50,153,257]
Cefquinome[218]
Chloramphenicol[117]
Diethylstilbestrol[86]
Furazolidone[258]
Moxidectin[196]
Nicarbazin[243]
Pesticides,anthelmintics and
antibiotics
[1]
Penicillin[181]
Sulfamethazine[225,212,234]
Sulfonamides[90,140,217]
Tetracyclines[6]
Thyreostats[32]
Veterinary drugs[191]
Apples Azoxystrobin,trifloxystrobin[93]
Pesticides[3]
Apple juice Pesticides[9,13,48]
Beans Pesticides[78]
Biological samples Beta-2-agonists[160]
Methomyl[155]
Pesticides[184]
Verapamil[119]
Biota Pcbs[36,138]
Surfactants[91]
Bovine tissues and
milk
Amoxicillin,ampicillin[74]
Cattle and fish Sulfonamides[113]
Cheese Biogenic amines[35]
Chili peppers Aflatoxins[4]
Chocolate Fatty acids[64] Confections Coal-tar dyes[197]
Corn Carbofuran[211]
Crayfish Pesticides[229] Crustaceans and their
parasites
Carotenoids[61]
Cyanobacteria
cultures
Microsystins[56]
Dairy products PCBs,dibenzodioxins,
dibenzofurans
[169]
Eggs Furazolidone[75]Table1(continued)
Matrix Analyte(S)Reference
Fish Alcohol ethoxylates[175]
Alkylbenzene sulfonates[120]
DDT[135]
Ivermectin[216]
Mycotoxins[53,92]
Microcystins,nodularin[27]
Oxolinic acid[247]
Oxytetracycline[260]
Pesticides[227,255,256]
Pesticides and PCBs[207]
PCBs[29,224]
Sulfadimethoxine[214,221,259]
Sulfonamides[241,254]
Surfactants[170]
Triazenes[158]
Fish and mussels Alkylphenol ethoxylates[178]
Foods Aflatoxins[81]
Chloramphenicol[201]
Dioxins and PCBs[59]
Isoprocarb,deltamethrin[31]
N-methylcarbamates[46]
Fruit-green tea Phenolics[62]
Fruit juice Carbendazim[14]
Pesticides[101,130]
Fruits Avermectin[148]
Abamectin[166]
Benzoyl ureas[165]
Organophosphorous pesticides[187]
Pesticides[26,63,149,176] Fruits and nuts Pesticides[177]
Fruits and vegetables Carbamates[83,167]
Carotenoids[141]
Fungicides[127,128,131,137,189]
Organophosphorous pesticides[111]
Pesticides[40,41,144,202]
Pirimicarb,amitraz[80,208]
Fruits,vegetables and
cereals
Dithiocarbamates[82]
Pesticides[124]
Fruits,vegetables and
insects
Oxamyl and methomyl[248]
Garlic Pendimethalin[10]
Honey Insecticides[136]
Organophosphorous pesticides[114]
PAHs[103]
Pesticides[145]
Honeybees Pesticides[121]
Infant formula Retinyl acetate[174]
Tocopherol acetate,retinyl
palmitate
[183,186]
Vitamin K1[162,168]
Insects Pesticides[65]
Krill Astaxanthin and esters[22]
Leaves Isoflavones[58]
Marine Species Antibacterials[180]
Medical foods Beta-carotene[172]
Tocopherol acetate,retinyl
palmitate
[179]
Vitamin K1[156,164]
Medicinal plants Isoflavanoids[79]
Organophosphorous pesticides[129]
Pesticides[16,102]
Phenolic acids[118]
Milk Aminoglycoside antibiotics[45]
Carbamate insecticides[57]
Clorsulon[240,252]
152S.A.Barker/J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods70(2007)151–162
complete sample disruption and the interactions of the sample matrix with a solid support bonded-phase (SPE)or the surface chemistry of other solid support materials.
In its original conception,the blending of a bonded-phase [such as octadecylsilyl (ODS)-derivatized silica (C 18)]solid support material with a biological sample is seen as acting as both an abrasive,producing shearing and grinding forces that induce disruption of the sample architecture,and as a “bound ”solvent that assist in accomplishing complete sample disruption and dispersion.In this manner,the sample is dispersed over the surface of the bonded-phase support material,producing,through hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions of the various components,a unique mixed-character phase for conducting target analyte isolation.Indeed,blended samples (muscle tissue and ODS-silica support)have been examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM)and show that sample architecture is completely disrupted and that sample matrix components are,apparently,evenly distributed over the surface of the bonded-phase/support,forming an observable layer of approximately 100um in thickness,similar to that of some micelle or membrane bilayers [1].More recently,many applications of MSPD have involved the blending of samples with under-ivatized silicates (silica gel,sand,etc.)[for example,see 49,85,74,113,121,130]or other organic (graphitic fibers)[19,82]or inorganic (Florisil,alumina,etc.)[10,77,138,140]solids which cause sample disruption but do not,apparently,possess the same dispersive properties [159,237].
MSPD has found favor in its many applications because it eliminates most of the complications of performing classical liquid –liquid and/or solid phase extractions of solid and semi-solid samples,particularly complex biological samples.Indeed,all classical forms of liquid chromatography require that the sample be applied in a solubilized state to the head of the column.To accomplish this,the overall method must include steps to render the sample and its components into a non-viscous,particulate-free and relatively homogeneous liquid state.While many biological fluids,such as urine or blood plasma or serum,can be applied to columns directly,most other samples are not directly applicable to SPE,particularly the solids and semi-solids which are derived from biological origins.Such samples may be obtained from animal tissues or vegetable material and consist of a non-homogeneous array of fat and/or other tissues,such as fiber and pulp in the case of plants.
Thus,classical approaches for the preparation of solid or semi-solid samples for chromatography usually consist of
Table 1(continued )Matrix Analyte(S)
Reference Milk
Cypermethrin
[73]Doxycycline,fumequine [67]Enrofloxacin,ciprofloxacin [20]Fenbendazole [193]Ivermectin
[210]Organochlorine and phosphorous pesticides [206]PCBs and organochlorine pesticides [142]
Tetracyclines [262]Milk,muscle,organ tissues Methomyl [198]Pesticides [185]Sulfonamides [25]Milk,cheese,meat Tetracyclines
[188]Milk and eggs Alkylphenols,bisphenol A [24]Sulfonamides [106]Milk,eggs,avacados Pesticides [38]Milk,eggs,tissues Sulfonamides
[242]Milk,infant formula Vitamins A And E [60]Milk and meat Sulfonamides [253]Milk and urine Thyreostats
[23]Mycobacteria Biologic compounds [97]
Natural products [235,239,250]Okra Pesticides
[51]Olive oil
Benzo(a)pyrene
[84]Organophosphorous pesticides [87]Terbuthylazine [11]Olives,olive oil Pesticides [44]
Oranges Pesticides [66,125,147,203]Thiabendazole [69]Oysters
Pesticides
[238]Pistachio nuts diazinon,ethion [94]Plants
Aflatoxins [96]Alkylphenols [115]Carbendazin [85]Natural products [112]Pesticides [195]Rat feces Bilastine [146]Rice
Carbofuran [105]Isoprocarb [39]Pesticides
[54]Root bark Flavanones,xanthones [49]Sewer sludge,sediments Phenolics
[2]Soil
Fenpropathrin [99]Pesticides [12,104]Phenthoate [123]Uniconazole [109]Spinach
Carotenoids [25,108]Spinach and retina Carotenoids
[171]Lutein and zeaxanthin [154]Sugar cane Simazine [71]Starfish Saponins [150]Tea Caffeine [33]Pesticides [15]Tobacco Pesticides [18]Tomato
Glyposate,
aminomethylphosphonic acid [21]Tomato juice
Pesticides [100]Toothpaste,gingival tissues Tocopherols [126]Vegetables
Carotenoids [47]Pesticides [194]Pyrethroids [209]Tebufenpyrad
[42]
(continued on next page)
Table 1(continued )Matrix
Analyte(S)Reference Vegetable and fruit juices Herbicides [70]Wheat grain
Carbindazim [88]Carbofuran [89]Fungicides
[7]
DDT,1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p -chlorophenyl)ethane;PCBs,polychlorinated biphenyls;PAHs,polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.a
Excluding marine species.
153
S.A.Barker /J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods 70(2007)151–162
various combinations of methods of mincing,shredding, grinding,pulverizing and/or pressurizing of the sample to disrupt sample architecture.This step is usually followed by the addition of solvents,acids,bases,buffers,abrasives,salts, detergents and/or chelators in an effort to more completely disrupt cellular and architectural composition and initiate the extraction and fractionation of various sample components from the analyte(s)of choice.At this point in the preparation the sample may need to be filtered,centrifuged or otherwise treated to separate sample“debris”prior to further processing.In some of these steps,the analyst may encounter the creation of often intractable emulsions as a consequence of these actions.In many cases repeated centrifugation,re-extraction and sample manipulation may be required to render the sample suitable for application to an SPE column.
MSPD has been found to eliminate these complications in dealing with solid and semi-solid samples.This is achieved by literally combining the sample directly with the bonded-phase or other solid support,simultaneously accomplishing several steps in the more classical approach to sample preparation described above while producing a unique SPE extraction/ fractionation column for isolation of target analytes.
2.MSPD extraction
Thus,in the MSPD process,a sample(liver,fruit,etc.)is
placed in a glass or agate mortar containing an appropriate bonded-phase or other solid support material,such as octadecylsilyl(ODS)-derivatized silica(C18)or other suitable support.The solid support and sample are manually blended together using a glass or agate pestle,a step that takes about 30s.Internal standards or spikes may be added prior to this step. The blended material is then transferred and packed into a column suitable for conducting sequential elution with solvents.
The entire length of the column consists of blended sample components and their distribution in the bonded-phase and support,producing a new phase that exhibits unique character for sample fractionation.In this manner,an appropriate solvent or a sequence of solvents may be used to clean the column or directly isolate the compound(s)of choice.Co-columns, consisting of other solid phase or chromatographic supports, may also be incorporated into the column to assist in analyte isolation or further clean-up(Fig.1).
2.1.Factors to consider in performing a MSPD extraction
Several factors that have been examined for their effect in conducting MSPD extractions include1)the effect of average particle size diameter.As expected,very small particle sizes(3–10μm)lead to extended solvent elution times and the need for excessive pressures or vacuum to obtain adequate flow.A blend of silicas possessing a range of particle sizes(40–100μm) works quite well,and such materials also tend to be less expensive.2)Non-end-capped vs.end-capped materials or materials having a range of carbon loading(8–18%),3)the character of the bonded-phase.Depending on the polarity of the phase chosen,rather dramatic effects on the results may be observed.Applications requiring a lipophilic bonded-phase may use C18and C8materials interchangeably.4)The use of underivatized silica or other solid https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,e of non-modified or underivatized solids,such as sand,to blend samples do not work in exactly the same manner as originally described for bonded-phase solid supports,such as ODS.However,the same basic principles will apply;abrasion and sample disruption will occur during the blending process.However, the further disruption of the sample and component dispersion will only occur to the degree that the components interact with the chemical characteristics of the particulate surface and each other.All surfaces have a definable chemistry and many substances,including a variety of minerals,may well serve to enhance isolation of specific compounds or classes of compounds and may even be blended together to form unique interactions to accomplish desired results.To date,silica-based support materials(derivatized silica,silica gel,sand,Florisil) have been almost exclusively reported for use in MSPD.One recent report has demonstrated the use of an activated carbon fiber for the isolation of dithiocarbamates from fruits, vegetables and cereals[82]while another has reported the isolation of DDT[1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl]from fat samples[19].Two others have reported the use of polymeric materials(XAD-7)for sample dispersion and extraction of atrazine[151]or the antibiotic avoparcin[134].The blending of samples with alumina has also been used in several extraction methods[10,77,140].The further use and effect of synthetic polymer-based solid supports and of granular minerals is a subject for further study,particularly of supports that possess unique surface and/or pore chemistries,such as hydrophobic interaction supports.For silica-based materials,
however, Fig.1.Steps in a typical MSPD extraction.
154S.A.Barker/J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods70(2007)151–162
studies have shown that the pore size is of minor importance in MSPD.This effect could vary with the sample and should, nonetheless,be considered.5)the best ratio of sample to solid support material.The most often applied is1to4,respectively, but has varied from application to application.Most protocols use lipophilic bonded-phase(C18,C8)materials,blending2.0g of solid support with0.5g of sample.This ratio is dependent on the application and must be examined as a major variable during method development.Both smaller and greater ratios have been used successfully.6)Chemical modification of the matrix or matrix solid support blend.Addition of chelating agents,acids, bases,etc.at the time of blending affect the distribution and elution of target analytes from the sample.The elution profile of matrix components is likewise affected.7)The optimum choice of elution solvents and the sequence of their application to a column.Elution solvent sequence attempts to isolate the analyte or further clean the column of interfering substances with each solvent step.MSPD columns permit isolation of different polarity analytes or entire chemical classes of compounds in a single solvent or in differing polarity solvents passed through the column,making MSPD amenable to conducting multi-residue isolation and analysis on a single sample.Several recent studies have reported the use of hot water as an eluting solvent as well as the addition of pressure,a process known as pressurized-liquid extraction(PLE)or accelerated solvent extraction(ASE)[12,27,45,57,83,106,107,134].Such applica-tions demonstrate the potential to make extraction methods based on MSPD free of hazardous solvents and even less expensive to perform.Preconditioning of the support materials used for any MSPD application enhances analyte recovery and speeds the process of sample blending and dispersal.This is due to the breaking of surface tension differences that may exist between the sample and bonded-phase solid support.As with SPE,washing or rinsing the solid support materials also eliminates contaminants from the final eluates.8)The elution volume.It has been observed that for an8ml elution of a2g MSPD column blended with0.5g of sample that target analytes usually elute in the first4ml,approximately one column volume.This will vary for each application and should be examined to reduce the use of solvent and the unintended co-elution of potential interferences.Miniaturization of the MSPD technique,using smaller sample sizes and proportionately less support or solvent[56,65,146,149],as well as the potential for on-line LC methods,using valve switching to accomplish elution and concentration of the sample,may permit the overall use of less solvent and the opportunity for automation and9)the effect of the sample matrix itself.All of the components of the sample are dispersed throughout the column,covering much of the bonded-phase solid support surface,creating a new phase that can have dramatic effects on isolation in going from one matrix to another[1,159,161,163,199,226,231,236,237,246].
The eluates obtained in MSPD may be taken directly to instrumental analysis,being adequately“clean”for direct injection.However,in some cases additional steps are required to remove co-eluting matrix components.This may involve a more classical SPE approach,using a second solid phase material,co-column or a separate column technique.For example,bonded-phase or other support materials of varying character may be packed at the bottom of the MSPD column (co-column).Alternatively,the MSPD column may be eluted directly onto a standard SPE column or disc material.Some studies have applied a variety of such approaches,including liquid–liquid extraction.However,the advent and availability of LC/MS and MS/MS instrumentation make many of these extra steps unnecessary by simultaneously enhancing sensitivity and selectively.
3.MSPD and SPE
MSPD has been found to be physically and functionally different from classical SPE in several ways:1)it accomplishes complete sample disruption and dispersal onto particles of very small size,providing an enhanced surface area for subsequent extraction of the sample.In SPE sample disruption must be conducted as a separate step in preparing samples for SPE and many of the sample components must be discarded in the process of making the sample suitable for addition to an SPE column.2)In SPE the sample is usually absorbed onto the top of the column packing material,not throughout the column as in MSPD.3)The physical and chemical interactions of the components of the system are greater in MSPD and different,in many respects,from those seen in classical SPE or other forms of liquid chromatography.These have been previously reviewed [159,161,163,199,226,231,236,237,246]and encompass the interaction of a)the sample components with the solid support, b)the sample components with the bonded-phase,c)the analyte with the solid support,d)the analyte with the bonded-phase,e) the analyte with the dispersed sample components,f)all of the above interacting with the elution solvent(s)and their sequence of addition and g)the dynamic interactions of all of the above occurring simultaneously.Nonetheless,general chemical prin-ciples involved in conducting SPE and other forms of chromatography are also operable in applying MSPD.Thus, the chemical composition and characteristics of the solid support and bonded-phase are expected to affect the retention and elution of the analytes.These same properties will also apply to the dispersed sample components and the unique phase that is created.
4.Conclusions
The list of representative MSPD applications for the isolation of an assortment of compounds from a variety of matrices (Table1)illustrates the rather generic character of MSPD. Where examined,MSPD has been found,in many cases,to provide equivalent or superior results to older official methods conducted by more classical countercurrent extraction and/or SPE techniques.Further,it has been rather consistently observed that MSPD requires approximately95%less solvent and can be performed in90%less time when compared to such classical methods.The use of smaller sample sizes,combined with lower solvent consumption,purchase and disposal,make MSPD competitive with such methods on several levels and should be considered as an alternative when developing new
155
S.A.Barker/J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods70(2007)151–162
analytical protocols.This is especially the case for solid or semi-solid biological materials.The continuing development of new supports and bonded-phases and the potential for miniaturiza-tion and automation of the MSPD process suggest several areas for future uses and research.
References
[1]Barker SA,Long AR,Short CR.Isolation of drug residues from tissues
by solid phase dispersion.J Chromatogr1989;475:353–61.
[2]Blanco E,Casais MC,Mejuto MC,Cela R.Approaches for the
simultaneous extraction of tetrabromobisphenol A,tetrachlorobisphenol A,and related phenolic compounds from sewage sludge and sediment samples based on matrix solid-phase dispersion.Anal Chem2006;78: 2772–8.
[3]Domotorova Milena,Matisova Eva,Kirchner Michal,de Zeeuw Jaap.
MSPD combined with fast GC for ultratrace analysis of pesticide residues in non-fatty food.Acta Chim Slov2005;52:422–8.
[4]Zheng Ping,Sheng Xuan,Yu Xiaofeng,Hu Yanyun.Determination of
aflatoxins in hot chili products by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromatography.Sepu2006;24:62–4.
[5]Kristenson E Maria,Brinkman Udo A Th,Ramos Lourdes.Recent
advances in matrix solid-phase dispersion.Trends Analyt Chem2006;25: 96–111.
[6]Bogialli Sara,Curini Roberta,Di Corcia Antonio,Lagana Aldo,Rizzuti
Gabriella.A rapid confirmatory method for analyzing tetracycline antibiotics in bovine,swine,and poultry muscle tissues:matrix solid-phase dispersion with heated water as extractant followed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry.J Agric Food Chem2006;54: 1564–70.
[7]Michel Monika,Gnusowski Boguslaw,Buszewski https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,par-
ison of various extraction techniques to determine fungicide residue in wheat grain.J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol2006;29:247–61.
[8]Teixeira D Martins,Patao R Ferreira,Coelho A Varela,Teixeira da Costa
https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,parison between sample disruption methods and solid–liquid
extraction(SLE)to extract phenolic compounds from Ficus carica leaves.
J Chromatogr A2006;1103:22–8.
[9]Hu Xiaozhong,Chu Xiaogang,Yu Jianxin,Li Jing,Huang Xin,Lin
Yanfei,et al.Determination of22organochlorine and15pyrethroid pesticide residues in apple juice by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry.Fenxi Ceshi Xuebao2004;23
(47):38–42.
[10]Zhang Zhichao,Zeng Min,Li Chaoyang,Zhang Ling,Leng Lian.A
matrix solid-phase dispersion method using AgNO3-loaded basic alumina as solid phase for determination of pendimethalin in garlic.Nongyaoxue Xuebao2005;7:264–8.
[11]Ferrer Imma,Thurman Micahel,Zweigenbaaum Jerry.Analysis of
terbuthylazine in olive oil by liquid chromatography/ion-trap mass spectrometry and time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Huanjing Huaxue 2005;24:735–8.
[12]Shen Zhonglan,Cai Jibao,Gao Yun,Zhu Xiaolan,Su Qingde.A new
matrix solid phase dispersion–accelerate solvent extraction–gas chroma-tographic method for determination of organochlorine pesticides residues in soil.Fenxi Huaxue2005;33:1318–20.
[13]Li Jianke,Hu Qiuhui,Wu Rina,Zhang Haibin,Wu Jingjing.Matrix solid-
phase dispersion and gas chromatography determination of5organopho-sphorous pesticide residues in concentrated apple juice.Nanjing Nongye Daxue Xuebao2005;28:111–5.
[14]Grujic Svetlana,Radisic Marina,Vasiljevic Tatjana,Lausevic Mila.
Determination of carbendazim residues in fruit juices by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry.Food Addit Contam 2005;22:1132–7.
[15]Hu Yan-Yun,Zheng Ping,He You-Zhao,Sheng Guo-Ping.Response
surface optimization for determination of pesticide multiresidues by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography.J Chromatogr A 2005;1098:188–93.[16]Tang Feng,Yue Yongde,Hua Rimao,Cao Haiqun.Matrix solid-phase
dispersion microextraction and determination of pesticide residues in medicinal herbs by gas chromatography with a nitrogen–phosphorus detector.J AOAC Int2006;89:498–502.
[17]Barker Steven https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,e of matrix solid-phase dispersion for determining
pesticides in fish and foods.Methods Biotechnol2006;19:285–96. [18]Cai Jibao,Gao Yun,Zhu Xiaolan,Su Qingde.Matrix solid phase
dispersion—Soxhlet simultaneous extraction clean-up for determination of organochlorine pesticide residues in tobacco.Anal Bioanal Chem 2005;383:869–74.
[19]Furusawa N.Determination of DDT in animal fats after matrix solid-
phase dispersion extraction using an activated carbon fiber.Chromato-graphia2005;62:315–8.
[20]Choma Irena,Komaniecka Iwona.Matrix solid-phase dispersion
combined with thin-layer chromatography—direct bioautography for determination of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin residues in milk.J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol2005;28:2467–78.
[21]Garcia de Llasera MP,Gomez-Almaraz L,Vera-Avila LE,Pena-Alvarez
A.Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and determination by high-
performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection of residues of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in tomato fruit.J Chromatogr A2005;1093:139–46.
[22]Grynbaum Marc David,Hentschel Petra,Putzbach Karsten,Rehbein
Jens,Krucker Manfred,Nicholson Graeme,et al.Unambiguous detection of astaxanthin and astaxanthin fatty acid esters in krill(Euphausia superba Dana).J Sep Sci2005;28:1685–93.
[23]Zou Qiong-Hui,Liu Yuan,Xie Meng-Xia,Han Jie,Zhang Lei.A rapid
method for determination and confirmation of the thyreostats in milk and urine by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry.Anal Chim Acta2005;551:184–91.
[24]Shao Bing,Gao Ying-xin,Han Hao,Zhao Rong,Meng Juan,Qu Guo-
hua.Determination of alkylphenol and bisphenol A in milk and eggs by matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction–liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry.Huanjing Huaxue2005;24:483–4.
[25]Putzbach Karsten,Krucker Manfred,Grynbaum Marc David,Hentschel
Petra,Webb Andrew G,Albert Klaus.Hyphenation of capillary high-performance liquid chromatography to microcoil magnetic resonance spectroscopy—determination of various carotenoids in a small-sized spinach sample.J Pharm Biomed Anal2005;38:910–7.
[26]Soler Carla,Manes Jordi,Pico Yolanda.Routine application using single
quadrupole liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to pesticides analysis in citrus fruits.J Chromatogr A2005;1088:224–33.
[27]Bogialli Sara,Bruno Milena,Curini Roberta,Di Corcia Antonio,Lagana
Aldo,Mari Barbara.Simple assay for analyzing five microcystins and nodularin in fish muscle tissue:hot water extraction followed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry.J Agric Food Chem 2005;53:6586–92.
[28]Majors Ronaldo E.New technologies for the sample preparation of
organic compounds.Abstracts,37th middle atlantic regional meeting of the American Chemical Society,New Brunswick,NJ,United States,May 22–25,2005;2005.GENE-449.
[29]Pensado L,Casais MC,Mejuto MC,Cela R.Application of matrix solid-
phase dispersion in the analysis of priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fish samples.J Chromatogr A2005;1077:103–9. [30]Feng Xia-ping,Zhang Liang,Zhang Zhuo-heng,Chen Wei-gou.
Determination of chloramphenicol in animal food by MSPD and GC/ MS using PTV large volume injection.Zhongshan Daxue Xuebao.Ziran Kexueban2005;44:65–8.
[31]Yang Rong,Zhai Tongyu,Zhou Yaxuan,Liu Haiyan,Zang Xiaohuan.
Matrix solid-phase dispersion and high performance liquid chromato-graphic determination of trace isoprocarb and deltamethrin in food.
Shipin Kexue(Beijing,China)2004;25:158–60.
[32]Zhang Lei,Liu Yuan,Xie Meng-Xia,Qiu Yue-Ming.Simultaneous
determination of thyreostatic residues in animal tissues by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry.
J Chromatogr A2005;1074:1–7.
[33]Dawidowicz Aandrzej L,Wianowska Dorota.PLE in the analysis of plant
compounds.J Pharm Biomed Anal2005;37:1155–9.
156S.A.Barker/J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods70(2007)151–162
[34]Ruiz Maria Jose,Camean Ana Maria,Moreno Isabel Maria,Pico
Yolanda.Determination of microcystins in biological samples by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry.
J Chromatogr A2005;1073:257–62.
[35]Calbiani F,Careri M,Elviri L,Mangia A,Pistara L,Zagnoni I.Rapid
assay for analyzing biogenic amines in cheese:matrix solid-phase dispersion followed by liquid chromatography–electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry.J Agric Food Chem2005;53:3779–83.
[36]Martinez A,Ramil M,Montes R,Hernanz D,Rubi E,Rodriguez I,et al.
Development of a matrix solid-phase dispersion method for the screening of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated biphenyls in biota samples using gas chromatography with electron-capture detection.
J Chromatogr A2005;1072:83–91.
[37]Carro AM,Lorenzo RA,Fernandez F,Rodil R,Cela R.Multi-residue
screening of chlorinated and brominated compounds from aquaculture samples using matrix solid-phase dispersion—gas chromatography–mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A2005;1071:93–8.
[38]Lehotay Steven J,Mastovska Katerina,Yun Seon Jong.Evaluation of two
fast and easy methods for pesticide residue analysis in fatty food matrixes.
J AOAC Int2005;88:630–8.
[39]Yang,Rong,Ma,Jing-jun,Song,Shiang-ju.Matrix solid-phase
dispersion(MSPD)and high performance liquid chromatographic determination of trace isoprocarb in rice.Zhongguo Weisheng Jianyan Zazhi(2005),15(1),48,123.
[40]Feng Xiaping,Chen Weiguo,Wang Zhiyuan,Chen Jie,Cai Jingying.A
rapid and simple method for determination of organochlorine multi-pesticides in fruits and vegetables.Zhongguo Weisheng Jianyan Zazhi 2004;14:701–2.
[41]Langowska Barbara.Sorbents in MSPD technique for determination of
pesticide residues in plant material.Prog Plant Prot2003;43:224–30. [42]Giza Irena,Sztwiertnia Urszula.Determination of tebufenpyrad in
greenhouse vegetables by gas chromatography.Prog Plant Prot 2004;44:686–8.
[43]Tadeo JL,Sanchez-Brunete C,Perez RA.Herbicide residues.Food
Science and Technology(New York,NY,United States)(2004),138 (Handbook of Food Analysis,V olume2),1269–1295.
[44]Ferrer Carmen,Gomez M Jose,Garcia-Reyes Juan F,Ferrer Imma,
Thurman E Michael,Fernandez-Alba Amadeo R.Determination of pesticide residues in olives and olive oil by matrix solid-phase dispersion followed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and liquid chroma-tography/tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A2005;1069: 183–94.
[45]Bogialli Sara,Curini Roberta,Di Corcia Antonio,Lagana Aldo,Mele
Monica,Nazzari Manuela.Simple confirmatory assay for analyzing residues of aminoglycoside antibiotics in bovine milk:hot water extraction followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectro-metry.J Chromatogr A2005;1067:93–100.
[46]Borkovcova I,Janouskova E,Rehurkova I,Ruprich J.Determination of
n-methylcarbamates in foods.Cent Eur J Public Health2004;12:220–3.
[47]Putzbach Karsten,Krucker Manfred,Albert Klaus,Grusak Michael A,
Tang Guangwen,Dolnikowski Gregory G.Structure determination of partially deuterated carotenoids from intrinsically labeled vegetables by HPLC-MS and1H NMR.J Agric Food Chem2005;53:671–7.
[48]Chu Xiang-Gang,Hu Xiao-Zhong,Yao Hui-Yuan.Determination of266
pesticide residues in apple juice by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography–mass selective detection.J Chromatogr A2005;1063: 201–10.
[49]Teixeira D Martins,Teixeira da Costa C.Novel methods to extract
flavanones and xanthones from the root bark of Maclura pomifera.
J Chromatogr A2005;1062:175–81.
[50]Su Shu-Chu,Chou Hsiao-Hui,Chang Pi-Chiou,Liu Chao-Hong,Chou
Shin-Shou.Simultaneous determination of febantel,fenbendazole, oxfendazole and oxfendazole sulfone in livestock by matrix solid phase dispersion extraction technique and HPLC.Yaowu Shipin Fenxi 2004;12:244–53.
[51]Dorea Haroldo Silveira,Lopes Waneidi Gomez.Application of the matrix
solid phase dispersion(MSPD)technique in the analysis of pesticides in okra by GC–MS.Quim Nova2004;27:892–6.[52]Andreu Vicente,Pico Yolanda.Determination of pesticides and their
degradation products in soil:critical review and comparison of methods.
Trends Anal Chem2004;23:772–89.
[53]Lagana Aldo,Faberi Angelo,Fago Giovanna,Marino Aldo,Pastorini
Elisabetta,Samperi Roberto.Application of an innovative matrix solid-phase dispersion–solid-phase extraction–liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry analytical methodology to the study of the metabolism of the estrogenic mycotoxin zearalenone in rainbow trout liver and muscle tissue.Int J Environ Anal Chem2004;84:1009–16.
[54]Dorea Haroldo S,Lima Sobrinho Ledjane.Analysis of pesticide residues
in rice using matrix solid-phase dispersion(MSPD).J Braz Chem Soc 2004;15:690–4.
[55]Ramil Criado M,Hernanz Fernandez D,Rodriguez Pereiro I,Cela
Torrijos R.Application of matrix solid-phase dispersion to the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in fat by gas chromatography with electron-capture and mass spectrometric detection.J Chromatogr A 2004;1056:187–94.
[56]Camean Ana,Moreno Isabel M,Ruiz Maria J,Pico Yolanda.
Determination of microcystins in natural blooms and cyanobacterial strain cultures by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromato-graphy–mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem2004;380:537–44. [57]Bogialli Sara,Curini Roberta,Di Corcia Antonio,Lagana Aldo,Nazzari
Manuela,Tonci Michela.Simple and rapid assay for analyzing residues of carbamate insecticides in bovine milk:hot water extraction followed by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A2004;1054: 351–7.
[58]de Rijke Eva,de Kanter Frans,Ariese Freek,Brinkman Udo A Th,
Gooijer Cees.Liquid chromatography coupled to nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for the identification of isoflavone glucoside malonates in T.pratense L.leaves.J Sep Sci2004;27:1061–70. [59]Sandra P,David F,Tienpont B.From CGC–MS to MS-based analytical
decision makers.Chromatographia2004;60(Suppl1):S299–302. [60]Chase Jr G William,Lin Ye,Stoakes Vicky C,Eitenmiller Ronald R,
Long Austin R.An interlaboratory-verified method for the determination of vitamins A and E in milk-and soy-based infant formula by liquid chromatography with matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction.J AOAC Int2004;87:1173–8.
[61]Gaillard Maria,Juillet Cedrik,Cezilly Frank,Perrot-Minnot Marie-Jeanne.
Carotenoids of two freshwater amphipod species(Gammarus pulex and G.
roeseli)and their common acanthocephalan parasite Polymorphus minutus.
Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol2004;139B:129–36.
[62]Karasova G,Lehotay J.MSPD extraction of phenolic compounds from
fruit-green tea using various non-polar sorbents.J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol2004;27:2837–45.
[63]Soler Carla,Manes Jordi,Pico Yolanda.Liquid chromatography–
electrospray quadrupole ion-trap mass spectrometry of nine pesticides in fruits.J Chromatogr A2004;1048:41–9.
[64]Perret Daniela,Gentili Alessandra,Marchese Stefano,Sergi Manuel,
Caporossi Lidia.Determination of free fatty acids in chocolate by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom2004;18:1989–94.
[65]Kristenson EM,Shahmiri S,Slooten CJ,Vreuls RJJ,Brinkman UATh.
Matrix solid-phase dispersion micro-extraction of pesticides from single insects with subsequent GC–MS analysis.Chromatographia 2004;59:315–20.
[66]Cardosa Maria Helena WM,Bastos Liucia Helena P,Neves Tatiane S,
Abrantes Shirley.Implementation of matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD)technique for the determination of pesticide residues in oranges.
Cienc Tecnol Aliment(Campinas,Brazil)2004;24:298–302.
[67]Choma Irena,Pilorz Karol.A novel application of matrix solid-phase
dispersion for determination of doxycycline and flumequine residues in milk.J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol2004;27:2143–51.
[68]Hu Xiaozhong,Yu Jianxin,Yan Zhigang,Ni Lansun,Lin Yanfei,Wang
Peng,et al.Determination of multiclass pesticide residues in apple juice by gas chromatography–mass selective detection after extraction by matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int2004;87:972–85.
[69]Albero Beatriz,Sanchez-Brunete Consuelo,Tadeo Jose L.Determination
of thiabendazole in orange juice and rind by liquid chromatography with
157
S.A.Barker/J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods70(2007)151–162
fluorescence detection and confirmation by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry after extraction by matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int2004;87:664–70.
[70]Albero B,Sanchez-Brunete C,Donoso A,Tadeo JL.Determination of
herbicide residues in juice by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A2004;1043: 127–33.
[71]Tseng Su-Hsiang,Lin Yu-Ju,Chang Pi-Chiou,Chou Shin-Shou,Chang
Hung-Min.Determination of simazine residue in sugarcane by applica-tion of matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)extraction technique.
Yaowu Shipin Fenxi2004;12:74–8.
[72]Garcinuno RM,Ramos L,Fernandez-Hernando P,Camara C.Optimiza-
tion of a matrix solid-phase dispersion method with subsequent clean-up for the determination of ethylene bisdithiocarbamate residues in almond samples.J Chromatogr A2004;1041:35–41.
[73]Sassine Andre,Moura Sergio,Leo Viviane Morais,Bustillos Oscar Vega.
Cypermethrin residues determination in the milk of a lactating dairy cow by gas chromatography–ion trap mass spectrometry.J Anal Toxicol 2004;28:238–41.
[74]Bogialli Sara,Capitolino Vittorio,Curini Roberta,Di Corcia Antonio,
Nazzari Manuela,Sergi Manuel.Simple and rapid liquid chromatogra-phy–tandem mass spectrometry confirmatory assay for determining amoxicillin and ampicillin in bovine tissues and milk.J Agric Food Chem 2004;52:3286–91.
[75]Ding Lan,Xie Mengxia,Liu Yuan,Shan Jihao,Yang Qingfeng,Liu
Suying.Determination of furazolidone residue in eggs by high performance liquid chromatography.Fenxi Huaxue2004;32:139–42. [76]Karasova Gabriela,Brandsteterova Eva,Lachova Miroslava.Matrix solid
phase dispersion as an effective preparation method for food samples and plants before HPLC analysis.Czech J Food Sci2003;21:219–34. [77]Furusawa N.A toxic reagent-free method for normal-phase matrix solid-
phase dispersion extraction and reversed-phase liquid chromatographic determination of aldrin,dieldrin,and DDTs in animal fats.Anal Bioanal Chem2004;378:2004–7.
[78]Lopes Waneide Gomes,Dorea Haroldo Silveira.Determination of
pesticides in beans by matrix solid-phase dispersion(MSPD).Pesticidas 2003;13:73–82.
[79]Xiao HB,Krucker M,Albert K,Liang XM.Determination and
identification of isoflavonoids in Radix astragali by matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array and mass spectrometric detection.J Chromatogr A 2004;1032:117–24.
[80]Yang Rong,Liu Haiyan,Lu Xiaofang.Matrix solid-phase dispersion
(MSPD)and high performance liquid chromatographic determination of trace pirimicarb and amitraz in fruit and vegetable.Hebei Nongye Daxue Xuebao2003;26:114–7.
[81]Blesa J,Soriano JM,Molto JC,Manes J.Limited survey for the presence
of aflatoxins in foods from local markets and supermarkets in Valencia, Spain.Food Addit Contam2004;21:165–71.
[82]Blasco C,Font G,Pico Y.Determination of dithiocarbamates and
metabolites in plants by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry.
J Chromatogr A2004;1028:267–76.
[83]Bogialli Sara,Curini Roberta,Di Corcia Antonio,Nazzari Manuela,
Tamburro Davide.A simple and rapid assay for analyzing residues of carbamate insecticides in vegetables and fruits:hot water extraction followed by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry.J Agric Food Chem2004;52:665–71.
[84]Bogusz Maciej J,El Hajj Samir Abu,Ehaideb Zeyad,Hassan Huda,Al-
Tufail Mohammad.Rapid determination of benzo[a]pyrene in olive oil samples with solid-phase extraction and low-pressure,wide-bore gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and fast liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection.J Chromatogr A2004;1026:1–7.
[85]Michel Monika,Buszewski Boguslaw.Optimization of a matrix solid-
phase dispersion method for the determination analysis of carbendazim residue in plant material.J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 2004;800:309–14.
[86]Ding Yayun,Xu Xiaoyun,Xie Mengxia,Yang Qingfeng,Liu Suying.
Matrix solid-phase dispersion coupled with gas chromatography–mass
spectrometry for the analysis of trace residue of diethylstilbestrol in animal tissue.Fenxi Huaxue2003;31:1356–9.
[87]Albero Beatriz,Sanchez-Brunete Consuelo,Tadeo Jose L.Determination
of organophosphorus pesticides in fruit juices by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography.J Agric Food Chem2003;51: 6915–21.
[88]Michel Monika,Buszewski Boguslaw.Isolation and determination of
carbendazim residue from wheat grain by matrix solid-phase dispersion and HPLC.J Sep Sci2003;26:1269–72.
[89]Yang Rong.Matrix solid-phase dispersion and high performance liquid
chromatographic determination of trace carbofuran in wheat.Hebei Daxue Xuebao Ziran Kexueban2003;23:269–71.
[90]Kishida Kunihiro,Furusawa Naoto.Toxic/harmful solvents-free techni-
que for HPLC determination of six sulfonamides in meat.J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol2003;26:2931–9.
[91]de V oogt Pim,Saez Monica,Gonzalez-Mazo Eduardo.Sample handling
for the determination of surfactants in https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,pr Anal Chem 2003;40:429–41.
[92]Lagana Aldo,Bacaloni Alessandro,Castellano Maryanna,Curini
Roberta,De Leva Ilaria,Faberi Angelo,et al.Sample preparation for determination of macrocyclic lactone mycotoxins in fish tissue,based on on-line matrix solid-phase dispersion and solid-phase extraction cleanup followed by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.J AOAC Int2003;86:729–36.
[93]Giza I,Sztwiertnia U.Gas chromatographic determination of azoxystrobin
and trifloxystrobin residues in apples.Acta Chromatogr2003;13:226–9.
[94]Husain SW,Kiarostami V,Morrovati M,Tagebakhsh MR.Multiresidue
determination of diazinon and ethion in pistachio nuts by use of matrix solid phase dispersion with a lanthanum silicate co-column and gas chromatography.Acta Chromatogr2003;13:208–14.
[95]Kastelan-Macan Marija,Babic Sandra.Pesticides.Chromatographic
science series,vol.89.Handbook of Thin-Layer Chromatography,3rd edition;2003.p.767–805.
[96]Blesa J,Soriano JM,Molto JC,Marin R,Manes J.Determination of
aflatoxins in peanuts by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromatography.J Chromatogr A2003;1011:49–54.
[97]Hines Murray E,Styer Eloise L.Preliminary characterization of
chemically generated Mycobacterium avium subsp.paratuberculosis cell wall-deficient forms(spheroplasts).Vet Microbiol2003;95:247–58.
[98]Morzycka Bozena,Matrix solid phase dispersion—new prospects in
analysis of pesticide residues.Pestycydy(Warsaw)(2003),V olume Date 2002,(1–4),61–69.
[99]Li Zhao-yang,Zhang Zhi-chao,Zhou Qi-lin,Zhu Chang-shou,Wang
Qing-min,Wang Qin-sun.Matrix solid-phase dispersion method for determination of fenpropathrin in soil.Fenxi Shiyanshi2003;22:13–5. [100]Albero B,Sanchez-Brunete C,Tadeo JL.Determination of endosulfan isomers and endosulfan sulfate in tomato juice by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography.J Chromatogr A2003;1007:137–43. [101]Tadeo JL,Sanchez-Brunete C.Analysis of pesticide residues in fruit juices by matrix-solid phase dispersion and gas chromatographic determination.Chromatographia2003;57:793–8.
[102]Zuin Vania G,Yariwake Janete H,Lancas Fernando M.Analysis of pesticide residues in Brazilian medicinal plants:matrix solid phase dispersion versus conventional(European pharmacopoeia)methods.
J Braz Chem Soc2003;14:304–9.
[103]Albero Beatriz,Sanchez-Brunete Consuelo,Tadeo Jose L.Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in honey by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry.J AOAC Int 2003;86:576–82.
[104]Li Zhao-Yang,Zhang Zhi-Chao,Zhou Qi-Lin,Wang Qing-Min,Gao Ru-Y u,Wang Qin-Sun.Stereo-and enantioselective determination of pesticides in soil by using achiral and chiral liquid chromatography in combination with matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int2003;86:521–8. [105]Yang Rong.Determination of trace carbofuran in rice with matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)-high performance liquid chromatography.
Sepu2003;21:295.
[106]Bogialli Sara,Curini Roberta,DiCorcia Antonio,Nazzari Manuela,Polci Maria Letizia.Rapid confirmatory assay for determining12sulfonamide
158S.A.Barker/J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods70(2007)151–162
antimicrobials in milk and eggs by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry.J Agric Food Chem2003;51: 4225–32.
[107]Bogialli Sara,Curini Roberta,Di Corcia Antonio,Nazzari Manuela,Sergi Manuel.Confirmatory analysis of sulfonamide antibacterials in bovine liver and kidney:extraction with hot water and liquid chromatography coupled to a single-or triple-quadrupole mass spectrometer.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom2003;17:1146–56.
[108]Glaser T,Lienau A,Zeeb D,Krucker M,Dachtler M,Albert K.
Qualitative and quantitative determination of carotenoid stereoisomers in
a variety of spinach samples by use of MSPD before HPLC-UV,HPLC-
APCI-MS,and HPLC-NMR on-line coupling.Chromatographia 2003;57:S/19–25.
[109]Li Zhao-Yang,Zhang Zhi-Chao,Liu Yi-Shan,Zhou Qi-Lin,Gao Ru-Yu, Wang Qin-Sun.Determination of uniconazole in soil with an enantio-selective way.Gaodeng Xuexiao Huaxue Xuebao2003;24:840–2. [110]Blaszczyk Alfred,Jasiczak Jan.Rapid and economical methods for extraction of pesticides from food products.Wiad Chem2002;56: 1035–52.
[111]Morzycka Bozena.Determination of organophosphorus pesticides in fruits and vegetables by matrix solid-phase dispersion method.J Plant Prot Res2002;42:17–22.
[112]Sanvoss Martin.Application of LC-NMR and LC-NMR-MS hyphenation to natural products analysis.On-line LC-NMR and related techniques;
2002.p.111–28.
[113]Bogialli Sara,Curini Roberta,Di Corcia Antonio,Nazzari Manuela, Samperi Roberto.A liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry assay for analyzing sulfonamide antibacterials in cattle and fish muscle tissues.
Anal Chem2003;75:1798–804.
[114]Fernandez M,Pico Y,Manes J.Rapid screening of organophosphorus pesticides in honey and bees by liquid chromatography–mass spectro-metry.Chromatographia2002;56:577–83.
[115]Zhao Meiping,Li Yuanzong,Chang Wenhao.Analysis of phenolic environmental estrogens.Fenxi Huaxue2003;31:103–9.
[116]Bazulic D,Sapunar-Postruznik Jasenka,Drincic Helena Kubala,Grubelic Mirela,Oraic D.Determination of hexachlorobenzene(HCB)in the perirenal and dorsal fatty tissues of pigs.Acta Vet Hung2002;50:111–5. [117]Kubala-Drincic Helena,Bazulic Davorin,Sapunar-Postruznik Jasenka, Grubelic Mirela,Stuhne Goran.Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and gas chromatographic determination of chloramphenicol in muscle tissue.J Agric Food Chem2003;51:871–5.
[118]Ziakova Alica,Brandsteterova Eva,Blahova Eva.Matrix solid-phase dispersion for the liquid chromatographic determination of phenolic acids in Melissa officinalis.J Chromatogr A2003;983:271–5.
[119]Walles Markus,Borlak Juergen,Levsen Karsten.Application of restricted access material(RAM)with precolumn-switching and matrix solid-phase dispersion(MSPD)to the study of the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of Verapamil.Anal Bioanal Chem2002;374:1179–86.
[120]Tolls Johannes,Samperi Roberto,Di Corcia Antonio.Bioaccumulation of LAS in Feral Fish Studied by a Novel LC-MS/MS Method.Environ Sci Technol2003;37:314–20.
[121]Morzycka Bozena.Simple method for the determination of trace levels of pesticides in honeybees using matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography.J Chromatogr A2002;982:267–73.
[122]van Bennekom EO,Brouwer L,Laurant EHM,Hooijerink H,Nielen MWF.
Confirmatory analysis method for zeranol,its metabolites and related mycotoxins in urine by liquid chromatography-negative ion electrospray tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Chim Acta2002;473:151–60. [123]Li Zhao-Yang,Zhang Zhi-Chao,Zhou Qi-Lin,Gao Ru-Yu,Wang Qin-Sun.Fast and precise determination of phenthoate and its enantiomeric ratio in soil by the matrix solid-phase dispersion method and liquid chromatography.J Chromatogr A2002;977:17–25.
[124]Michel Monika,Buszewski Boguslaw.HPLC determination of pesticide residue isolated from food matrices.J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 2002;25:2293–306.
[125]Blasco C,Font G,Pico https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,parison of microextraction procedures to determine pesticides in oranges by liquid chromatography-mass spectro-metry.J Chromatogr A2002;970:201–12.[126]Lienau Annette,Glaser Tobias,Krucker Manfred,Zeeb Daniel,Ley Fritz, Curro Frederick,et al.Qualitative and quantitative analysis of tocopherols in toothpastes and gingival tissue employing HPLC NMR and HPLC MS coupling.Anal Chem2002;74:5192–8.
[127]Morzycka Bozena.Multiresidue matrix solid-phase dispersion method for the determination of fungicides in fruits and vegetables.Chem Anal (Warsaw,Poland)2002;47:571–83.
[128]Navarro M,Pico Y,Marin R,Manes J.Application of matrix solid-phase dispersion to the determination of a new generation of fungicides in fruits and vegetables.J Chromatogr A2002;968:201–9.
[129]Feng Xiuqiong,Tang Qingyong.Multiresidue determination of organo-phosphorus pesticides in Chinese medicinal herbs.Nongyao Kexue Yu Guanli2002;23:17–20.
[130]Perret Daniela,Gentili Alessandra,Marchese Stefano,Sergi Manuel, D'Ascenzo Giuseppe.Validation of a method for the determination of multiclass pesticide residues in fruit juices by liquid chromatography/ tandem mass spectrometry after extraction by matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int2002;85:724–30.
[131]Blasco Cristina,Pico Yolanda,Font Guillermina.Monitoring of five postharvest fungicides in fruit and vegetables by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry.J AOAC Int 2002;85:704–11.
[132]Sandra Pat,David Frank.High-throughput capillary gas chromatography for the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and fatty acid methyl esters in food samples.J Chromatogr Sci2002;40:248–53.
[133]Jing Legang.New development in determination of food pesticide residues.Shipin Kexue(Beijing,China)2002;23:148–51.
[134]Curren Meredith SS,King Jerry W.New sample preparation technique for the determination of avoparcin in pressurized hot water extracts from kidney samples.J Chromatogr A2002;954:41–9.
[135]Nowak Ronald M,Lehmann Robert G,Lange Gary M,Karpovich David S.Accumulation of DDT in fish from the Pine River in Michigan: comparison with other sites worldwide.Abstracts of papers,223rd ACS National Meeting,Orlando,FL,United States,April7–11,2002;2002.
CHED-432.
[136]Sanchez-Brunete Consuelo,Albero Beatriz,Miguel Ester,Tadeo Jose Luis.Determination of insecticides in honey by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography with nitrogen–phosphorus detection and mass spectrometric confirmation.J AOAC Int2002;85:128–33. [137]Blasco C,Pico Y,Manes J,Font G.Determination of fungicide residues in fruits and vegetables by liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A2002;947: 227–35.
[138]Gomez-Ariza JL,Bujalance M,Giraldez I,Velasco A,Morales E.
Determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in biota samples using simultaneous pressurized liquid extraction and purification.J Chromatogr A2002;946:209–19.
[139]Ahmed Farid E.Analyses of pesticides and their metabolites in foods and drinks.Trends Anal Chem2001;20:649–61.
[140]Kishida Kunihiro,Furusawa Naoto.Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of residual sulfonamides in chicken.J Chromatogr A2001;937:49–55. [141]Fernandez-Alba AR,Lopez Martinez MD,Contreras M.Evaluation of the relationship between carotenoids and colour measures by chromato-graphic and colorimetric based procedures:application to fruits and vegetables.Special publication—Royal Society of Chemistry,269 (Biologically-Active Phytochemicals in Food);2001.p.280–2. [142]Yague Cristina,Bayarri Susana,Lazaro Regina,Conchello Pilar,Arino Agustin,Herrera Antonio.Multiresidue determination of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in milk by gas chromatography with electron-capture detection after extraction by matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int2001;84:1561–8.
[143]Loveland PM,Reddy AP,Pereira CB,Field JA,Bailey GS.Application of matrix solid-phase dispersion in the determination of dibenzo[a,l] pyrene content of experimental animal diets used in a large-scale tumor study.J Chromatogr A2001;932:33–41.
[144]Pous Ximo,Ruiz M Jose,Pico Yolanda,Font Guillermina.Determination of imidacloprid,metalaxyl,myclobutanil,propham,and thiabendazole in
159
S.A.Barker/J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods70(2007)151–162
fruits and vegetables by liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-mass spectrometry.Fresenius'J Anal Chem 2001;371:182–9.
[145]Albero Beatriz,Sanchez-Brunete Consuelo,Tadeo Jose L.Multiresidue determination of pesticides in honey by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography with electron-capture detection.J AOAC Int 2001;84:1165–71.
[146]Berrueta LA,Fernandez-Armentia M,Bakkali A,Gonzalo A,Lucero ML,Orjales A.Matrix solid-phase dispersion technique for the determination of a new antiallergic drug,bilastine,in rat faeces.
J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl2001;760:185–90.
[147]Valenzuela Ana I,Pico Yolanda,Font Guillermina.Determination of five pesticide residues in oranges by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromatography to estimate daily intake of consumers.J AOAC Int 2001;84:901–9.
[148]Valenzuela AI,Popa DS,Redondo MJ,Manes https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,parison of various liquid chromatographic methods for the analysis of avermectin residues in citrus fruits.J Chromatogr A2001;918:59–65.
[149]Kristenson EM,Haverkate EGJ,Slooten CJ,Ramos L,Vreuls RJJ, Brinkman UAT.Miniaturized automated matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction of pesticides in fruit followed by gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric analysis.J Chromatogr A2001;917:277–86.
[150]Sandvoss M,Weltring A,Preiss A,Levsen K,Wuensch https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,bination of matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and direct on-line liquid chromatography–nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy–tandem mass spectrometry as a new efficient approach for the rapid screening of natural products:application to the total asterosaponin fraction of the starfish Asterias rubens.J Chromatogr A2001;917:75–86.
[151]Curren Meredith SS,King Jerry W.Ethanol-modified subcritical water extraction combined with solid-phase microextraction for determining atrazine in beef kidney.J Agric Food Chem2001;49:2175–80. [152]Crescenzi C,Bayoudh S,Cormack PAG,Klein T,Ensing K.Determina-tion of clenbuterol in bovine liver by combining matrix solid-phase dispersion and molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography/electrospray ion trap multiple-stage mass spectro-metry.Anal Chem2001;73:2171–7.
[153]Zhang Su-xia,Li Jun-suo,Qian Chuan-fan.MSPD clean-up and HPLC determination of benzimidazoles in beef muscle.Zhongguo Shouyi Xuebao2000;20:569–71.
[154]Dachtler Markus,Glaser Tobias,Kohler Konrad,Albert Klaus.
Combined HPLC-MS and HPLC-NMR on-line coupling for the separation and determination of lutein and zeaxanthin stereoisomers in spinach and in retina.Anal Chem2001;73:667–74.
[155]Rakoczy Ilona,Kovacs Aniko.Matrix solid-phase dispersion isolation and liquid-chromatographic determination of methomyl in biological tissues.Z Zag Nauk Sadow2000;43:217–21.
[156]Chase Jr G William,Eitenmiller RR,Long AR.Liquid chromatographic analysis of vitamin K1in medical foods using matrix solid-phase dispersion.J Food Compos Anal2000;13:765–71.
[157]Zhong Weike,Hao Jian,Fan Yaobo,Wang Minjian.Development in pesticide residue analysis of food.Fenxi Huaxue2000;28:904–10. [158]Gaunt Patricia,Barker Steven A.Matrix solid phase dispersion extraction of triazines from catfish tissues;examination of the effects of temperature and dissolved oxygen on the toxicity of atrazine.Int J Environ Pollut 2000;13:284–312.
[159]Barker SA.Matrix solid-phase dispersion.J Chromatogr A2000;885:115–27. [160]dos Ramos FJ.Beta-2-agonist extraction procedures for chromatographic analysis.J Chromatogr A2000;880:69–83.
[161]Barker SA.Applications of matrix solid-phase dispersion in food analysis.J Chromatogr A2000;880:63–8.
[162]Chase Jr G William,Eitenmiller Ronald R,Long Austin R.Liquid chromatographic analysis of vitamin K1in milk-based infant formula with matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int1999;82:1140–5. [163]Barker Steven A.Sorbent technologies principles and applications.
Residue analysis in food;2000.p.37–71.
[164]Chase Jr G William,Thompson Brian.Accelerated solvent extraction of vitamin K1in medical foods in conjunction with matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int2000;83:407–10.[165]Valenzuela AI,Pico Y,Font G.Liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-mass spectrometric analysis of benzoylurea insecticides in citrus fruits.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom2000;14: 572–7.
[166]Valenzuela AI,Redondo MJ,Pico Y,Font G.Determination of abamectin in citrus fruits by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A2000;871:57–65.
[167]Fernandez M,Pico Y,Manes J.Determination of carbamate residues in fruits and vegetables by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A2000;71:43–56. [168]Chase Jr G William,Eitenmiller RR,Long AR.The liquid chromato-graphic analysis of vitamin K1in soy based infant formula using matrix solid phase dispersion.J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol2000;23:423–32. [169]Ramos L,Eljarrat E,Hernandez LM,Rivera J,Gonzalez MJ.Levels of polychlorinated biphenyls,polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and diben-zofurans in commercial yoghurt samples in https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,parison with different dairy products.Anal Chim Acta1999;402:241–52.
[170]Tolls Johannes,Haller Manuela,Sijm Dick THM.Extraction and isolation of linear alkylbenzenesulfonate and its sulfophenylcarboxylic acid metabolites from fish samples.Anal Chem1999;71:5242–7. [171]Glaser Tobias,Dachtler Markus,Albert Klaus.Study of carotenoid stereoisomers in spinach and in the retina by HPLC-NMR and HPLC-MS coupling.GIT Labor-Fachz1999;43:904–9.
[172]Chase Jr G William,Eitenmiller Ronald R,Long Austin R.Analysis of beta-carotene in medical food by liquid chromatography with matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int1999;82:663–8.
[173]Batulic Davorin,Sapunar-Postruznik Jasenka,Bilic Sara.Significance of the quality of florisil in organochlorine pesticide analysis.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol1998;49:319–25.
[174]Chase Jr G William,Eitenmiller Ronald R,Long Austin R.A liquid chromatographic method for the analysis of retinyl acetate in soy based infant formula using matrix solid phase dispersion.J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol1999;22:1205–12.
[175]Tolls Johannes,Haller Manuela,Sijm Dick THM.Extraction and isolation of linear alcohol ethoxylates from fish.J Chromatogr A 1999;839:109–17.
[176]Valenzuela AI,Lorenzini R,Redondo MJ,Font G.Matrix solid-phase dispersion microextraction and determination by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection of pesticide residues in citrus fruit.
J Chromatogr A1999;839:101–7.
[177]Dorea Haroldo Silveira,Fernando Mauro Lancas.Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction of organophosphorus and synthetic pyrethroid pesticides in cashew nut and passion fruit.J Microcolumn Sep1999;11: 367–75.
[178]Zhao M,van der Wielen F,de V oogt P.Optimization of a matrix solid-phase dispersion method with sequential clean-up for the determination of alkylphenol ethoxylates in biological tissues.J Chromatogr A 1999;837:129–38.
[179]Chase Jr G William,Eitenmiller Ronald R,Long Austin R.A liquid chromatographic method for analysis of all-rac-alpha-tocopheryl acetate and retinyl palmitate in medical food using matrix solid-phase dispersion in conjunction with a zero reference material as a method development tool.J AOAC Int1999;82:107–11.
[180]Kinoshita Masayasu.Analysis of synthetic antibacterials in cultured marine products with matrix solid-phase dispersion.Shokuhin Eisei Kenkyu1998;48:91–7.
[181]McGrane Marie,O'Keeffe Michael,Smyth Malcolm R.Multi-residue analysis of penicillin residues in porcine tissue using matrix solid phase dispersion.Analyst(Cambridge,United Kingdom)1998;123:2779–83. [182]Horne Elizabeth,O'Keeffe Michael,Desbrow Claire,Howells Anne.A novel sorbent for the determination of clenbuterol in bovine liver.Analyst (Cambridge,United Kingdom)1998;123:2517–20.
[183]Chase Jr G William,Eitenmiller Ronald R,Long Austin R.Liquid chromatographic method for the analysis of all-rac-alpha-tocopheryl acetate and retinyl palmitate in soy-based infant formula using matrix solid phase dispersion.J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol1998;21:2853–61. [184]Matos Lino Celeste,Ferreira Azzolini Clara B,Valente Nunes Domingos S,Rocha Silva Jose M,Noronha da Silveira M Irene.Methods for the
160S.A.Barker/J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods70(2007)151–162
determination of organochlorine pesticide residues in human serum.
J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl1998;716:147–52.
[185]Wu Shuguang,Hofmann Charles K.Matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD):a new isolation technique for the analysis of pesticide residues in natural products.Book of abstracts,216th ACS National Meeting, Boston,August23–27;1998.ANYL-111.
[186]Chase Jr G William,Long Austin R.Liquid chromatographic method for analysis of all-rac-alpha-tocopheryl acetate and retinyl palmitate in milk-based infant formula using matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int 1998;81:582–6.
[187]Torres Carmen M,Pico Yolanda,Marin Rosa,Manes Jordi.Evaluation of organophosphorus pesticide residues in citrus fruits from the Valencian Community(Spain).J AOAC Int1997;80:1122–8.
[188]Brandsteterova Eva,Kubalec Pavel,Bovanova Ludmila,Simko Peter, Bednarikova Alena,Machackova Lubomira.SPE and MSPD as pre-separation techniques for HPLC of tetracyclines in meat,milk,and cheese.Z Lebensm Unters Forsch A Eur Food Res Technol1997;205: 311–5.
[189]Torres CM,Pico Y,Manes https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,parison of octadecylsilica and graphitized carbon black as materials for solid-phase extraction of fungicide and insecticide residues from fruit and vegetables.J Chromatogr A1997;778:127–37.
[190]Crouch Michael D,Barker Steven A.Analysis of toxic wastes in tissues from aquatic species.Applications of matrix solid-phase dispersion.
J Chromatogr A1997;774:287–309.
[191]Le Boulaire Stephanie,Bauduret Jean-Claude,Andre Francois.Veter-inary drug residues survey in meat:an HPLC method with a Matrix Solid Phase Dispersion Extraction.J Agric Food Chem1997;45:2134–42. [192]Yago Lane S.Matrix solid phase dispersion:the next step in solid phase extraction for food samples?An overview of the technology.Semin Food Anal1996;1:45–54.
[193]Kappel LC,Barker SA.Fenbendazole-related drug residues in milk from treated dairy cows.J Vet Pharmacol Ther1996;19:416–22.
[194]Viana E,Molt JC,Font G.Optimization of a matrix solid-phase dispersion method for the analysis of pesticide residues in vegetables.
J Chromatogr A1996;754:437–44.
[195]Tekel Jozef,Hatrik Stefan.Pesticide residue analyses in plant material by chromatographic methods:clean-up procedures and selective detectors.
J Chromatogr A1996;754:397–410.
[196]Alvinerie M,Sutra JF,Capela D,Galtier P,Fernandez-Saurez A,Horne E.
Matrix solid-phase dispersion technique for the determination of moxidectin in bovine tissues.Analyst(Cambridge,United Kingdom) 1996;121:1469–72.
[197]Kai Shigemi,Nikkawa Takayasu,Takahashi Atsuko,Koizumi Akiko, Hyoudou Yukio,Suzuki Sumiko.Preparation of sample solution for determination of acid coal-tar dyes in confectionery by the matrix solid-phase dispersion method.Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi1996;37:146–50. [198]Daun Robert J,Ryan David L.Magnitude of residues of methomyl in edible tissues and milk of dairy cows.Book of abstracts,212th ACS National Meeting,Orlando,FL,August25–29;1996.AGRO-045. [199]Barker Steven A,Floyd Z Elizabeth.Matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD):implications for the design and use of new bonded surface chemistries.Special publication—Royal Society of Chemistry,173 (Chemically Modified Surfaces:Recent Developments);1996.p.66–71. [200]Obana Hirotaka,Hori https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,test analytical methods for the residual pesticides in foods.Jpn J Toxicol Environ Health1996;42:1–16. [201]Castilho MC,Ramos F,Silveira EMA.Chloramphenicol:review of its analytical methodology in food products.Rev Port Farm1995;45:100–9. [202]Torres CM,Pico Y,Manes J.Analysis of pesticide residues in fruit and vegetables by matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)and different gas chromatography element-selective detectors.Chromatographia 1995;41:685–92.
[203]Torres CM,Pico Y,Redondo MJ,Manes J.Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction procedure for multiresidue pesticide analysis in oranges.
J Chromatogr A1996;719:95–103.
[204]Johnston JJ,Petty EE.A comparison of solvent extraction,solid phase extraction and matrix solid phase dispersion for the quantification of organochlorine pesticide residues in biological matrixes.Book of
Abstracts,210th ACS National Meeting,Chicago,IL,August20–24, Pt.1;1995.AGRO-005.
[205]Boyd D,O'Keeffe M,Smyth MR.Matrix solid phase dispersion linked to solid phase extraction for beta-agonists in liver samples:an update.Anal Proc1995;32:301–3.
[206]Schenck Frank J,Wagner Roberta.Screening procedure for organo-chlorine and organophosphorus pesticide residues in milk using matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)extraction and gas chromatographic determination.Food Addit Contam1995;12:535–41.
[207]Ling Y-C,Huang I-P.Multiresidue-matrix solid-phase dispersion method for determining16organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in fish.Chromatographia1995;40:259–66.
[208]Yang Rong,Fu Chengguany.Matrix solid-phase dispersion and high performance liquid chromatographic determination of trace Pirimicarb and Amitraz in fruits and vegetables.Hebei Daxue Xuebao Ziran Kexueban1994;14:29–33.
[209]Ling Y-C,Huang I-P.Multi-residue matrix solid-phase dispersion method for the determination of six synthetic pyrethroids in vegetables followed by gas chromatography with electron capture detection.J Chromatogr A 1995;695:75–82.
[210]Schenck Frank J.Isolation and quantification of ivermectin in bovine milk by matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)extraction and liquid chromatographic determination.J Liq Chromatogr1995;18:349–62. [211]Yang Rong,Fu Chengguang.Matrix solid-phase dispersion and high performance liquid chromatographic determination of trace carbofuran in corn.Fenxi Ceshi Xuebao1994;13:72–5.
[212]Shearan Paula,O'Keeffe Michael.Novel approach to the‘on-site’testing for sulfamethazine in pork carcasses.Analyst(Cambridge,United Kingdom)1994;119:2761–4.
[213]Rosen Johan,Hellenaes Karl-Erik,Toernqvist Paulina,Shearan Paula.
Automated extraction of acetylgestagens from kidney fat by matrix solid phase dispersion.Analyst(Cambridge,United Kingdom)1994;119: 2635–7.
[214]Walker Calvin C,Barker Steven A.Extraction and liquid chromato-graphic analysis of sulfadimethoxine and4-N-acetylsulfadimethoxine residues in channel catfish(Ictalurus punctatus)muscle and plasma.
J AOAC Int1994;77:1460–6.
[215]Pico Yolanda,Molto Juan C,Manes Jordi,Font Guillermina.Solid phase techniques in the extraction of pesticides and related compounds from foods and soils.J Microcolumn Sep1994;6:331–59.
[216]Iosifidou Eleni,Shearan Paula,O'Keefe Michael.Application of the matrix solid phase dispersion technique for the determination of ivermectin residues in fish muscle tissue.Analyst(Cambridge,United Kingdom)1994;119:2227–9.
[217]Tamura Hiroshi,Yotoriyama Mamoru,Kurosaki Kanako,Shinohara Nobukatu.High performance liquid chromatographic analysis of sulfona-mides in livestock products using matrix solid-phase dispersion(MSPD) method with silica gel.Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi1994;35:271–5. [218]Barker Steven A,Kappel Leonard C,Short Charles R.Tissue distribution and clearance of the cephalosporin cefquinome in the bovine.Residues Vet.Drugs Food,Proc.2nd.EuroResidue Conf.,vol.1;1993.p.165–9. [219]Boyd Damien,O'Keeffe Michael,Smyth Malcolm R.Matrix solid-phase dispersion as a multiresidue extraction technique for beta-agonists in bovine liver tissue.Analyst(Cambridge,United Kingdom)1994;119: 1467–70.
[220]Fukushima Shigehiko,Taguchi Shuzo,Nishimune Takahiro,Sueki Kenji.
Determination of five sulfa drugs,furazolidone and clopidol in chicken tissues by matrix solid-phase dispersion isolation method.Osaka-Furitsu Koshu Eisei Kenkyusho Kenkyu Hokoku,Shokuhin Eisei-Hen 1993;24:19–24.
[221]Walker Calvin C,Barker Steven A.Extraction and enzyme immunoassay of sulfadimethoxine residues in channel catfish(Ictalurus punctatus) muscle.J AOAC Int1994;77:908–16.
[222]Barker Steven A,Long Austin R.Preparation of milk samples for immunoassay and liquid chromatographic screening using matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int1994;77:848–54.
[223]McLaughlin Lee G,Henion Jack D,Kijak Philip J.Multiresidue confirmation of aminoglycoside antibiotics in bovine kidney by ion spray
161
S.A.Barker/J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods70(2007)151–162
high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.
Biol Mass Spectrom1994;23:417–29.
[224]Ling Y-C,Chang M-Y,Huang I-P.Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and gas chromatographic screening of polychlorinated biphenyls in fish.J Chromatogr A1994;669:119–24.
[225]Shearan Paula,O'Keeffe Michael,Smyth Malcolm https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,parison of matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)with a standard solvent extraction method for sulfamethazine in pork muscle using high-performance liquid and thin-layer chromatography.Food Addit Contam1994;11:7–15. [226]Barker Steven A,Long Austin R,Isolation of drugs or drug metabolites from biological specimens via matrix solid phase dispersion.U.S.(1993), 10pp.Cont.of U.S.Ser.No.893,903,abandoned.
[227]Lott Heidi M,Barker Steven https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,parison of a matrix solid phase dispersion and a classical extraction method for the determination of chlorinated pesticides in fish muscle.Environ Monit Assess 1993;28:109–16.
[228]Walker Calvin C,Lott Heidi M,Barker Steven A.Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and the analysis of drugs and environmental pollutants in aquatic species.J Chromatogr1993;642:225–42. [229]Lott Heidi M,Barker Steven A.Extraction and gas chromatographic screening of14chlorinated pesticides in crayfish(Procambarus clarkii) hepatopancreas.J AOAC Int1993;76:663–8.
[230]Shaikh Badar,Moats William A.Liquid chromatographic analysis of antibacterial drug residues in food products of animal origin.
J Chromatogr1993;643:369–78.
[231]Barker Steven A.How to analyze those messy biological samples.
Chemtech1993;23:42–5.
[232]Boyd Damien,Shearan Paula,Hopkins JP,O'Keeffe Michael,Smyth Malcolm R.Matrix solid-phase dispersion linked to immunoassay techniques for the determination of clenbuterol in bovine liver samples.
Anal Proc1993;30:156–7.
[233]Boyd D,Shearan P,Hopkins JP,O'Keeffe M,Smyth MR.Application of matrix solid phase dispersion for the determination of clenbuterol in liver samples.Anal Chim Acta1993;275:221–6.
[234]Renson C,Degand G,Maghuin-Rogister G,Delahaut Ph.Determination of sulfamethazine in animal tissues by enzyme immunoassay.Anal Chim Acta1993;275:323–8.
[235]Hines II Murray E,Frazier Ken S.Differentiation of mycobacteria on the basis of chemotype profiles by using matrix solid-phase dispersion and thin-layer chromatography.J Clin Microbiol1993;31:610–4.
[236]Barker Steven,Hawley Rex.Efficient biological analysis using MSPD.
Am Lab1992;24:42–3.
[237]Barker Steven A,Long Austin R,Hines II Murray E.Disruption and fractionation of biological materials by matrix solid-phase dispersion.
J Chromatogr1993;629:23–34.
[238]Lott Heidi M,Barker Steven A.Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and gas chromatographic screening of14chlorinated pesticides in oysters (Crassostrea virginica).J AOAC Int1993;76:67–72.
[239]Hines II Murray E,Jaynes Jesse M,Barker Steven A,Newton Joseph C, Enright Frederick M,Snider III Theron G.Isolation and partial characterization of glycolipid fractions from Mycobacteriuum avium serovar2(Mycobacterium paratuberculosis18)that inhibit activated macrophages.Infect Immun1993;61:1–7.
[240]Schenck Frank J,Wagner Roberta,Bargot William.Determination of clorsulon residues in milk using a solid-phase extraction cleanup and liquid chromatographic determination.J Liq Chromatogr1993;16:513–20. [241]Reimer Gerry J,Suarz Agripina.Liquid chromatographic confirmatory method for five sulfonamides in salmon muscle tissue by matrix solid-phase dispersion.J AOAC Int1992;75:979–81.
[242]Agarwal Vipin K.High-performance liquid chromatographic methods for the determination of sulfonamides in tissue,milk and eggs.J Chromatogr 1992;624:411–23.
[243]Schenck Frank J,Barker Steven A,Long Austin R.Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and liquid chromatographic determination of nicarbazin in chicken tissue.J AOAC Int1992;75:659–62.
[244]Schenck Frank J,Barker Steven A,Long Austin R.Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and liquid chromatographic determination of ivermectin in bovine liver tissue.J AOAC Int1992;75:655–8.[245]Barker Steven A,Long Austin R.The application of matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)to the extraction and subsequent analysis of drug residues in animal tissues.Anal.Antibiot./Drug residues Food Prod.
Anim.Origin,[Proc.Am.Chem.Soc.Agric.Food Chem.Div.Symp.;
1992.p.119–32.Meeting Date1991.
[246]Barker Steven A,Long Austin R.Tissue drug residue extraction and monitoring by matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)-HPLC analysis.
J Liq Chromatogr1992;15:2071–89.
[247]Jarboe Herman H,Kleinow Kevin M.Matrix solid-phase dispersion isolation and liquid chromatographic determination of oxolinic acid in channel catfish(Ictalurus punctatus)muscle tissue.J AOAC Int 1992;75:428–32.
[248]Stafford Steven C,Lin Willy.Determination of oxamyl and methomyl by high-performance liquid chromatography using a single-stage postcol-umn derivatization reaction and fluorescence detection.J Agric Food Chem1992;40:1026–9.
[249]McLaughlin Lee G,Henion Jack D.Determination of aminoglycoside antibiotics by reversed-phase ion-pair high-performance liquid chroma-tography coupled with pulsed amperometry and ion spray mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr1992;591:195–206.
[250]Hines II ME,Long AR,Snider III TG,Barker SA.Lysis and fractionation of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and Escherichia coli by matrix solid-phase dispersion.Anal Biochem1991;195:197–206.
[251]Haagsma Nel.Analytical aspects of veterinary drug residues.Mikrochim Acta1991;2:63–70.
[252]Schenck Frank J,Barker Steven A,Long Austin R.Matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)isolation and liquid chromatographic determination of clorsulon in milk.J Liq Chromatogr1991;14:2827–34.
[253]Van Poucke LSG,Depourcq GCI,Van Peteghem CH.A quantitative method for the detection of sulfonamide residues in meat and milk samples with a high-performance thin-layer chromatographic method.
J Chromatogr Sci1991;29:423–7.
[254]Reimer Gerry J,Suarez Agripina.Development of a screening method for five sulfonamides in salmon muscle tissue using thin-layer chromato-graphy.J Chromatogr1991;555:315–20.
[255]Long Austin R,Crouch Michael D,Barker Steven A.Multiresidue matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)extraction and gas chromatographic screening of nine chlorinated pesticides in catfish(Ictalurus punctatus) muscle tissue.J AOAC1991;74:667–70.
[256]Long Austin R,Soliman Maher M,Barker Steven A.Matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)extraction and gas chromatographic screening of nine chlorinated pesticides in beef fat.J AOAC1991;74:493–6.
[257]Long Austin R,Hsieh Lily C,Malbrough Marsha S,Short Charles R, Barker Steven A.Matrix solid phase dispersion(MSPD)extraction and liquid chromatographic determination of five benzimidazole anthelmin-tics in pork muscle tissue.J Food Compos Anal1990;3:20–6. [258]Long Austin R,Hsieh Lily C,Malbrough Marsha S,Short Charles R, Barker Steven A.Matrix solid-phase dispersion(MSPD)isolation and liquid chromatographic determination of furazolidone in pork muscle tissue.J AOAC1991;74:292–4.
[259]Long Austin R,Hsieh Lily C,Malbrough Marsha S,Short Charles R, Barker Steven A.Matrix solid phase dispersion isolation and liquid chromatographic determination of sulfadimethoxine in catfish(Ictalurus punctatus)muscle tissue.J AOAC1990;73:868–71.
[260]Long Austin R,Hsieh Lily C,Malbrough Marsha S,Short Charles R, Barker Steven A.Matrix solid phase dispersion isolation and liquid chromatographic determination of oxytetracycline in catfish(Ictalurus punctatus)muscle tissue.J AOAC1990;73:864–7.
[261]Long Austin R,Malbrough Marsha S,Hsieh Lily C,Short Charles R, Barker Steven A.Matrix solid phase dispersion isolation and liquid chromatographic determination of five benzimidazole anthelmintics in fortified beef liver.J AOAC1990;73:860–3.
[262]Long Austin R,Hsieh Lily C,Malbrough Marsha S,Short Charles R, Barker Steven A.Matrix solid-phase dispersion(MSPD)isolation and liquid chromatographic determination of oxytetracycline,tetracycline, and chlortetracycline in milk.J AOAC1990;73:379–84.
162S.A.Barker/J.Biochem.Biophys.Methods70(2007)151–162
ERP 仓库管理系统
身体仓库管理系统 1、模块说明:每个模块一般可分为六组:基本资料、日常作业、凭证打印、清单与报表、 批次处理、查询作业 1.1 基本资料:产品类别设定、编码原则设定、产品编码、仓别设定、单据性质设定 1.1.1 产品类别设定:此为后续报表数据收集索引和分类之依据 1.1.2 编码原则设定:据此不同公司可采取不同的分段和方式进行自动编码,包 括产品编码、供应商编码、客户资料编码、人员编码等, 都要依此进行自定义。 Eg: A 一般产品编码通用原则为:大分类(3码)+中分类(3码)+小分类(3码)+ 流水码(4码),共计13码左右即可。 Eg: B 编码不必赋予太多特殊意义,亦造成编码上的混乱,以简单明了,易 识别为原则。 1.1.3 产品编码:包括基本项目、采购、生管、仓库、业务、品管、生产、财务 会计、其它,其可根据不同部门使用状况来分类定义,同 时便于基础资料的收集与输入,及日后使用之管理和维护。 1.1.4 仓别设定:此为各仓别属性设定之基础 1.1.5 单据性质设定:此为各“日常作业”之单据性质设定基础。 Eg:A库存异动单对库存的影响可分为:增加、减少 调拨单对库存的影响为:平调 成本开帐/调整单对成本的影响可分为:增加、减少 Eg:B可依不的部门或个人进行单据别的区别使用和管理。 Eg:C单据的编码方式:单别+单据号,或可采用自由编码的方式进行等 Eg:D单据表尾的备注与签核流程等。 Eg:E单据电脑审核流程。 1.2 日常作业:库存异动建立作业、调拨建立作业、成本开帐/调整建立作业、盘点资 料建立作业、批号管理建立作业、借入/出建立作业、借入/出还回作 业 1.2.1 库存异动建立作业:此单据适用于非生产性物料的异动(或增或减),及库存 盘盈亏之调整用,如没有上线制令管理系统亦可通过 此作业进行库存异动作业。 1.2.2 调拨单建立作业:此单据适用于各仓之间的物料调拨之用,不对库存变化 产生影响。 1.2.3 成本开帐/调整建立作业:此单据适用于系统开帐之各仓库存成本资料的输 入,亦是日常“成本重计作业”所产生之单据。 1.2.4 盘点资料建立作业:此单据适用于盘点时库存数量之输入 1.2.5 批号管理建立作业:此单据适用于物料在产品生产过程中的使用和追溯的 管理,及先进先出原理 1.2.6 借入/出建立作业:此单据适用于所有借入/出作业记录之凭证 1.2.7 借入/出还回建立作业:此单据适用所有借入/出还回作业记录之凭证,如无 法归还之作业,则通过进货或销货来做关联性作 业。 1.3 凭证打印:库存异动单凭证、调拨单凭证、成本开帐/调整单凭证、盘点清单凭证、 批号管理凭证、借入/出凭证、借入/出还回凭证
岗位技能要求矩阵参考
岗位技能要求矩阵填写指导意见一、目的技能要求矩阵的核心是明晰团队能力现状与需求的差距,用以确定未来的发展方向,是一项 非常重要的基础性工作,为课件、培训、技能评估、晋升做好准备工作。: 二、编制 1、技能水平评分标准 0——不作要求; 1——学习知晓:参加过培训,测试合格;但需要在别人的帮助与指导下进行工作。 2——独立应用:接受培训,进行实际工作半年以上,能力评估达标,能够独立上岗。年能力评估达标,并没有发生因能力缺失而造成——熟练应用:达到独立应用的水平,连续23 3次以上成功应急操作的经验。事故发生,或具有年以上该技能的实践经验,具备一定的培训与辅导——指导他人:达到熟练应用的水平,有54 技巧。、责任目标2主要从宏观、微观角度阐述员工对责任目标的知晓、应用、理解与执行。 公司总经理及总经理办公会议成员作为政策的制定者和推行者,应具备指导他人如何有序开展工作的能力标准;专业部门的部门负责人作为政策实施的组织者、策划者、监管者,也应具备指导他人的能力;其他部门部长、车间主任应具备熟练应用能力,领会并组织团队进行执行公司的政策、方针、目标、计划等;各级管理人员应在职责权限范围内,领会公司政策和发展方向,独立运用到本职工作中;基层岗位,包含班组长、主操、副操等,需要知晓公司宏观的责任目标方面内容。 根据技能因素与岗位需求的紧密程度需要特别指出。 (1)方针、政策与目标 主要包括公司的经营方针、经营目标、安全\环保\质量等政策与目标,主要是指宏观方面。 公司总经理及总公司办公会议成员需要达到指导他人的能力标准; 部门部长、车间主任——熟练应用; 管理人员——独立应用; 基层岗位(班长、主操、副操)——学习知晓。 (2)目标与指标 主要指公司级年度/月度计划、目标,如质量目标、环境目标等。 部门部长、车间主任——熟练应用; 管理人员、班长——独立应用; 主操、基层岗位(副操)——学习知晓。 (3)激励机制 主要指激励制度、薪资考核制度、福利政策、奖惩制度等。 部门部长、车间主任——熟练应用; 管理人员——独立应用; 基层岗位——学习知晓。 (4)安全文化 主要包括安全文化的宣导、推行、监督等。
仓库管理系统使用手册
仓库管理系统 ——使用手册
目录 第1章系统概述 (1) 1.1引言 (1) 1.2系统特点....................................................... 错误!未定义书签。第2章系统安装 ............................................ 错误!未定义书签。 2.1系统环境要求............................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.2单机版的安装............................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.3网络版的安装............................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.3.1 程序包文件介绍....................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.3.2 数据库的安装与配置............................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.3.3 客户端的安装与配置............................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.4系统注册....................................................... 错误!未定义书签。第3章基本操作 (2) 3.1系统启动 (2) 3.2重新登录 (2) 3.3修改密码 (2) 3.4记录排序 (3) 3.5快速查找功能 (3) 3.7窗口分隔 (3) 3.8数据列表属性设置 (3) 3.9数据筛选 (4) 3.10数据导入 (4) 3.11报表设计 (5)
仓库管理系统需求分析说明书
智能仓库管理系统 需求规格说明书 拟制:仇璐佳日期:2010年3月17日星期三审核:日期: 批准:日期: 文档编号:DATA-RATE-SRS-01 创建日期:2010-03-17 最后修改日期:2020-04-24 版本号:1.0.0 电子版文件名:智能仓库管理系统-需求规格说明书-
文档修改记录
基于web智能仓库管理系统详细需求说明书(Requirements Specification) 1.引言 1.1 编写目的 本系统由三大模块构成,分别是:系统设置,单据填开,库存查询。 其中: 系统设置包括:管理员的增加,修改,删除,以及权限管理;仓库内货物的基本资料的增加,修改,删除;工人,客户等的基本资料的增加,修改,删除。 单据填开模块包括:出库单,入库单,派工单,等单据的填开及作废操作。 库存查询系统包括:库存情况的查询,各项明细的查询,工人工资的查询,正在加工产品查询等。 报表导出模块包括:按月,按季度,按年的报表导出功能。 1.2 背景说明 (1)项目名称:基于web智能仓库管理系统 (2)项目任务开发者:东南大学成贤学院06级计算机(一)班仇璐佳,软件基本运行环境为Windows环境,使用MyEclipse7.1作为开发工具,使用struts2作为系统基本框架,Spring作为依赖注入工具,hibernate对MySql所搭建的数据库的封装,前台页面采用ext的js框架,动态能力强,界面友好。 (3)本系统可以满足一般企业在生产中对仓库管理的基本需求,高效,准确的完成仓库的进出库,统计,生产,制造等流程。 1.3 术语定义 静态数据--系统固化在内的描述系统实现功能的一部分数据。
仓库管理系统(软件需求说明书)
1引言 (2) 1.1编写目的 (2) 1.2背景 (2) 1.3定义 (3) 1.4参考资料 (3) 2任务概述 (3) 2.1目标 (3) 2.2用户的特点 (9) 2.3假定和约束 (9) 3需求规定 (9) 3.1对功能的规定 (9) 3.2对性能的规定 (9) 3.2.1精度 (9) 3.2.2时间特性要求 (9) 3.2.3灵活性 (9) 3.3输人输出要求 (9) 3.4数据管理能力要求 (10) 3.5故障处理要求 (10) 3.6其他专门要求 (10) 4运行环境规定 (11) 4.1设备 (11) 4.2支持软件 (11) 4.3接口 (11) 4.4控制 (11)
软件需求说明书 1引言 1.1编写目的 企业的物资供应管理往往是很复杂的,烦琐的。由于所掌握的物资种类众多,订货,管理,发放的渠道各有差异,各个企业之间的管理体制不尽相同,各类统计计划报表繁多,因此物资管理必须实现计算机化,而且必须根据企业的具体情况制定相应的方案。 根据当前的企业管理体制,一般物资供应管理系统,总是根据所掌握的物资类别,相应分成几个科室来进行物资的计划,订货,核销托收,验收入库,根据企业各个部门的需要来发放物资设备,并随时按期进行库存盘点,作台帐,根据企业领导和自身管理的需要按月,季度,年来进行统计分析,产生相应报表。为了加强关键物资,设备的管理,要定期掌握其储备,消耗情况,根据计划定额和实际消耗定额的比较,进行定额的管理,使得资金使用合理,物资设备的储备最佳。 所以一个完整的企业物资供应管理系统应该包括计划管理,合同托收管理,仓库管理,定额管理,统计管理,财务管理等模块。其中仓库管理是整个物资供应管理系统的核心。 开发本系统的目的在于代替手工管理、统计报表等工作,具体要求包括: 数据录入:录入商品信息、供货商信息、名片、入库信息、出库信息、退货信息等信息; 数据修改:修改商品信息、供货商信息、名片、帐号等信息; 统计数据:统计仓库里面的商品的数量,种类,并计算库存总价值; 数据查询:输入查询条件,就会得到查询结果; 数据备份:定期对数据库做备份,以免在数据库遇到意外破坏的时候能够恢复数据库,从而减少破坏造成的损失。
仓库管理系统说明书
二、仓库信息管理系统分析与设计 (一)《仓库信息管理系统》的需求建模 1、需求分析 仓库信息管理系统要能完成以下功能: 仓库存放的货物品种繁多,堆存方式以及处理方式也非常复杂,随着业务量的增加,仓库管理者需要处理的信息量会大幅上升,因此往往很难及时准确的掌握整个仓库的运作状态。针对这一情况,为了减轻仓库管理员和操作员的工作负担,此系统在满足仓库的基本管理功能基础上发挥信息系统的智能化。 根据要求可将系统分为四个模块 (1)用户登录模块 普通操作员和管理人员登录此系统,执行仓库管理的一些操作,但是普通操作员和管理人员所能执行的功能不一样。 (2)仓库管理模块 管理员工作需要登陆系统,才能够进行操作,系统中的各项数据都不允许外人随便查看和更改,所以设置登陆模块是必须的。可以执行仓库进货,退货,领料,退料;商品调拨,仓库盘点等功能。(3)业务查询模块 在用户登录系统后,可以执行库存查询,销售查询,仓库历史记录查询。 (4)系统设置模块 显示当前仓库系统中的信息,在系统中可以执行供应商设置,仓库设置。 2、功能模块分析 (1)登录模块 ①普通操作员:显示当天仓库中的所有库存的信息。 ②管理员:修改仓库中的库存信息。 ③用户注销:在用户执行完仓库功能时,注销。 ④用户退出。 (2)管理模块 ①仓库库存的进货与退货; ②仓库中的库存需要领料和退料功能; ③仓库也可以完成不同地区的商品在此仓库的商品调拨任务; ④用户人员也可以在当天之后对仓库中的库存进行盘点。 (3)查询模块 ①显示当前仓库商品信息,并执行库存查询; ②显示仓库信息,对商品的销售量进行查询; ③此系统还可以对仓库历史记录进行查询。 (4)设置模块 ①供应商设置 ②仓库设置 3、工作内容及要求 ①进一步细化需求分析的内容,识别出系统的参与者,并完成用例图; ②将用例图中的每个用例都写成相应的事件流文档; ③进一步使用活动图来描述每个用例,为后续的系统设计做好准备;
仓库管理系统(详细设计说明书)
1引言 (3) 1.1编写目的 (3) 1.2背景 (3) 1.3定义 (3) 1.4参考资料 (3) 2程序系统的结构 (4) 3用户登录界面程序设计说明 (5) 3.1程序描述 (5) 3.2功能 (5) 3.3性能 (5) 3.4输人项 (6) 3.5输出项 (6) 3.6算法 (6) 3.7流程逻辑 (6) 3.8接口 (7) 3.9存储分配 (7) 4仓库管理模块(02)设计说明 (7) 4.1程序描述 (7) 4.2功能 (8) 4.3性能 (8) 4.4输人项 (8) 4.5输出项 (8) 4.6算法 (8) 4.7流程逻辑 (9) 4.8接口 (10) 5仓库查询模块(03)设计说明 (11) 5.1程序描述 (11) 5.2功能 (11) 5.3性能 (11) 5.4输人项 (11) 5.5输出项 (11) 5.6算法 (12) 5.7流程逻辑 (12) 6系统设置模块(04)设计说明 (13) 6.1程序描述 (13) 6.2功能 (13) 6.3性能 (13) 6.4输人项 (13) 6.5输出项 (13) 6.6算法 (14)
6.7流程逻辑 (14) 6.8接口 (14) 6.9测试计划 (14)
详细设计说明书 1引言 1.1编写目的 本文档为仓库管理系统详细设计文档(Design Document),对作品进行系统性介绍,对使用的技术机制进行分析,对各个模块进行功能描述,并给出主要数据流程和系统结构 本文档的预期读者是本系统的需求用户、团队开发人员、相关领域科研人员 1.2背景 项目名称:仓库管理系统--详细设计说明书 项目任务开发者:大连交通大学软件学院R数学072班张同骥06,软件基本运行环境为Windows环境 1.3定义 Mysql:数据库管理软件 DBMS:数据库管理系统 Windows 2003/XP:运行环境 JSP :软件开发语言 Myeclipse :开发工具 1.4参考资料 《软件工程应用实践教程》清华大学出版社 《系统分析与设计》清华大学出版社 《数据库系统概论》高等教育出版社 《Windows网络编程》清华大学出版社 《VC技术》清华大学出版社
岗位技能要求矩阵_参考
岗位技能要求矩阵填写指导意见 一、目的 技能要求矩阵的核心是明晰团队能力现状与需求的差距,用以确定未来的发展方向,是一项 非常重要的基础性工作,为课件、培训、技能评估、晋升做好准备工作。 二、编制: 1、技能水平评分标准 0 ――不作要求; 1――学习知晓:参加过培训,测试合格;但需要在别人的帮助与指导下进行工作。 2――独立应用:接受培训,进行实际工作半年以上,能力评估达标,能够独立上岗。 3――熟练应用:达到独立应用的水平,连续2年能力评估达标,并没有发生因能力缺失而造成 事故发生,或具有3次以上成功应急操作的经验。 4――指导他人:达到熟练应用的水平,有5年以上该技能的实践经验,具备一定的培训与辅导 技巧。 2、责任目标 主要从宏观、微观角度阐述员工对责任目标的知晓、应用、理解与执行。 公司总经理及总经理办公会议成员作为政策的制定者和推行者,应具备指导他人如何有序开展工 作的能力标准;专业部门的部门负责人作为政策实施的组织者、策划者、监管者,也应具备指导他人 的能力;其他部门部长、车间主任应具备熟练应用能力,领会并组织团队进行执行公司的政策、方针、目标、计划等;各级管理人员应在职责权限范围内,领会公司政策和发展方向,独立运用到本职工作中;基层岗位,包含班组长、主操、副操等,需要知晓公司宏观的责任目标方面内容。 根据技能因素与岗位需求的紧密程度需要特别指出。 (1)方针、政策与目标 主要包括公司的经营方针、经营目标、安全环保质量等政策与目标,主要是指宏观方面。 公司总经理及总公司办公会议成员需要达到指导他人的能力标准; 部门部长、车间主任一一熟练应用; 管理人员一一独立应用; 基层岗位(班长、主操、副操)一一学习知晓。 (2)目标与指标 主要指公司级年度/月度计划、目标,如质量目标、环境目标等。 部门部长、车间主任一一熟练应用; 管理人员、班长一一独立应用; 主操、基层岗位(副操)——学习知晓。 (3)激励机制 主要指激励制度、薪资考核制度、福利政策、奖惩制度等。 部门部长、车间主任一一熟练应用; 管理人员——独立应用;
(仓库管理)仓库管理系统软件设计说明书改后
(仓库管理)仓库管理系统软件设计说明书改后
仓库管理系统 软件设计说明书
目录 1. 介绍 (1) 1.1 目的 (1) 1.2 范围 (1) 1.3 定义、缩写词 (1) 1.4 内容概览 (1) 2. 体系结构表示方法 (1) 3. 系统要达到的目标和限制 (2) 4. 用例视图 (2) 4.1 系统用例图 (2) 4.2 产品类别 (3) 4.3 检索产品 (4) 4.4 产品详细 (5) 4.5 管理员注册 (6) 4.6 查看订单 (7) 4.7 下订单 (8) 4.8 管理员登录系统 (9) 4.9 管理员退出系统 (10) 4.10 日常管理 (11) 4.11 商品信息管理 (12) 4.12 供应信息管理 (12) 4.13 名片信息管理 (13) 4.14 配送状态处理 (14) 5. 逻辑视图 (16) 5.1 总览 (16) 5.2 主要Package的介绍 (17) 6. 过程视图 (19) 6.1 管理员盘点 (19) 6.2 产品管理 (20) 6.3 订单处理数据 (22) 6.4 仓库物流管理 (23)
6.5 管理员查询 (24) 7. 部署视图 (24) 8. 流程逻辑 (25) 9. 规模和性能 (26) 10. 质量 (26)
软件设计说明书 1. 介绍 1.1 目的 本文档为仓库管理系统详细设计文档(Design Document),对作品进行系统性介绍,对使用的技术机制进行分析,对各个模块进行功能描述,并给出主要数据流程和系统结构 本文档的预期读者是本系统的需求用户、团队开发人员、相关领域科研人员 1.2 范围 对作品进行系统性介绍,对使用的技术机制进行分析,对各个模块进行功能描述,并给出主要数据流程和系统结构 1.3 定义、缩写词 Mysql:数据库管理软件 DBMS:数据库管理系统 Windows 2003/XP:运行环境 JSP :软件开发语言 Myeclipse :开发工具 1.4 内容概览 ?仓库管理系统 管理员将各项产品进行编排设备号,位置号,从而有效划分区域管理 ?设置系统 设置各项分类的标签,便于其他人进行查询及复查 ?仓库查询系统 进入系统后客户或者管理员有效快捷查询产品各项目录 ?用户登录系统 用户如果要进行查询操作,需要输入正确的用户名和密码,如果输入错误,则停留在登录页; 2. 体系结构表示方法 这篇文档使用一系列视图反映系统架构的某个方面; 用例视图:概括了架构上最为重要的用例和它们的非功能性需求; 逻辑视图:展示了描述系统关键方面的重要用例实现场景(使用交互图); 部署视图:展示构建在处理节点上的物理部署以及节点之间的网络配置(使用部署图);
仓库管理系统需求说明书
《管理信息系统》报告书 2013-2014 学年第 1 学期 仓库管理系统 专业: 信息管理与信息系统 班级: 2班 姓名: XXXXX 学号: 20113444 电话: XXXXXXXXXX 指导教师:王老师 信息科学与工程学院 2013.12.13
1引言 1.1背景 随着社会经济的发展和工业生产的加速,仓库的进出更为频繁,仓库信息更为重要。传统仓库管理完全由人来完成,以手工记录为主,当企业的物流业务成长到一定规模之后,随着订单数量的增加,客户需求不断个性化,执行效率就成为物流发展的瓶颈,单纯依靠人力资源的增加已不能提升出入库执行的速度,反而带来成本的大幅度上升与差错频频。计算机信息管理技术的迅速发展恰恰解决了这个问题,它使计算机技术与现代的管理技术相互配合,来更加准确、高速地完成工业企业日常的仓库管理工作。使企业能够以最少的人员来完成更多的工作。 随着我国市场经济的进一步开展,强大的信息保障,有力的电子化管理,使各大企业在国内经济市场的大潮中把现代高科技的信息技术发挥的淋漓尽致。越来越多有远见的企业家,不惜重金从国外购买高新技术,高的投资、合理的管理往往换来巨大的利润。经营的物质技术手段由简单落后转变成 高科技与人工手段并存,进而更多地将高科技应用到零售商业。国内实施WMS的条件日益成熟。主 要是物流业在过去的两年里随着国家经济的发展,而日新月异,现代一体化物流的管理思想日益为企业所接受,对仓库有了新定位和认识,从而对管理系统也提出了新的要求。所以从仓库管理的周期来考虑,一个能够高效管理的仓库系统就是一个优秀的仓库系统。 1.2开发目的及意义 对于中小型企业,仓库管理工作主要是进货商品的入库管理和销售商品的出库管理及库存商品的保管管理。现有的管理工作主要依靠手工完成,工作量大,且效率不高。为了能更好地利用现代信息技术的成果,提高管理工作的效率和水平,以适应企业发展的需要,决定开发库存管理系统。 商品流通的仓储及配送中心的出入库,库存、配送等管理,能够使管理工作节省人力。减少差错、提高工作效率,并保障。商品流转的顺利进行应用计算机系统与手持终端的结合可以方便、准确地完成商品流转的相关管理。
样品前处理技术
环境样品前处理技术及其进展一 1.样品前处理在分析化学中的地位 一个完整的样品分析过程,包括从采样开始到写出报告,大致可以分为以下五个步获:(1)样品采集,(2)样品处理,(3)分析测定,(4)数据处理,(5)报告结果.统计结果表明〔幻,上述五个步骤中各步所需的时间相差甚多,各步所需的时间占全部分析时间的百分率为:样品采集6.%,样品处理61.0%,分析测试6.%;数据处理与报告27.0%.其中,样品处理所需的时间最长,约占整个分析时间的三分之二.这是因为在过去几十年中,分析化学的发展集中在研究方法的本身,如何提高灵敏度、选择性、及分析速度;如何应用物理与化学中的理论来发展新颖的分析方法与技术,以满足高新技术对分析化学提出的新目标与高要求;如何采用高新技术的成果改进分析仪器的性能、速度、及自动化的程度,因而忽视了对样品前处理方法与技术的研究,造成目前这种严峻的局面.目前,花在样品前处理上的时间,比样品本身的分析测试所需的时间,几乎多了一个数量级.通常分析一个样品只需几分钟至几十分钟,而分析前的样品处理却要几小时甚至几十小时.因此,样品前处理方法与技术的研究引起了广大分析化学家的关注,各种新技术与新方法的探索与研究已成为当代分析化学的重要课题与发展方向之一,快速、简便、自动化的前处理技术不仅可以省时、省力,而且可以减少由于不同人员的操作及样品多次转移带来的误差,对避免使用大量溶剂及减少对环境的污染也有深远的意义.样品前处理研究的深入开展必将对环境分析化学的发展起到积极的推动作用,达到一个新的高度. 2.样品前处理的目的 从环境中采集的样品,无论是气体、液体或固体,几乎都不能未经处理直接进行分析测定.特别是许多环境样品以多相非均一态的形式存在,如大气中所含的气溶胶与飘尘,废水中含的乳液、固体微粒与悬浮物,土城中还有水份、微生物、砂砾及石块等. 所以,采集的环境样品必须经过处理后才能进行分析测定。 经过前处理的样品,首先可以起到浓缩被测痕量组份的作用,从而提高方法的灵敏度,降低最小检测极限.因为环境样品中有毒有害物质的浓度很低,难以直接测定,经过前处理富集后,就很容易用各种仪器分析测定,从而降低了测定方法的最小检测极限;其次可以消除基体对测定的干扰,提高方法的灵敏度。否则基体产生的讯号可以大到部份或完全掩盖痕量被测物的讯号,不但对选择分析方法最佳操作条件的要求有所提高,而且增加了测定的难度,容易带来较大的测量误差;还有通过衍生化的前处理方法,可以使一些在通常检测器上没有响应或响应值较低的化合物转化为具有很高响应值的化合物,如硝基烃在目前各种检测器上响应值均较低,把它还原为氨基烃再经三氟乙酸衍生处理后,生成带电负性很强的化合物,它们在电子捕获检测器上具有极高的灵敏度.衍生化通常还用于改变被侧物质的性质,提高被测物与基体或其他干扰物质的分离度,从而达到改善方法灵敏度与选择性的目的,此外,样品经前处理后就变得容易保存或运翰。因为环境样品浓度低,
仓库管理系统详细设计说明书
仓库管理系统 详细设计说明书 班级:xx 姓名:xx 学号:xx 日期:xx年xx月xx日
目录 第一章需求分析 (3) 一、问题背景及描述 (3) 二、功能分析 (3) 三、建立系统流程图 (3) 四、建立数据流图 (5) 五、建立数据字典 (7) 六、算法描述 (9) 七、建立E-R图 (10) 八、建立状态图 (12) 第二章概要设计............................................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。 一、软件体系结构模型........................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 二、用面向数据流的方法设计系统软件结构....................................... 错误!未定义书签。 三、数据库逻辑结构设计....................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。第三章详细设计 (14) 一、数据库物理结构设计....................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 二、模块过程设计与界面设计 (14) 第四章数据库设计 (20) 一、数据字典的设计 (20) 二、数据表的设计 (21) 第五章编码和单元测试................................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。第六章程序运行 (22) 一、登陆界面 (22) 二、主控制界面 (23) 三、客户管理子模块界面 (24) 四、用户管理子模块界面 (25) 五、产品入库子模块界面 (26) 六、产品出库子模块界面 (27) 七、产品查询子模块界面 (30) 八、修改产品信息子模块界面 (30) 九、帮助信息子模块界面....................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。第七章心得体会 (32) 参考文献........................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
仓库管理系统使用说明书
仓库管理系统使用手册 项目名称:仓库管理系统 小组成员:杜彦军、付东娜、王丽、邢白雪、郭雨辰 编写日期:2013年12 月13日
目录 1、引言 (3) 1.1 编写目的 (3) 1.2 编写背景 (3) 2、软件概述 (3) 3、开发环境搭建 (3) 3.1安卓软件开发包下载 (3) 3.2 软件的安装 (3) 4、详细使用说明 (7) 4.1 用户管理模块 (7) 4.1.1 用户注册 (7) 4.1.2 用户登录 (12) 4.1.3 用户密码修改 (15) 4.2 基本信息模块 (19) 4.1.2 商品信息管理 (19) 4.1.3 客户信息管理 (26) 4.1.4 供应商信息管理 (32) 4.3 库存管理模块 (39) 4.3.1 商品入库信息管理 (39) 4.3.2 商品出库信息管理 (45) 4.3.3 库存信息查询 (51) 4.4 关于模块 (52)
1、引言 1.1 编写目的 为了使用户更好的了解和使用本产品,使用户更进一步的了解本产品方便正确操作使用,特别编写了用户使用说明手册。 1.2 编写背景 仓储在企业的整个供应链中起着只至关重要的作用,如果不能保障正确的进货和库存的控制及发货,将会导致管理费用的增加,服务的质量难以保证,从而影响企业的竞争力。传统简单、静态的仓库管理已无法保证企业各种资源的有效使用。如今的仓库作业和库存控制作业已十分复杂化多样化,仅靠工人记忆和手工录入不但费时费力,而且容易出错,给企业带来巨大的损失。 为了更好的保障企业的利益,我们出开发了android版仓库管理系统。 2、软件概述 3、开发环境搭建 3.1安卓软件开发包下载 (1)java JDK下载:https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,/javase/downloads/index.jsp (2)Eslipse下载:https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html,/downloads (3)Android SDK1.5:https://www.sodocs.net/doc/ed4819475.html, (4)ADT插件 3.2 软件的安装 (1)安装JDK完成即可,无需配臵环境变量。
仓库管理软件使用说明书样本
百度文库 韦氏盈创仓库管理系统用户手册 厦门韦氏盈创科技有限公司-版权所有
目录 1引言 (3) 编写目的 (3) 参考资料 (3) 术语和缩略词 (3) 2软件概述 (4) 软件功能 (4) 软件运行 (5) 本系统运行在PC 及其兼容机上,使用WINDOWS 操作系统,在软件安装后,直接点 击相应图标,就可以显示出软件的主菜单,进行需要的软件操作。 (5) 系统要求 (5) 3系统使用 (5) 系统登录 (5) 人员信息维护 (6) 3.2.1个人密码修改 (7) 3.2.2权限设置 (7) 3.2.3添加新成员 (8) 3.2.4人员信息浏览 (9) 货品信息维护 (10) 3.3.1货品信息查询 (10) 3.3.2货品信息增加 (11) 3.3.3货品信息删改 (11) 仓库信息维护 (12) 3.4.1仓库信息浏览 (12) 3.4.2仓库信息添加 (13) 存放规则维护 (13) 3.5.1存放规则浏览 (14) 3.5.2添加存放规则 (14) 货物进出记录 (15) 3.6.1货物进出浏览 (15) 3.6.2货物进出添加 (16) 库存信息 (16) 系统功能 (17)
1引言 编写目的 韦氏盈创仓库管理系统是一个公司工作中不可缺少的一部分,他对于公司的人员以及财务的管理者和被管理者都非常重要。所以仓库管理系统应该为管理者和被管理者提供充足的信息和快捷的数据处理手段,但长期以来,人们使用传统的人工方式或性能较低的仓库管理系统来管理公司日常事务,操作流程比较繁琐,错误率比较高。一个成功的管理系统应提供快速的信息检索功能,增加和修改功能。参考资料 《软件需求规格说明书》 《概要设计说明书》 《详细设计说明书》 术语和缩略词 . 人工智能 API (Application Programming Interface) 应用(程序)编程接口Software Quality Assurance软件质量保证 UI Testing界面测试
仓库管理系统详细设计说明书
仓库管理系统详细设计说明书
仓库管理系统 详细设计说明书 班级:xx 姓名:xx 学号:xx 日期:xx年xx月xx日
目录 第一章需求分析 ........................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 一、问题背景及描述.............................................. 错误!未定义书签。 二、功能分析 ......................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 三、建立系统流程图.............................................. 错误!未定义书签。 四、建立数据流图.................................................. 错误!未定义书签。 五、建立数据字典.................................................. 错误!未定义书签。 六、算法描述 ......................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 七、建立E-R图 ...................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 八、建立状态图...................................................... 错误!未定义书签。第二章概要设计 ........................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 一、软件体系结构模型.......................................... 错误!未定义书签。 二、用面向数据流的方法设计系统软件结构....... 错误!未定义书签。 三、数据库逻辑结构设计 ...................................... 错误!未定义书签。第三章详细设计 ........................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 一、数据库物理结构设计 ...................................... 错误!未定义书签。 二、模块过程设计与界面设计 .............................. 错误!未定义书签。第四章数据库设计 ....................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 一、数据字典的设计.............................................. 错误!未定义书签。 二、数据表的设计.................................................. 错误!未定义书签。第五章编码和单元测试 ............................................... 错误!未定义书签。第六章程序运行 ........................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
仓库管理软件使用说明书样本
韦氏盈创仓库管理系统 V1.0 用户手册 厦门韦氏盈创科技有限公司-版权所有
目录 1引言 (3) 1.1编写目的 (3) 1.2参考资料 (3) 1.3术语和缩略词 (4) 2软件概述 (4) 2.1软件功能 (4) 2.2软件运行 (5) 2.3系统要求 (5) 3系统使用 (5) 3.1系统登录 (5) 3.2人员信息维护 (6) 3.2.1个人密码修改 (7) 3.2.2权限设置 (7) 3.2.3添加新成员 (8) 3.2.4人员信息浏览 (9) 3.3货品信息维护 (10) 3.3.1货品信息查询 (10) 3.3.2货品信息增加 (11) 3.3.3货品信息删改 (12) 3.4仓库信息维护 (12) 3.4.1仓库信息浏览 (13) 3.4.2仓库信息添加 (13) 3.5存放规则维护 (14) 3.5.1存放规则浏览 (14)
3.5.2添加存放规则 (15) 3.6货物进出记录 (16) 3.6.1货物进出浏览 (16) 3.6.2货物进出添加 (16) 3.7库存信息 (17) 3.8系统功能 (18) 1引言 1.1编写目的 韦氏盈创仓库管理系统是一个公司工作中不可缺少的一部分,他对于公司的人员以及财务的管理者和被管理者都非常重要。所以仓库管理系统应该为管理者和被管理者提供充足的信息和快捷的数据处理手段,但长期以来,人们使用传统的人工方式或性能较低的仓库管理系统来管理公司日常事务,操作流程比较繁琐,错误率比较高。一个成功的管理系统应提供快速的信息检索功能,增加和修改功能。 1.2参考资料 《软件需求规格说明书》 《概要设计说明书》 《详细设计说明书》
(仓库管理)仓库管理系统使用说明书
(仓库管理)仓库管理系统 使用说明书
目录1、引言2 1.1编写目的2 1.2编写背景2 2、软件概述3 3、开发环境搭建3 3.1安卓软件开发包下载3 3.2软件的安装3 4、详细使用说明7 4.1用户管理模块7 4.1.1用户注册7 4.1.2用户登录12 4.1.3用户密码修改15 4.2基本信息模块19 4.1.2商品信息管理19 4.1.3客户信息管理26 4.1.4供应商信息管理32 4.3库存管理模块39 4.3.1商品入库信息管理39 4.3.2商品出库信息管理45 4.3.3库存信息查询51 4.4关于模块52
1、引言 1.1编写目的 为了使用户更好的了解和使用本产品,使用户更进一步的了解本产品方便正确操作使用,特别编写了用户使用说明手册。 1.2编写背景 仓储在企业的整个供应链中起着只至关重要的作用,如果不能保障正确的进货和库存的控制及发货,将会导致管理费用的增加,服务的质量难以保证,从而影响企业的竞争力。传统简单、静态的仓库管理已无法保证企业各种资源的有效使用。如今的仓库作业和库存控制作业已十分复杂化多样化,仅靠工人记忆和手工录入不但费时费力,而且容易出错,给企业带来巨大的损失。 为了更好的保障企业的利益,我们出开发了android版仓库管理系统。 2、软件概述 3、开发环境搭建 3.1安卓软件开发包下载 (1)javaJDK下载:.downloads/ (2)Eslipse下载: (3)ADT插件 3.2软件的安装 (1)安装JDK完成即可,无需配置环境变量。
(2)解压exlipse,无需安装,解压后,直接打开就行。 (3)安装SDK: 在AndroidDevelopers下载android-sdk_r05-,下载完成后解压到任意路径。 ·运行SDK,点击AvailablePackages。如果没有出现可安装的包,请点击Settings,选中Misc中的"Force..."这项,再点击AvailablePackages。 ·选择希望安装的SDK及其文档或者其它包,点击InstallationSelected、AcceptAll、InstallAccepted,开始下载安装所选包 ·在用户变量中新建PATH值为:AndroidSDK中的tools绝对路径(本机为D:\AndroidDevelop\android-sdk-windows\tools)。“确定”后,重新启动计算机。重启计算机以后,进入cmd命令窗口,检查SDK是不是安装成功。 运行android–h如果有类似以下的输出,表明安装成功: (4)安装ADT (1)打开浏览器,进入Android开发者官方主页,地址 (2)“./”。 (3)单击“SDK”选项卡,单击页面右侧的“ADT16.0.1”链接。(3)滚动页面到“DownloadingtheADTPlugin”,复制
仓库管理系统使用手册
仓库管理系统使用 手册 1
仓库管理系统使用手册 -------版本: Sck V1.0 目录 1 简介 .............................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。 2 基础操作 ...................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.1 供应商资料录入................................................. 错误!未定义书签。 2.2 公司信息基本资料录入..................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.3 公司人员基本资料录入..................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.4 客户信息基本资料录入..................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.5 产品信息基本资料录入..................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.6 入库操作............................................................. 错误!未定义书签。 2.7 出库操作............................................................. 错误!未定义书签。 3 查询操作 ...................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 3.1 入库明细查询..................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 3.2 出库明细查询..................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 3.3 库存量查询......................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 4 其它操作 ...................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 4.1 修改个人信息..................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 4.2 公告栏................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。 4.3 邮件..................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
